Methods Employed in the Isolation of Microorganisms - Pure Culture | 11th Microbiology : Chapter 5 : Cultivation of Microorganisms
Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 5 : Cultivation of Microorganisms
Pure Culture
Pure Culture
In nature, microorganisms usually exist as complex multispecies
community. A single species has to be characterized in order to know the
morphology, pathogenicity and molecular genomic pattern of the organism. For
characterizing a species we have to isolate the organisms in pure form. Pure
culture or axenic culture is a culture containing only one type of organism.
The descendents of a single organism in pure culture is called a strain. A
strain forms a single colony. Colony is a cluster of microorganisms in which
all the characters of the family remain same. With the advent of the pure
culture techniques many microorganisms are being identified.
Methods Employed in the Isolation of Microorganisms
Though there are many methods designed for isolation of
microorganisms, pour plate method, spread plate method and streak plate method
are widely used in the field of Microbiology.
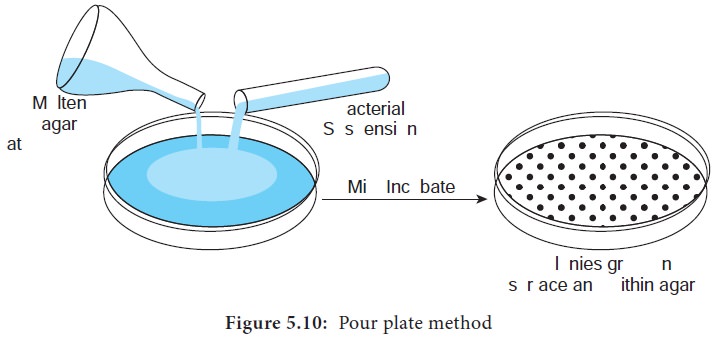
i) Pour plate method
·
It is the used for the isolation and counting of colony forming
bacteria in the specified sample.
·
In this technique a sample is diluted several times to reduce
the density of the microbial population.
·
A very small amount of diluted sample (1ml or 0.1ml) is mixed
with the molten agar at a temperature of 45°C.
· The mixture is poured into the sterile petridish (In 1887, Juluis Richard Petri, a worker in Koch’s laboratory, designed the Petriplate.) in an aseptic condition and plates are incubated at a specific temperature for a given period of time.
·
Plates are incubated in an inverted manner.
·
After incubation, the colonies are formed in a discrete pattern
both on the surface of agar and also embedded within the medium.
·
Pour plate can be also used to deter-mine the number of cells in
a popula-tion.(Figure 5.10)
Disadvantages of pour plate method
i) Loss of viability of heat sensitive organisms coming into contact with hot agar.
ii) Reduced growth of obligate aerobes in the depth of agar.
iii) Colonies embedded within the agar are much smaller than
that of surface and may be confluent or invisible.
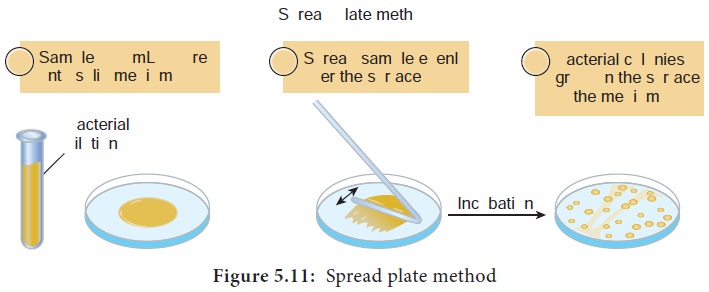
ii) Spread plate method
·
Spread plate method is an easy and direct method of isolating a
pure culture.
·
In this technique a specified amount of diluted inoculum (0.1ml
or less) of microbial culture is seeded on agar plate.
·
After inoculation of the sample on the agar medium, the inoculum
is evenly spread on the surface with the help of a sterile glass L rod (a bent
glass rod)
·
Microorganisms are evenly distributed in the entire surface of
agar.
·
The dispersed microorganisms develop into isolated colonies.
·
In this method, the plates are incubated at a specified
temperature for a given period of time.
·
After incubation the plates are observed for the growth of
discrete colonies.
·
The number of colonies are equal to the number of viable
organism. This method can be used to count the microbial population (Figure
5.11).
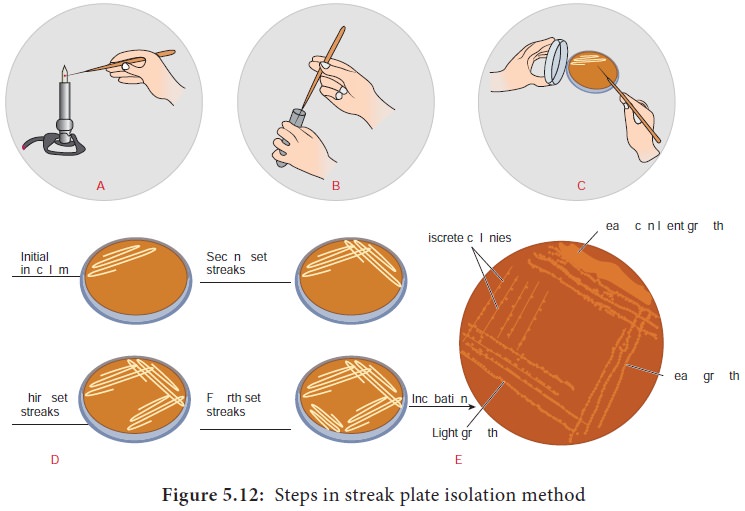
iii) Streak plate technique
·
The streak plate technique is one of the most commonly used
methods for isolating pure culture of bacteria.
·
In this method,
a loopful of inoculum from a sample is taken and it is streaked across
the surface of the sterile solid medium.
·
Different streaking patterns can be used to separate individual
bacterial cell on the agar surface.
·
After the first sector is streaked the inoculated loop is
sterilized and inoculum for the second sector is obtained from the first
sector.
·
Similar process is followed for streaking the further areas in
the sectors.
·
Since the inoculum is serially diluted during streaking patterns
the dilution gradient is established across the surface of the medium.
·
After streaking, plates are incubated at a specific temperature
for a given period of time.
·
After incubation, plates are observed for growth of colonies
(based on the streaking pattern and density of culture growth of microbes are
abundant in the first sector in comparison with the formation of separated
discrete colonies in the fourth sector of the agar medium).
·
Each isolated colony is assumed to be grown from a single
bacteria and thus represent a clone of pure culture.
·
Successful isolation depends on spatial separation of single
cells (Figure 5.12).
Related Topics