Chapter: Mechanical : Human Resource Management(HRM) : Perspectives In Human Resource Management
Role of Human Resource Management
INCLUSIVE GROWTH AND
AFFIRMATIVE ACTION OF HR IN AN ORGANISATION
•
Affirmative action should provide
consistent, fair and ethical leadership to meet present and future HR
challenges.
NEW TRENDS IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Attitude Surveys
Better Communication Channels Change in the
Work-Life
Job Redesign Job Enlargement
New approaches to compensation and rewards Career
Planning
Performance Appraisal Decentralisation
Breaking down the hierarchical structure
Facilitating Empowerment
Initiating and facilitating process of
change Enlarging the knowledge base
Developing team spirit
Facilitating the employees desires of
self-actualisation.
Role of Human Resource Management(HRM)
The role of HRM is to
plan, develop and administer policies and programs designed to make optimum use
of an organizations human resources. It is that part of management which is
concerned with the people at work and with their relationship within
enterprises. Its objectives are: (a) Effective utilization of human
resources,
(b) Desirable
working relationships among all members of the organizations, and (c)
Maximum individual development.
Human resources
function as primarily administrative and professional. HR staff focused on
administering benefits and other payroll and as playing a part in the firm‘s
overall strat
HR professionals have
an all encompassing role. They are required to have a thorough knowledge of the
organization and its intricacies and complexities.
The ultimate goal of
every HR person should be to develop a linkage between the employee and
organization because employee‘s commitment to the
The first and foremost
role of HR personnel is to impart continuous education to the employees about
the changes and challenges facing the country in general and their organization
in particular. The employees should know about the balance sheet of the
company, sales progress, and diversification of plans, share price movements,
turnover and other details about the company. The HR professionals should
impart such knowledge to all employees through small booklets, video films and
lectures.
The primary responsibilities of Human Resource
managers are:
To develop a thorough knowledge of corporate
culture, plans and policies. To act as an internal change agent and consultant
To initiate change and act as an expert and
facilitator
To
actively involve in
company‘s strategy fo
To keep communication
line open between the HRD function and individuals and groups both within and
outside the organization\
To identify and evolve HRD strategies in consonance
with overall business strategy.
To facilitate the
development of various organizational teams and their working relationship with
other teams and individuals.
To try and relate
people and work so that the organization objectives are achieved efficiently
and effectively.
To diagnose problems
and determine appropriate solution particularly in the human resource areas.
To provide co-ordination and support services for
the delivery of HRD programmes and services To evaluate the impact of an HRD
intervention or to conduct research so as to identify, develop or test how HRD
In general has improved individual and organizational performance.
According to Dave Ulrich
HR play‘s four
key r
1. Strategic
Partner Role-Turning strategy into results by
building organizations that create value;
2. Change
Agent Role- making change happen, and in particular, help it
happen fast
3. Employees
Champion Role—managing the talent or the intellectual
capital within a firm
4. Administrative
Role—Trying
to get things to happen better, faster and cheaper.
The role HR in
organizations has undergone an extensive change and many organizations have
gradually oriented themselves from the traditional personnel management to a
human resources management approach.
The basic approach of
HRM is to perceive the organization as a whole. Its emphasis is not only on
production and productivity but also on the quality of life. It seeks to
achieve the paramount development of human resources and the utmost possible
socio-economic development.
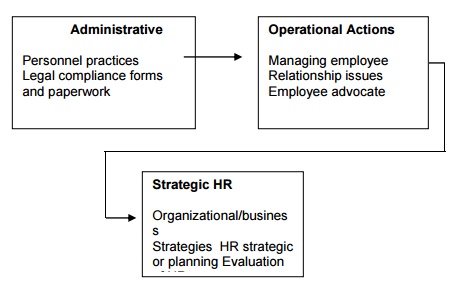
Current Classification of HR roles
According to R.L Mathis and J. H. Jackson (2010)
several roles can be fulfilled by HR management. The nature and extent of these
roles depend on both what upper management wants HR management to do and what
competencies the HR staff have demonstrated. Three roles are typically
identified for HR.
1.
Administrative Role of HR
The administrative role of HR management has been
heavily oriented to administration and recordkeeping including essential legal
paperwork and policy implementation. Major changes have happened in the
administrative role of HR during the recent years. Two major shifts driving the
transformation of the
administrative
role are: Greater use of technology and Outsourcing.
Technology has been widely used to improve the
administrative efficiency of HR and the responsiveness of HR to employees and
managers, more HR functions are becoming available electronically or are being
done on the Internet using Web-based technology. Technology is being used in
most HR activities, from employment applications and employee benefits
enrollments to e-learning using Internet-based resources.
Increasingly, many HR administrative functions are
being outsourced to vendors. This outsourcing ofHR administrative activities
has grown dramatically in HR areas such as employee assistance (counseling),
retirement planning, benefits administration, payroll services, and
outplacement services.
2.
Operational and Employee Advocate Role for HR
HR managers manage most HR activities in line with
the strategies and operations that have been identified by management and
serves as employee ―champion‖for employee issues and concerns.
HR often has been viewed as the ―employee
advocate‖in organizations. They act as the voice for employee concerns, and
spend considerable time on HR ―crisis management,‖dealing with employee
problems that are both work-related and not work-related. Employee advocacy
helps to ensure fair and equitable treatment for employees regardless of
personal background or circumstances.
Sometimes the HR‘sadvocate role may create conflict
with operating managers. However, without the HR advocate role, employers could
face even more lawsuits and regulatory complaints than they do now.
The operational role requires HR professionals to
cooperate with various departmental and operating managers and supervisors in
order to identify and implement needed programs and policies in the
organization. Operational activities are tactical in nature. Compliance with
equal employment opportunity and other laws is ensured, employment applications
are processed, current openings are filled through interviews, supervisors are
trained, safety problems are resolved, and wage and benefit questions are
answered. For carrying out these activities HR manager matches HR activities
with the strategies of the organization.
3.
Strategic Role for HR
The administrative role traditionally has been the
dominant role for HR. However, as Figure 1.4 indicates that a broader
transformation in HR is needed so that significantly less HR time and fewer HR
staffs are used just for clerical work.
Differences between the operational and strategic
roles exist in a number of HR areas. The strategic HR role means that HR
professionals are proactive in addressing business realities and focusing on
future business needs, such as strategic planning, compensation strategies, the
performance of HR, and measuring its results. However, in some organizations,
HR often does not play a key role in formulating the strategies for the
organization as a whole; instead it merely carries them out through HR
activities.
Many executives, managers, and HR professionals are
increasingly seeing the need for HR management to become a greater strategic
contributor to the ―business‖success of organizations. HR should be responsible
for knowing what the true cost of human capital is for an employer. For
example, it may cost two times key employees‘annual salaries to replace them if
they leave. Turnover can be controlled though HR activities, and if it is
successful in saving the company money with good retention and talent
management strategies, those may be important contributions to the bottom line
of organizational performance.
The role of HR as a strategic business partner
is often described as ―having a seat at the table,‖and contributing to the
strategic directions and success of the organization. That means HR is involved
in devising strategy in addition to implementing strategy. Part
of HR‘scontribution is to have financial expertise and to produce
financial results, not just to boost employee morale or administrative
efficiencies. Therefore, a significant concern for chief financial officers
(CFOs) is whether HR executives are equipped to help them to plan and meet
financial requirements.
However, even though this strategic role of HR is
recognized, many organizations still need to make significant progress toward
fulfilling it. Some examples of areas where strategic contributions can be made
by HR are:
Evaluating mergers and acquisitions for
organizational ―compatibility,‖structural changes, and staffing needs
Conducting workforce planning to anticipate the
retirement of employees at all levels and identify
workforce
expansion in organizational strategic plans
Leading site selection efforts for new facilities or
transferring operations to international outsourcing locations based on
workforce needs
Instituting HR management systems to
reduce administrative time, equipment, and staff by using HR technology
Working with executives to develop a revised sales
compensation and incentives plan as new products
It is the era when for the competitive triumph of
the organization there is a need to involve HRM significantly in an integrated
manner, which demands such capabilities from the HR specialists.
The role of HR shifted from a facilitator to a
functional peer with competencies in other functions, and is acknowledged as an
equal partner by others. The HR is motivated to contribute to organizational
objectives of profitability and customer satisfaction, and is seen as a vehicle
for realization of quality development. The department has a responsibility for
monitoring employee satisfaction, since it is seen as substitute to customer
satisfaction.
According to McKinsey‘s7-S framework model HR plays
the role of a catalyst for the organization. According to this framework,
effective organizational change is a complex relationship between seven S‘s.
HRM is a total matching process between the three Hard S‘s(Strategy, Structure
and Systems) and the four Soft S‘s(Style, Staff, Skills and Super-ordinate
Goals). Clearly, all the S‘shave to complement each other and have to be
aligned towards a single corporate vision for the organization to be effective.
It has to be realized that most of the S‘sare determined directly or indirectly
by the way Human Resources are managed, and therefore, HRM must be a part of
the total business strategy.
Related Topics