Chapter: Mobile Computing : Mobile ADHOC Networks
Routing - Mobile Adhoc Networks
ROUTING
Routing is the process of selecting best paths
in a network. In the past, the term routing also meant forwarding network
traffic among networks. However, that latter function is better described
as forwarding. Routing is
performed for many kinds
of networks, including the
telephone network (circuit switching), electronic data networks (such as the
Internet), and transportation networks. This article is concerned primarily
with routing in electronic data networks using packet switching technology.
In packet switching networks, routing directs
packet forwarding (the transit of logically addressed network packets from
their source toward their ultimate
destination) through intermediate
nodes. Intermediate nodes are typically
network hardware devices such as routers, bridges, gateways,
firewalls, or switches. General-purpose computers can also forward packets and
perform routing, though they are not specialized hardware and may suffer from
limited performance.
The routing process usually directs forwarding
on the basis of routing tables, which maintain a record of the routes to
various network destinations. Thus, constructing routing tables, which are held
in the router's memory, is very important for efficient routing. Most routing
algorithms use only one network path at a time. Multipath routing techniques
enable the use of multiple alternative paths.
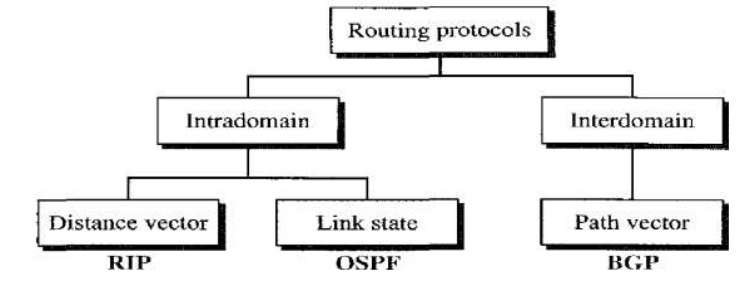
In internetworking, the process of moving a
packet of data from source to destination. Routing is usually performed by a
dedicated device called a router. Routing is a key feature of the Internet
because it enables messages to pass from one computer to another and eventually
reach the target machine. Each intermediary computer performs routing by
passing along the message to the next computer. Part of this process involves
analyzing a routing table to determine the best path.
Routing is often confused with bridging, which
performs a similar function. The principal difference between the two is that
bridging occurs at a lower level and is therefore more of a hardware function
whereas routing occurs at a higher level where the software component is more
important. And because routing occurs at a higher level, it can perform more
complex analysis to determine the optimal path for the packet.
Related Topics