Chapter: Network Programming and Management : Simple Network Management
SNMP Management Information
SNMP MANAGEMENT INFORMATION
• The foundation of Network Management System is creation of
database that contains information about the elements to be managed.
• An MIB is an structured collection of information about objects that are
part of the
network(servers, workstations, routers, bridges etc.)
• Each system in a network maintains a MIB that
reflects the status of the managed resources at that system. NME (Network
Management Entity) can monitor the resources at that system by reading the
values of objects in the MIB and may control the resources at that system by
modifying those values.
To serve these needs, the MIB must meet certain
objectives:
•
Data
base where manageable objects are defined.
•
The
objects or objects used to represent a particular resources must be the same at
each system. (Keeping data regarding active, passive or total open connections
with any two of these data which must be uniform)
•
A common
scheme for representation must be used to support interoperability.
The first points details the objects types and
the second point details the type of structure for uniformity.
Structure Management Information
Structured Management Information explains ―How
to write and define MIB‖. The SMI defines the general framework within
which a MIB can be defined and constructed . The SMI identifies the data type
that can be used in the MIB and specifies how within MIB are represented and
named.
For the sake of simplicity, SMI must do the
following:
•
Provide
a standardized technique for defining the structure of a particular MIB
•
Provide
standardized technique for defining individual objects, including the systems
and the value of each object.
•
Provide
a standardized technique for encoding object values.
MIB
Structure
- The Internet Naming Hierarchy
- Objects Types
- Simple/Tabular Objects
- Instances Identification
The
Internet Naming Hierarchy
All managed objects in the SNMP environment are
arranged in a hierarchical or tree structure. The leaf objects of the tree are
the actual managed objects, each of which represents
some resources, activity or related information
that is to be managed. The tree structure itself defines a grouping of objects
into logically related sets. Each object is named by the sequence of the
identifiers from the root to the object
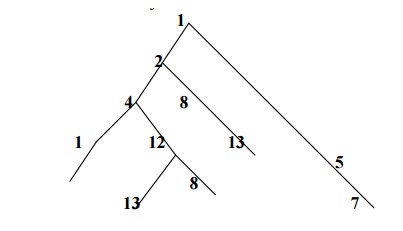
The
object identifier is : 1.2.4.12.3
Object
Types:
A restricted subset of ASN.1 is used to
describe objects types
Two ASN.1 classes are used :
Universal
Types Application Independent
Application-Wide Types :
- Defined in the context of a particular
application
- Each application, including SNMP, is
responsible for defining its own application-wide data types
Following data types are permitted :
Integer (ex. : 5, - 10)
Octet string (ex. : protocol)
Null (object with no
value associated)
Object identifier (ex. :
1.3.6.1.2)
And the constructor type (used to build tables)
: Sequence, Sequence- of
RFC 1155 defines the following application-wide data types :
Network address , IP address : Internet 32- bit address
Counter : Non- negative integer (can be
incremented but not decremented)
Gauge : Non- negative integer
that may increase or decrease
Timeticks : Non- negative
integer counting the time in hundredths of second
Opaque : Arbitrary data transmitted in the form of an octet string
Simpler And Tabular Objects
Simple Objects : Object with a unique instance within the agent.
Its type
is one of the following : integer, octet string, null, object identifier,
network address, IP address, counter, gauge,
time ticks or opaque.
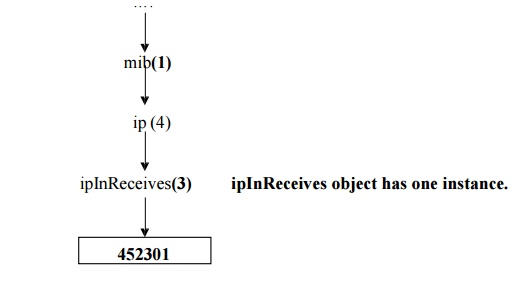
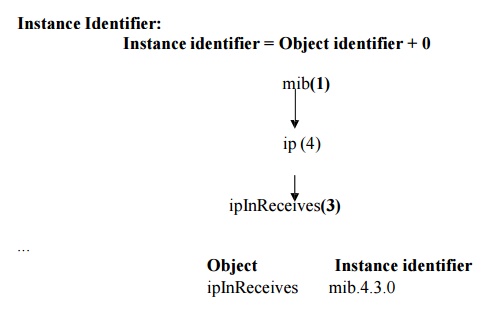
Example:
The ipInreceives object has one instance
Tabular Objects :
Two-dimensional table containing zero or more
rows .
Each row
is made of one or more simple objects ( components ).
One or more components are used as indexes to
unambiguously identifying the rows
The definition of tables is based on ASN.1
types ―Sequence" and "Sequence-
of "ASN.1 type.
• The table is indexed by ifIndex.
•Each row is an instance of the ifIndex,
ifPhysAddress and ifAdminStatus objects

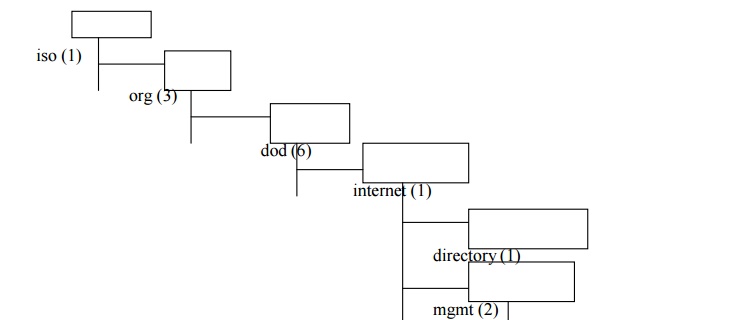
The internet node has the object identifier
value of 1.3.6.1. This value serves as the prefix for the nodes at the next
lower level of the tree.
directory: reserved for future use with OSI directory
experimental : Used to identify objects used in internet experiments.
private : used to identify objects defined
unilaterally.
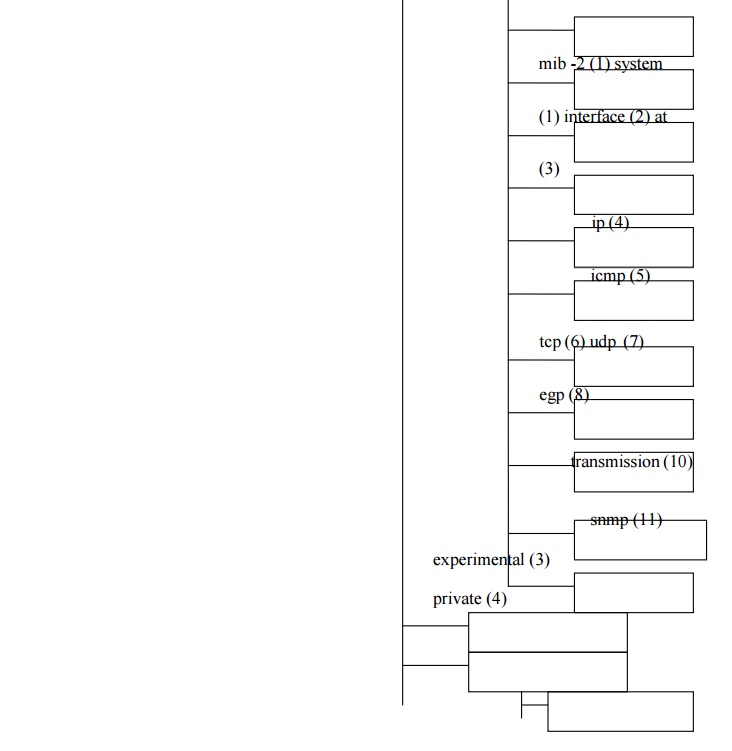
The mgmt
subtree consists of the definition of management information Bases that have
been approved by the IAB (Internet Activity Board). At present two version of
the MIB have been developed, mib -1
and mib-2. The second MIB is an
extension of the first. Both are provided with the same object identifier in the
subtree . Additional objects can be defined by
•
By
expanding mib-2
•
By
creating experimental mib
•
By
creating private extensions under private tree structure.
MIB I defined 114 objects in 8 groups where as
MIB II defined 173 objects with 10 groups.
Standard MIB’S:
MIB II object grouping is given above in the tree format: The only addition with respect
to MIB I were addition transmission and snmp node objects as shown. MIB I was issued
as RFC 1156 and the MIB II was defined in the RFC 1213. In this some additional
object group are added. The mib II group is sub divided into the following
groups.
•
system: overall information about the system.
•
interfaces: information about each of
the interfaces from the system to a sub network
•
at : address translation: description of address translation table for
the internet to subnet address
mapping
•
ip : information related to the implementation and execution
experience of the IP on this system.
•
icmp: information related to the implementation and execution experience
of ICMP on this system.
•
tcp: information related to the implementation and execution
experience of UDP on this sytem.
•
egp: information related to the implementation and execution
experience of EGP (External Gateway
Protocol) on this system.
•
dot3 (transmission): information about the transmission schemes
and access protocols at each system
interface.
•
snmp: information related to the implementation and execution
experience of SNMP on this system.
Related Topics