Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 17 : E-Commerce Security Systems
Security technologies in E-Commerce transaction
Security
technologies in E-Commerce transaction
Since a large amount of confidential information
are involved in E-Commerce activities it must be transmitted through safe and
secured network. Sophisticated security technologies are required to ensure the
security of E-Commerce transactions. At present, the security technologies in
E-Commerce transactions are roughly classified into
● Encryption
technology
● Authentication
technology
● Authentication
protocols
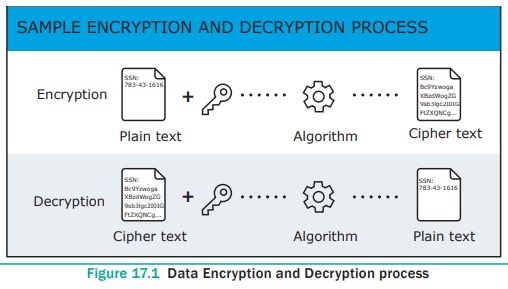
1. Encryption technology
Encryption technology is an effective information
security protection. It is defined as converting a Plaintext into meaningless
Ciphertext using encryption algorithm thus ensuring the confidentiality of the
data. The encryption or decryption process uses a key to encrypt or decrypt the
data. At present, two encryption technologies are widely used. They are
symmetric key encryption system and an asymmetric key encryption system.
Symmetric key encryption
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a Symmetric
key data encryption method. It was introduced in America in the year 1976, by
Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
DES is the typical block algorithm that takes a
string of bits of cleartext (plaintext) with a fixed length and, through a
series of complicated operations, transforms it into another encrypted text of
the same length. DES also uses a key to customize the transformation, so that,
in theory, the algorithm can only be deciphered by people who know the exact
key that has been used for encryption. The DES key is apparently 64 bits, but
in fact the algorithm uses only 56. The other eight bits are only used to
verify the parity and then it is discarded.
Today, it is considered that DES is not safe for
many applications, mainly because of its relatively smaller key size (56-bit).
Asymmetric or Public key encryption
Asymmetric encryption also called as RSA
(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) algorithm.
It uses public-key authentication and digital
signatures. Until 1970s, there were only symmetric cryptosystems in which
transmitter and receiver must have the same key. This raises the problem of key
exchange and key management. Unlike a symmetric encryption, the communicating
parties need not know other’s private-key in asymmetric encryption. Each user
generates their own key pair, which consists of a private key and a public key.
A public-key encryption method is a method of converting a plaintext with a
public key into a ciphertext from which the plaintext can be retrieved with a
private key.
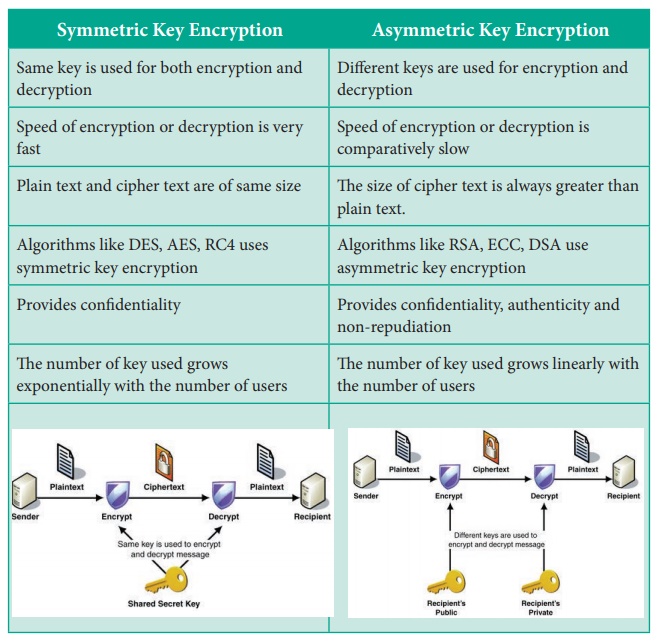
Symmetric Key Encryption
1. Same key is used for both encryption and
decryption
2. Speed of encryption or decryption is very fast
3. Plain text and cipher text are of same size
4. Algorithms like DES, AES, RC4 uses symmetric key
encryption
5. Provides confidentiality
6. The number of key used grows exponentially with the number of users
Asymmetric Key Encryption
1. Different keys are used for encryption and
decryption
2. Speed of encryption or decryption is
comparatively slow
3. The size of cipher text is always greater than
plain text.
4. Algorithms like RSA, ECC, DSA use asymmetric key
encryption
5. Provides confidentiality, authenticity and
non-repudiation
6. The number of key used grows linearly with the number of users
In 1976, Whitfield
Diffie and Martin e. Hellman, devised an algorithm called public key
encryption. The algorithm can be understood using color game. This how could
“A” and “B” get a secret key without letting “C” finding it out. The trick is
based on 2 facts
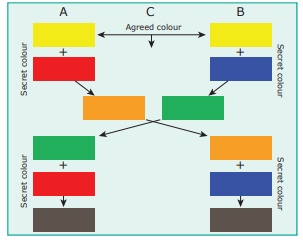
● It is easy to mix
2 colors together to get 3rd color
Given a mixed color
it’s hard to reverse it in order to find the exact original colors
1. First A and B
agree publicly on a starting color (yellow)
2. Now A select a
random colour (red) mix it with yellow and send new color (yellow+red=orange)
to B.
3. Similarly B
selects a random colour (blue) mix it with yellow and send new colour
(yellow+blue=green) to A.
4. Hacker “C” may
have two new colours (orange) and (green) but not the A’s (red) or B’s (blue)
private colours.
5. After
interchanging colors, A adds his own private (red) to B’s mixture (green) and
arrive at a third secret colour(black).
6. Also B adds his
own private (blue) to A’s mixture (orange) and arrive at a same third secret
color (black).
7. C is unable to
have the exact color (black), since C needs one of the private color to do so.
2. Authentication Technology
The main role of security certification is to ensure Authentication, Integrity and Non-repudiation. This can be achieved through digital signatures and digital certificates.
Digital certificates
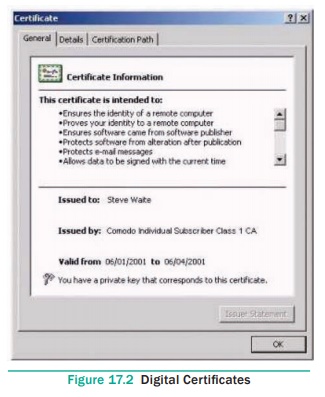
A digital certificate (also known as public key
certificate) is an electronic document used to prove the ownership of a public
key. This certificate includes the information about the sender’s identity,
digital signature and a public key.
A digital certificate function is similar to the
function of identification cards such as passports and driving licenses.
Digital certificates are issued by recognized Certification Authorities (CA).
When someone requests a digital certificate, the authority verifies the
identity of the requester, and if the requester fulfills all requirements, the
authority issues it. When the sender uses a certificate to sign a document
digitally, receiver can trust the digital signature because he trusts that CA
has done their part verifying the sender’s identity.
Common digital certificate systems are X.509 and
PGP.
● Pretty Good Privacy (PGP): Phil Zimmermann
developed PGP in 1991. It is a decentralized encryption program that provides
cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP encryption
uses a serial combination of hashing, data compression, symmetric-key
cryptography and asymmetric-key cryptography and works on the concept of “web
of trust”.
● The X.509 system is a centralized system in which
the authenticity of the key is guaranteed by the hierarchy of certification
authorities formally certifying the key relationship with the identity of its
owner. Due to its clear responsibility, it is easier to implant in the law,
X.509 is currently world wide accepted certification technology.
The digital
certificate are being issued by a licensed
Certifying Authority (CA). NIC, Safescript, TCS MTNL, e-Mudhra are some of the authorized
Certifying Authorities under Government of India.
Digital signature
A digital signature is a mechanism that is used to verify that a particular digital document, message or transaction is authentic.
It provides the receiver the guarantee that the
message was actually generated by the sender. It also confirms that the
information originated from the signer and has not been altered by a cracker in
the middle. Digital signatures can provide the added assurances of evidence to
the origin, identity and status, as well as acknowledging the consent of the
sender.
Digital signatures use a standard, worldwide
accepted format, called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), to provide the highest
levels of security and universal acceptance. In many countries, digital
signatures have the same legal significance as the traditional forms of signed
documents. Digital signatures are widely used for avoiding forging or tampering
of important documents such as financial documents or credit card data.
A security token is a hardware
component that are used to identify and authenticate users.

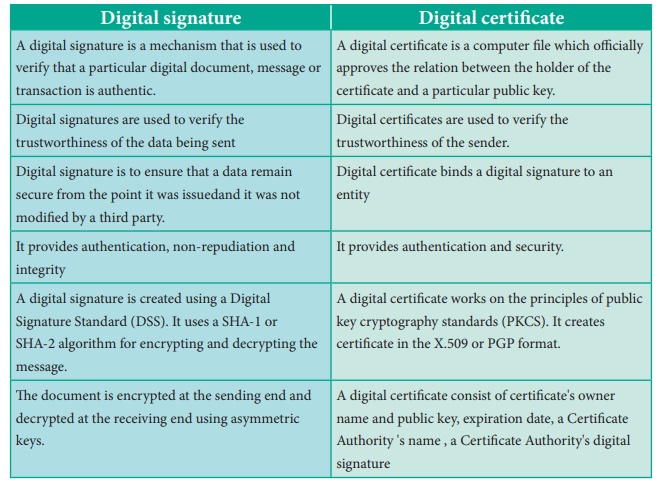
Digital signature
1. A digital signature is a mechanism that is used
to verify that a particular digital document, message or transaction is
authentic.
2. Digital signatures are used to verify the
trustworthiness of the data being sent
3. Digital signature is to ensure that a data
remain secure from the point it was issuedand it was not modified by a third
party.
4. It provides authentication, non-repudiation and
integrity
5. A digital signature is created using a Digital
Signature Standard (DSS). It uses a SHA-1 or SHA-2 algorithm for encrypting and
decrypting the message.
6. The document is encrypted at the sending end and decrypted at the receiving end using asymmetric keys.
Digital certificate
1. A digital certificate is a computer file which
officially approves the relation between the holder of the certificate and a
particular public key.
2. Digital certificates are used to verify the
trustworthiness of the sender.
3. Digital certificate binds a digital signature to
an entity
4. It provides authentication and security.
5. A digital certificate works on the principles of
public key cryptography standards (PKCS). It creates certificate in the X.509
or PGP format.
6. A digital certificate consist of certificate's owner name and public key, expiration date, a Certificate Authority 's name , a Certificate Authority's digital signature
3. Authentication protocols
At present, there are two kinds of security
authentication protocols widely used in E-Commerce, namely Secure Electronic
Transaction (SET) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Secure Electronic Transaction
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET)
is a security protocol for electronic payments with credit cards, in particular
via the Internet. SET was developed in 1996 by VISA and MasterCard, with the
participation of GTE, IBM, Microsoft and Netscape.
The implementation of SET is based on the use of
digital signatures and the encryption of transmitted data with asymmetric and
symmetric encryption algorithms. SET also use dual signatures to ensure the
privacy.
The SET purchase involves three major participants:
the customer, the seller and the payment gateway. Here the customer shares the
order information with the seller but not with the payment gateway. Also the
customer shares the payment information only with the payment gateway but not
with the seller. So, with the SET, the credit card number may not be known to
the seller and will not be stored in seller’s files also could not be recovered
by a hacker.
The SET protocol guarantees the security of online
shopping using credit cards on the open network. It has the advantages of
ensuring the integrity of transaction data and the non -repudiation of
transactions. Therefore, it has become the internationally recognized standard
for credit card online transaction.
SET system incorporates the following key features:
● Using
public key encryption and private key encryption ensure data confidentiality.
● Use
information digest technology to ensure the integrity of information.
● Dual signature technology to ensure the identity
of both parties in the transaction

Secure Sockets Layers
The most common Cryptographic protocol is Secure
Sockets Layers (SSL). SSL is a hybrid encryption protocol for securing
transactions over the Internet. The SSL standard was developed by Netscape in
collaboration with MasterCard, Bank of America, MCI and Silicon Graphics. It is
based on a public key cryptography process to ensure the security of data
transmission over the internet. Its principle is to establish a secure
communication channel (encrypted) between a client and a server after an
authentication step.
The SSL system acts as an additional layer, to
ensure the security of data, located between the application layer and the
transport layer in TCP. For example, a user using an internet browser to
connect to an SSL secured E- Commerce site will send encrypted data without any
more necessary manipulations. Secure Sockets Layers (SSL) was renamed as
Transport Layer Security (TLS) in 2001. But still it is popularly known under
the name SSL. TLS differs from SSL in the generation of symmetric keys.
Today, all browsers in the market support SSL, and
most of the secure communications are proceeded through this protocol. SSL
works completely hidden for the user, who does not have to intervene in the
protocol. The only thing the user has to do is make sure the URL starts with
https:// instead of http:// where the “s” obviously means secured. It is also
preceded by a green padlock.
3D Secure
“3- D Secure is a secure payment protocol on the
Internet. It was developed by Visa to increase the level of transaction
security, and it has been adapted by MasterCard. It gives a better
authentication of the holder of the payment card, during purchases made on
websites. The basic concept of this (XML-based) protocol is to link the
financial authorization process with an online authentication system. This
authentication model comprise 3 domains (hence the name 3D) which are:
1. The Acquirer Domain
2. The Issuer Domain
3. The interoperability Domain
Related Topics