Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 10 : Rural Economics
Rural Poverty
Rural
Poverty
Rural
poverty refers to the existence of poverty in rural areas. Poverty in India has
been defined as the situation in which an individual fails to earn sufficient
income to buy the basic minimum of subsistence. Poverty line is a hypothetical
line based on income or consumption levels that divides the population as
people below poverty line and above poverty line. On the basis of recommended
nutritional intake, persons consuming less than 2,400 calories per day in rural
areas are treated as they are under rural poverty.
As per
the Planning Commission estimates, the percentage of people living below
poverty in rural areas was 54.10 which accounted for 33.80 per cent during
2009-10. Poverty is deepest among members of scheduled castes and tribes in the
rural areas. In 2005 these groups accounted for 80 per cent of rural poor,
although their share in the total rural population is much smaller. In 2015,
more than 80 crores of India’s people lived in villages. One quarter of village
population (22 crores people) list below the poverty line. India is the home to
22 per cent of the world’s poor. It is needless to state that the country has
been successful in reducing the proportion of poor people, in spite of
increasing of population.
1. Causes for Rural Poverty
Various
forces responsible for rural poverty are highlighted below:
1.
The distribution of land is highly skewed in rural
areas. Therefore, majority of rural people work as hired labour to support
their families.
2.
Lack of
Non-farm Employment: Non-farm employment opportunities do not match the increasing labour force. The
excess supply of labour in rural areas reduces the wages and increases the
incidence of poverty.
3.
Lack of
Public Sector Investment: The root cause of rural poverty in our country is
lack of public sector investment on
human resource development.
4.
Inflation: Steady
increase in prices affects the purchasing power of the rural poor leading to rural poverty.
5.
Low Productivity: Low
productivity of rural labour and farm activities is a cause as well as the effect of poverty.
6.
Unequal
Benefit of Growth: Major gains of economic development are enjoyed
by the urban rich people leading to
concentration of wealth. Due to defective economic structure and policies,
gains of growth are not reaching the poor and the contributions of poor people
are not accounted properly.
7.
Low Rate
of Economic Growth: The rate of growth of India is always below the target and it has benefited the rich.
The poor are always denied of the benefits of the achieved growth and
development of the country.
8.
More
Emphasis on Large Industries: Huge investment in large
industries catering to the needs of
middle and upper classes in urban areas are made in India. Such industries are
capital-intensive and do not generate more employment opportunities.
Therefore,
poor are not in a position to get employed and to come out from the poverty in
villages.
9.
Social
Evils: Social evils prevalent in the society like custom, believes etc.
increase unproductive expenditure.
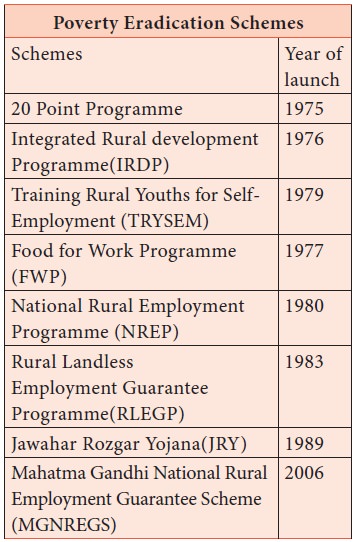
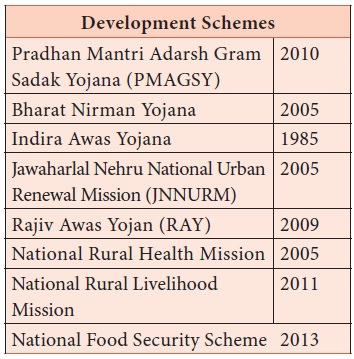
2. Remedial Measures to Rural Poverty
Since
rural unemployment and rural poverty are interrelated, creation of employment
opportunities would support elimination of poverty. Poverty alleviation schemes
and programmes have been implemented, modified, consolidated, expanded and
improved over time. However, unemployment, begging, rag picking and slumming
continues. Unless employment is given to all the people poverty cannot be
eliminated. Who will bell the cat?
Related Topics