Chapter: Object Oriented Programming and Data Structure : Inheritance and Polymorphism
Public, Private, Protected inheritance
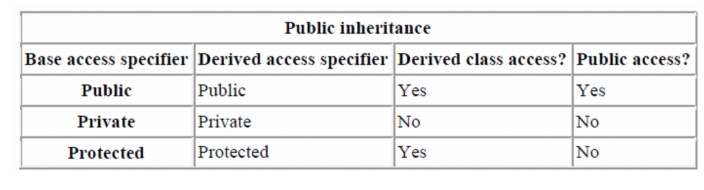
Public inheritance
Public
inheritance is by far the most commonly used type of inheritance. In fact, very
rarely will you use the other types of inheritance, so your primary focus
should be on understanding this section. Fortunately, public inheritance is
also the easiest to understand. When you inherit a base class publicly, all
members keep their original access specifications. Private members stay
private, protected members stay protected, and public members stay public.
class
Base
{
public:
intm_nPublic;
private:
intm_nPrivate;
protected:
intm_nProtected;
};
class
Pub: public Base
{
// Public
inheritance means:
// m_nPublic
stays public
// m_nPrivate
stays private
// m_nProtected
stays protected Pub()
{
// The
derived class always uses the immediate parent's class access specifications
// Thus, Pub
uses Base's access specifiers
m_nPublic
= 1; // okay: anybody can access public members
m_nPrivate
= 2; // not okay: derived classes can't access private members in the base
class!
m_nProtected
= 3; // okay: derived classes can access protected members
}
};
int
main()
{
// Outside
access uses the access specifiers of the class being accessed.
// In this
case, the access specifiers of cPub. Because Pub has inherited publicly from
Base,
// no access
specifiers have been changed.
Pub cPub;
cPub.m_nPublic
= 1; // okay: anybody can access public members
cPub.m_nPrivate
= 2; // not okay: can not access private members from outside class
cPub.m_nProtected = 3; // not okay: can not access protected members from
outside class
}
This is
fairly straightforward. The things worth noting are:
1.
Derived classes can not directly access private members of the base class.
2. The
protected access specifier allows derived classes to directly access members of
the base class while not exposing those members to the public.
3. The
derived class uses access specifiers from the base class.
4. The
outside uses access specifiers from the derived class.
To
summarize in table form:
Private inheritance
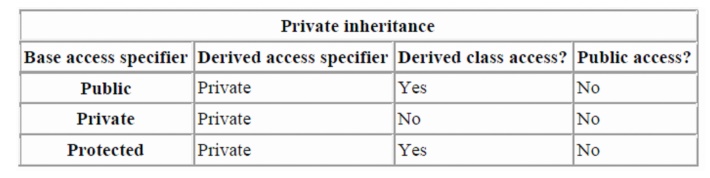
With
private inheritance, all members from the base class are inherited as private.
This means private members stay private, and protected and public members
become private. Note that this does not affect that way that the derived class
accesses members inherited from its parent! It only affects the code trying to
access those members through the derived class.
class
Base
{
public:
intm_nPublic; private: intm_nPrivate; protected: intm_nProtected; };
class
Pri: private Base
{
// Private
inheritance means:
// m_nPublic
becomes private
// m_nPrivate
stays private
// m_nProtected
becomes private Pri()
{
//The
derived class always uses the immediate parent's class access specifications
//Thus,
Pub uses Base's access specifiers
m_nPublic
= 1; // okay: anybody can access public members
m_nPrivate
= 2; // not okay: derived classes can't access private members in the base
class!
m_nProtected
= 3; // okay: derived classes can access protected members
}
};
int
main()
{
// Outside
access uses the access specifiers of the class being accessed.
// Note that
because Pri has inherited privately from Base,
// all
members of Base have become private when access through Pri. PricPri;
cPri.m_nPublic
= 1; // not okay: m_nPublic is now a private member when accessed through Pri
cPri.m_nPrivate
= 2; // not okay: can not access private members from outside class
cPri.m_nProtected = 3; // not okay: m_nProtected is now a private member when
accessed through Pri
// However,
we can still access Base members as normal through Base:
Base
cBase;
cBase.m_nPublic
= 1; // okay, m_nPublic is public
cBase.m_nPrivate
= 2; // not okay, m_nPrivate is private cBase.m_nProtected = 3; // not okay,
m_nProtected is protected
}
To
summarize in table form:
Protected inheritance
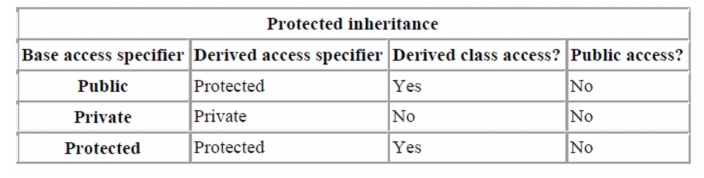
Protected
inheritance is the last method of inheritance. It is almost never used, except
in very particular cases. With protected inheritance, the public and protected
members become protected, and private members stay private.
To
summarize in table form:
Protected
inheritance is similar to private inheritance. However, classes derived from
the derived class still have access to the public and protected members
directly. The public (stuff outside the class) does not.
Related Topics