Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Rickettsia, Coxiella, Ehrlichia, and Bartonella
Rickettsial Disease
RICKETTSIAL DISEASE
The classic example of rickettsial disease is epidemic typhus, but the most impor- tant rickettsiosis in the United States is Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF). Both types of rickettsial disease are characterized by fever, rash, and myalgias/myositis. In RMSF, the rash appears first on the palms and soles, wrists, and ankles, and it migrates centripetally; in epidemic typhus, the rash begins on diseases may be fatal as the result of severe vascular collapse. The vectors also differ; for RMSF, the vector is a tick, and for epidemic typhus, a louse.
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
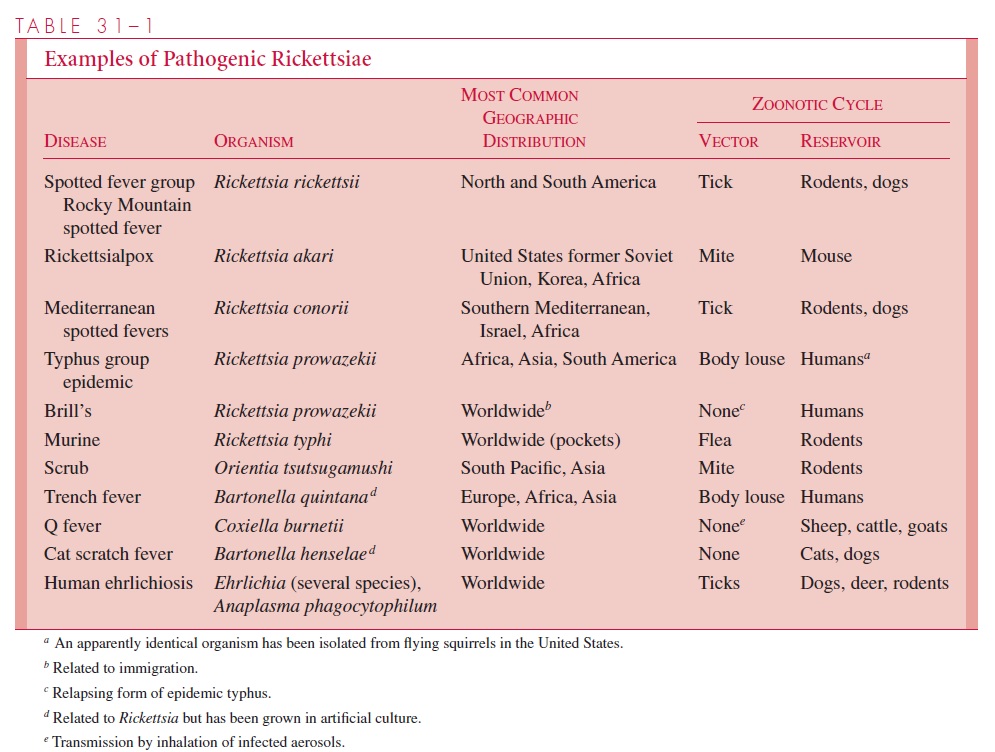
Most rickettsiae have animal reservoirs and are spread by insect vectors, which are prominent components of their life cycles (Table 31–1). Most rickettsial infections of humans result in clinical illness. Rickettsiae infect the vascular endothelium, and the primary pathologic lesion is a vasculitis in which rickettsiae multiply in the endothelial cells lining the small blood vessels. Focal areas of endothelial proliferation and perivascular infiltration
leading to thrombosis and leakage of red blood cells into the surrounding tissues account for the rash and petechial lesions. Vascular lesions occur throughout the body, producing the systemic manifestations of the disease. They are obviously most apparent in skin but most serious in the adrenal glands. An endotoxin-like shock has been demonstrated in animals on injection of whole rickettsial cells, but the nature and role of any toxin in human disease are unknown.
DIAGNOSIS
Culture of rickettsiae is both difficult and hazardous. Their isolation in fertile eggs or cell cultures is generally attempted only in reference centers with special facilities and personnel experienced in handling the organisms. For this reason, serologic tests are the primary means of specific diagnosis. A number of test systems using specific rickettsial
antigens have been developed, of which the indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) method is generally the most sensitive and specific. This test is usually available only in reference
laboratories. For rapid diagnosis, examination of biopsies such as skin lesions by immunofluorescence or immunoenzyme methods to detect antigens can be used.
Related Topics