Soil Microbiology - Rhizosphere | 11th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Soil Microbiology
Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 10 : Soil Microbiology
Rhizosphere
Rhizosphere
In 1904, L.Hiltner for the first time coined the term
“rhizosphere” to denote the area of intense microbiological activity that
extends several millimeters from the root system of the growing plants.
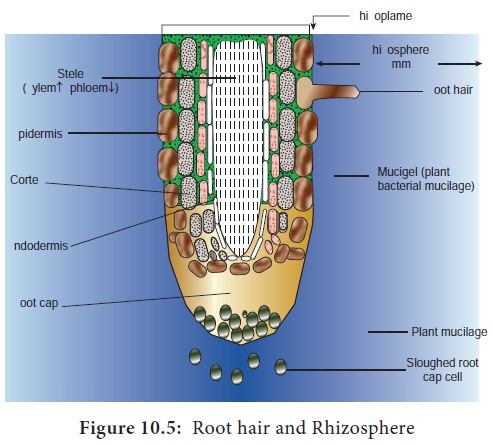
The region which is adjacent to the root system is called
rhizophere. The microbial population on and around root system is considerably
higher than the root free soil or non rhizophere soil. This may be due the
availability of nutrients from plants root in the form of root nodules,
secretion, lysates, mucigel and sloughed off cells (Figure 10.5).
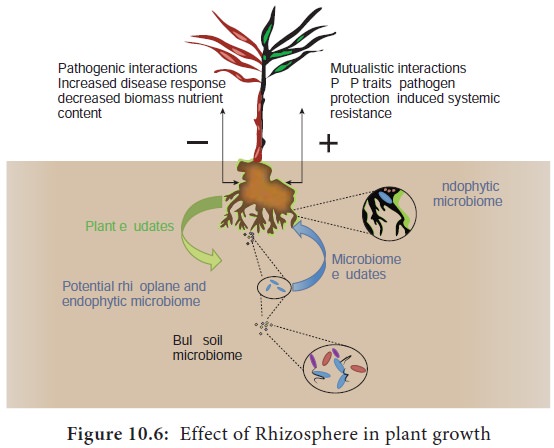
Rhizophere Effect
The rhizophere is a zone of increased microbial community as
well as microbial activities influenced by the root itself.
Greater rhizosphere effect is seen with bacteria (R: S values
ranging from
From the agronomic point of view, the abundance of Nitrogen
fixing and Phosphate solublising bacteria in the rhizosphere of crop plants
assumes a natural significance.
It has been reported that amino acid requiring bacteria exist in
the rhizosphere in large numbers than in the root free soil. The rhizosphere
effect improves the physiological conditions of the plant and ultimately result
in higher yield.
Related Topics