Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 2 : Optics
Human Eye
HUMAN EYE
The human eyes are most
valuable and sensitive organs responsible for vision. They are the gateway to
the wonderful world.
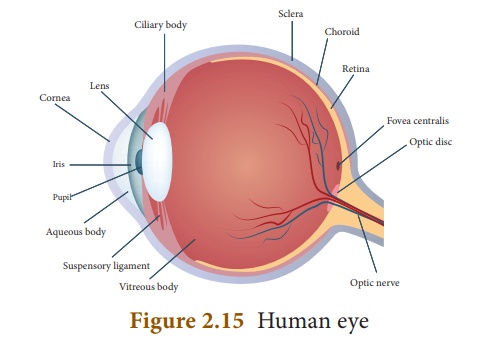
Structure of the eye
The eye ball is
approximately spherical in shape with a diameter of about 2.3 cm. It consists
of a tough membrane called sclera, which protects the internal parts of the
eye.
Important parts of human
eye are
Cornea: This is the thin and
transparent layer on the front surface of the eyeball as shown in figure
2.15. It is the main refracting surface. When light enters through the cornea,
it refracts or bends the light on to the lens.
Iris: It is the coloured
part of the eye. It may be blue, brown or green in colour. Every person
has a unique colour, pattern and texture. Iris controls amount of light
entering into the pupil like camera aperture.
Pupil: It is the centre part
of the Iris. It is the pathway for the light to retina.
Retina: This is the back
surface of the eye. It is the most sensitive part of human eye, on which
real and inverted image of objects is formed.
Ciliary muscles – Eye lens is fixed
between the ciliary muscles. It helps to change the focal length of the
eye lens according to the position of the object.
Eye Lens – It is the important
part of human eye. It is convex in nature.
Working of the eye

The transparent layer
cornea bends the light rays through pupil located at the centre part of the
Iris. The adjusted light passes through the eye lens. Eye lens is convex in
nature. So, the light rays from the objects are converged and a real and
inverted image is formed on retina. Then, retina passes the received real and
inverted image to the brain through optical nerves. Finally, the brain senses
it as erect image.
Power of Accommodation
The ability of the eye
lens to focus nearby as well as the distant objects is called power of
accommodation of the eye. This is achieved by changing the focal length of the
eye lens with the help of ciliary muscles.
Eye lens is made of a
flexible, jelly-like material. By relaxing and contracting the ciliary muscle,
the curvature and hence the focal length of the eye lens can be altered. When
we see distant objects, the ciliary muscle relaxes and makes the eye lens
thinner. This increases the focal length of the eye lens. Hence, the distant
object can be clearly seen. On the other hand, when we look at a closer object,
the focal length of the eye lens is decreased by the contraction of ciliary
muscle. Thus, the image of the closer object is clearly formed on the retina.
Persistence of vision
If the time interval
between two consecutive light pulses is less than 0.1 second, human eye cannot
distinguish them separately. It is called persistence of vision.
The far point and near point of the human eye
The minimum distance
required to see the objects distinctly without strain is called least distance
of distinct vision. It is called as near point of eye. It is 25 cm for normal
human eye.
The maximum distance up
to which the eye can see objects clearly is called as far point of the eye. It
is infinity for normal eye.
Related Topics