Plant Breeding - Seed Storage | 12th Botany : Chapter 9 : Plant Breeding
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 9 : Plant Breeding
Seed Storage
Seed Storage
Storage starts in the mother plant itself when it attains
physiological maturity. Storage may be defined as the preservation of viable
seeds from the time of collection until they are required for sowing. After
harvesting the seeds are either stored in ware houses or in transit or in
retail shop.
1. Classification of seeds based on storage
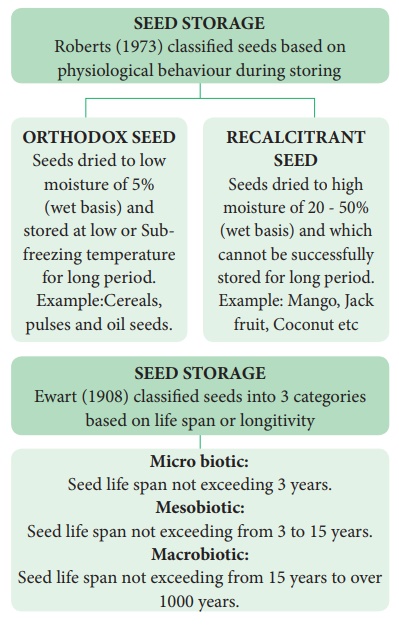
2. Methods of Seed Storage
i. Conventional Methods of Seed Storage
Conventional storage includes storage in Bamboo structure, mud and
earthen structure, wooden structure and underground structure. In village level
storage is done in large level in concrete/ cement silos, Metal or plastic
drums and metal silos. Improved rural level storage structure includes storage
in coal tar drum, udaipur bin, bamboo bin, pusa bin and metal bins.
ii. Modern Methods of Seed Storage
·
Seed storage in cryopreservation: It is the technique
of germplasm conservation (storage of cells, tissue, embryo or seeds) by
ultra-low temperature in liquid nitrogen at -196oC. It is not practical for
commercial seed storage purpose, but is useful to store the valuable germplasm
for use in future which cannot be preserved by conventional methods.
·
Seed storage in gene bank: In gene bank, seed storage is the
preservation of seed under controlled environmental condition which will
prolong the viability of the seeds for long periods. The temperature, relative
humidity and seed moisture content. Containers and distribution arrangement
vary for each and every type of seed.

·
Svalbard seed bank:
The seeds are stored in four ply sealed envelopes, and then placed
into plastic tote containers on metal shelving racks.The storage rooms are kept
a -18oC. The low temperature and
limited access to O2 will ensure low metabolic activity and delayed
seed ageing. The permafrost surrounding will help to maintain low temperature of
the seed when the electricity supply fails.
3. Seed Certification
Seed certification is a legally sanctioned system for quality
control of seed multiplication and production. The purpose of this
certification is to maintain the seeds and make them available to the public.
Through certification, high quality seeds and propagating materials of notified
kind and variety are grown and distributed to ensure genetic identity and
purity.
Related Topics