Chapter: Network Programming and Management : Simple Network Management
Remote Network Monitoring(RMON)
REMOTE NETWORK MONITORING(RMON)
With MIB
II, the network manager can obtain information that is purely local to
individual devices. That is, in a LAN with a number of devices on it each with
an SNMP agent, the manager can learn of the amount of traffic into and out of
each device, but cannot easily learn about the traffic on the LAN as a whole.
Network monitors are the devices that are traditionally employed to study the network
traffic as a whole. They are also called network analyzers, probes etc. They
may be standalone devices or may be workstations a server, or a router with
additional monitoring functionality. The monitor can produce summary
information, including error statistics, such as count of undersized packets
and the number of collision performance statistics (packet delivered per second
) etc. The monitor may also store packet for later analysis.
For
effective network management, they need to communicate with a central network
management station. In this context, they are referred to as remote monitors.
RMON Goals:
RMON
specification is a definition of a MIB. The effect is to define standards
network monitoring functions and interfaces for communicating between SNMP
based management consoles and remote monitors.
RMON goals as listed in RFC 1757 are given
below:
• Off line operation: The monitor should
collect fault, performance and configuration information continuously. It
accumulates statistics that may be retrieved by the manager at a later time. It
may also intimate the manager if an exception occurs.
•
Proactive monitoring: If it is not disruptive, the monitor can run
diagnostic and log network
performance. In case of failure in the net, the monitor may be able to notify
the management station of the failure and provide the management station with
information useful in diagnosing the failure.
•
Problem detection and reporting: Instead of proactive monitoring by running diagnostic
tools, it may check for congestion and error
condition passively. When one of
these conditions occur, the monitor can log this condition and attempt to
intimate the management station.
• Value-added data: The monitor may reduce the work load of management station by
performing analysis specific to the data collected on its subnet work.
• Multiple managers: An internetworking configuration may have more than one management
station to take care of improved reliability, to perform different functions
etc. The monitor can be configured to deal with more than one management
station concurrently.
Configuration using RMON : Following figure depicts the configuration using RMON.
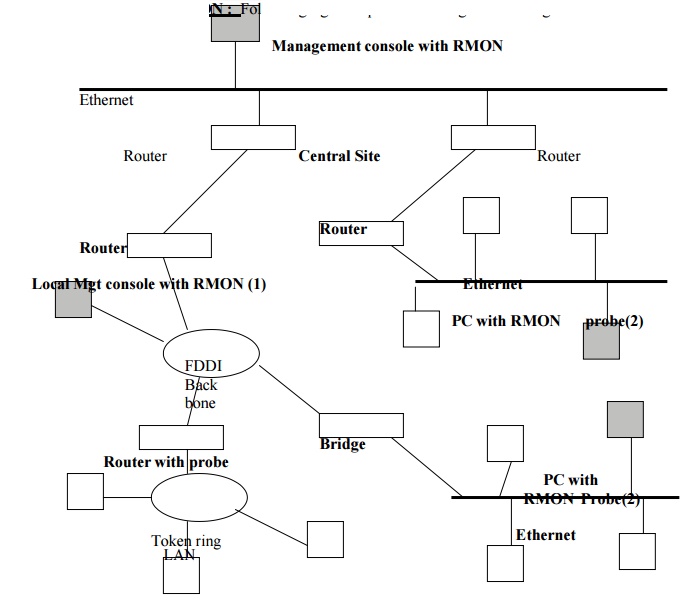
The top of the figure contains a management
station with dedicated RMON capability which is attached to the central LAN. ON
the two sub network, RMON MIB is implemented in personal computers.(1 & 2).
It may be used exclusively for network performance monitoring or may share
other functions. There are other RMON elements that are installed on router as
well.
A system
that implements the RMON MIB is referred to as RMON probe. The probe has an
agent similar to SNMP agent. The probe is capable of reading writing the local
RMON MIB in response to management action .
RMON MIB:
The RMON MIB is divided into ten groups
1. statistics : Maintains low level
utilization and error statistics for each sub net work monitored.
2. history:
records periodical statistical samples form
information available in the statistics group.
3. alarm: Allows the management consol user to set a
sampling interval and alarm threshold for
any counter or integer recorded by the RMON.
4. host: contains counters for various
types of traffic to and from hosts attached to the subnetwork.
5. hostTopN
: Contains sorted host statistics that report on
the hosts that top a list based on some
parameter in the host table.
6. matrix: shows error and utilization information in
matrix form, so the operator can retrieve
information for any pair of network addresses.
7. filter: allows the monitor to observe packets that
match a filter
8. packet
captures: governs how data is sent to
a management console.
9. event : gives
a table of all events generated by the
RMON probe.
10.
tokenRing : maintains statistics and configuration information for token ring
subnetwork.
Related Topics