Chapter: Flexible Alternating Current Transmission System : Introduction
Reactive Power Control
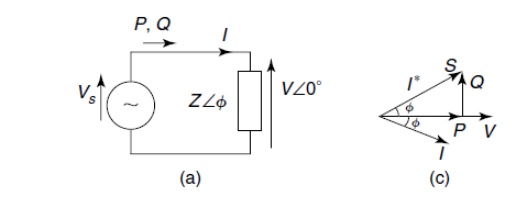
REACTIVE POWER CONTROL
Ø “To make
transmission networks operate within desired voltage limits and methods of
making up or taking away reactive power is called reactive-power control”.
Ø The AC
networks and the devices connected to them create associated time-varying
electrical fields related to the applied voltage and as well as magnetic fields
dependent on the current flow and they build up these fields store energy that
is released when they collapse”.
Ø Apart
from the energy dissipation in resistive components, all energy-coupling
devices (e.g: motors and generators) operate based on their capacity to store
and release energy.
Ø While the
major means of control of reactive power and voltage is via the excitation
systems of synchronous generators and devices may be deployed in a transmission
network to maintain a good voltage profile in the system.
Ø The shunt
connected devices like shunt capacitors or inductors or synchronous inductors
may be fixed or switched (using circuit breaker).
Ø The Vernier or smooth control of reactive power is also possible by varying effective susceptance characteristics by use of power electronic devices. Example: Static Var Componsator(SVC)” and a Thyristor Controlled Reactor (TCR).
Related Topics