Chapter: civil : Applied Hydraulic Engineering: Pumps
Pumps: Air Vessels
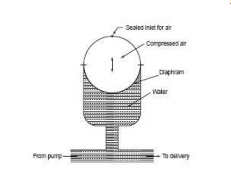
Air Vessels
Air
vessel is a strong closed vessel as shown in figure. The top half contains
compressed air and the lower portion contains water or the fluid being pumped.
Air and water are separated by a flexible diaphragm which can move up
or down depending on the difference
in pressure between the fluids. The
air charged at
near total delivery pressure/suction pressure from the
top and sealed. The air vessel is connected to the pipe lines very near the
pump, at nearly the pump level. On the delivery side, when at the beginning and
up to the middle of the delivery stroke the head equals hs + hf + ha , higher
than the static and friction heads. At this time part of the water from pump
will flow into the air vessel and the remaining will flow through the delivery
pipe. This will increase the compressed air pressure. At the middle stroke
position the head will be sufficient to just cause flow. The whole of the flow
from pump will flow to the delivery pipe. At the second half of the stroke the
head will be equal to hs + hf - ha. At the position the head will be not
sufficient to cause flow. The compressed air pressure will act on the water and
water charged earlier into the air vessel will now flow out. Similar situation
prevails on the suction side. At the start and up to the middle of the suction
stroke the head at the pump is higher than static suction head by the amount of
acceleration head. The flow will be more and part will flow into the air
vessel. The second half of the stroke water will flow out of the air vessel.
In this
process the velocity of water in the delivery pipe beyond the air vessel is
uniform, and lower than the maximum velocity if air vessel is not fitted.
Similar situation prevails in the suction side also. The effect is not only to
give uniform flow but reduce the friction head to a considerable extent saving
work. Without air vessel the friction head increases, reaches a maximum value
at the mid stroke and then decreases to zero. With air vessel the friction head
is lower and is constant throughout the stroke. This is due to the constant
velocity in the pipe.
The advantages of
installing air vessels are:
(i)
The flow fluctuation is reduced and a uniform
flow is obtained.
(ii)
The friction work is reduced.
(iii)
The acceleration head is reduced considerably.
(iv)
Enables the use of higher speeds.
Related Topics