Science - Solved Problems: Optics | 10th Science : Chapter 2 : Optics
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 2 : Optics
Solved Problems: Optics
Optics Science
SOLVED PROBLEMS
Problem 1
Light rays travel from vacuum into a glass whose refractive index is 1.5. If the angle of incidence is 30┬░, calculate the angle of refraction inside the glass.
Solution:
accorting to SnellŌĆÖs law,
sin i / sin r = ┬Ą2/ ┬Ą1
┬Ą1 sin i = ┬Ą2 sin r
Here ┬Ą1 = 1.0,
┬Ą2 = 1.5, i = 30┬░
(1.0) sin 30┬░ = 1.5 sin r
1├Ś 1/2 = 1.5 sin r
sin r = 1/(2├Ś1.5) = 1/3 = (0.333)
r= sinŌĆō1 (0.333)
r = 19.45┬░
Problem-2
A beam of light passing through a diverging lens of focal length 0.3m appear to be focused at a distance 0.2m behind the lens. Find the position of the object.
Solution:
f = ŌłÆ0.3 m, v = ŌłÆ0.2 m
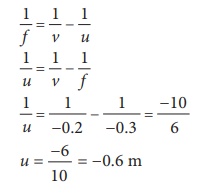
Problem-3
A person with myopia can see objects placed at a distance of 4m. If he wants to see objects at a distance of 20m, what should be the focal length and power of the concave lens he must wear?
Solution:
Given that x = 4m and y = 20m.
Focal length of the correction lens is
f = ŌĆēŌĆēŌĆēxy / ŌĆēxŌłÆyŌĆē (Refer eqn.2.7)
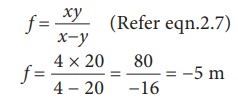
Power of the correction lens
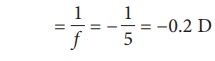
Problem-4
For a person with hypermeteropia, the near point has moved to 1.5m. Calculate the focal length of the correction lens in order to make his eyes normal.
Solution:
Given that, d = 1.5m; D = 25cm = 0.25m (For a normal eye).
From equation (2.8), the focal length of the correction lens is
f = ŌĆēd ├Ś D / ŌĆēd ŌłÆ D = ŌĆē1.5 ├Ś 0.25 / 1.5 ŌłÆ 0.25 = ŌĆē0.375 /ŌĆē1.25 = 0.3 m
Related Topics