Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Soil Microbiology
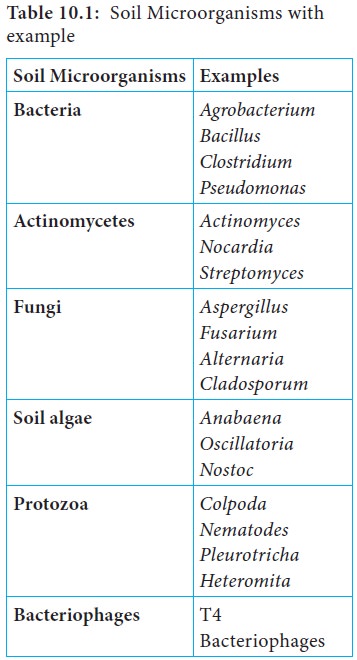
Soil Microorganisms
Soil Microorganisms
Soil contain five major groups of microorganisms. They are
Bacteria, Actinomycetes, Fungi, Algae and Protozoa (Table 10.1).
Soil Bacteria
Among the soil microorganisms, bacteria are most dominant group
of organisms. All kinds of bacteria are found in soil.
This is because all kinds of organic refuse are disposed on the
soil
Many of the soil bacteria perform useful functions like
decomposition of organic matter, conversion of soil constituents into useful
materials, production of antibiotics in the soil and biogeochemical cycling of
elements like Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Iron, Sulphur and Manganese. The
bacterial population of the soil exceed the population of all other groups of
microorganisms in both number and variety.
Soil Actinomycetes
The actinomycetes population is present as many as millions per
gram of soil. The most predominant genera present in the soil are Nocardia, Streptomyces and Micromonospora. Actinomycetes are
capable of degrading many complex organic substances and therefore play an
important role in building soil fertility. One of the most notable
characteristics of the actinomycetes is their ability to produce antibiotics.
Examples: Streptomycin, neomycin, erythromycin and tetracycline.
Soil Fungi
Next to bacterial population in soil, fungi dominates in all
kinds of soil. It possess filamentous mycelium composed of individual hyphae.
All environmental factors which influence the distribution of bacteria and
actinomycetes also influence the fungal flora of soil. The quality and quantity
of organic matter present in the soil have a direct influence on the fungal
numbers in soil. Fungi are dominant in acidic soils because acidic environment
is not supportive for the existence of either bacteria or actinomycetes.
Soil Algae
Soil algae are ubiquitous in nature wherever moisture and
sunlight are available. They are visible to the unaided eye in the form of
green scum on the surface of soils. Numerically, they are not as many as Fungi,
Bacteria or Actinomycetes. Some of the common algae in Indian soil are Chlorella, Chalmydomonas, Chlorochytrium,
Chlorococcum and Oedogonium.
Blue green algae, or Cyanophyceae,
are responsible for Nitrogen fixation. The amount of Nitrogen they fix depends
more on physiological and environmental factors rather than the organism’s
abilities. These factors include intensity of sunlight, concentration of
inorganic and organic Nitrogen sources and ambient temperature and stability.
Soil Protozoa
Soil protozoa are unicellular. They are characterized by a cyst in their life cycle which can help the species to withstand adverse soil conditions. The protozoans prefer certain species of bacteria for their nutrition. Protozoa are abundant in the upper layer of the soil and their numbers are directly dependent on bacterial population.
Factors Influencing Microbial Population in Soil
The major factors that influence the microbial community in soil
are
·
Moisture
·
pH
·
Temperature
·
Gases
·
Organic and inorganic fertilizer
·
Organic matter of soil
·
Types of vegetation and growth stages
·
Ploughing
·
Season
·
Depth of soil
Related Topics