Chapter: Transmission and Distribution : Insulators and Cables
Potential Distribution Over Suspension Insulator String
POTENTIAL DISTRIBUTION OVER
SUSPENSION INSULATOR STRING
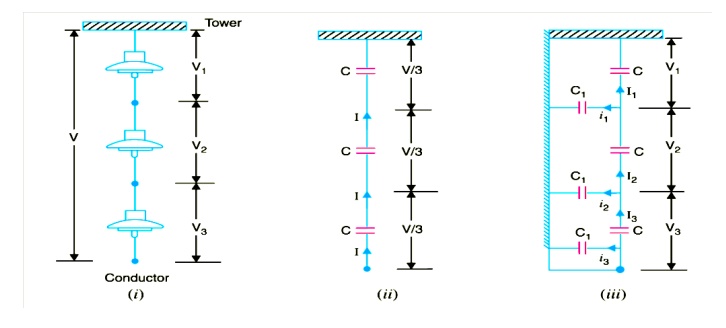
A string of suspension insulators consists of a number of
porcelain discs connected in series through metallic links. Fig. shows 3-disc
string of suspension insulators. The porcelain portion of each disc is in
between two metal links. Therefore, each disc forms a capacitor C as shown in
Fig. This is known as mutual capacitance or self-capacitance. If there were
mutual capacitance alone, then charging current would have been the same
through all the discs and consequently voltage across each unit would have been
the same i.e., V/3 as shown However, in actual practice, capacitance also
exists between metal fitting of each disc and tower or earth. This is known as
shunt capacitance C1. Due to shunt capacitance, charging current is not the
same through all the discs of the string Therefore, voltage across each disc
will be different. Obviously, the disc nearest to the line conductor will have
the maximum* voltage. Thus referring to Fig V3
will be much more than V2 or V1. The following points
may be noted regarding the potential
distribution over a string of suspension insulators:
o
The voltage impressed on a string of suspension
insulators does not distribute itself uniformly across the individual discs due
to the presence of shunt capacitance.
o
The disc nearest to the conductor has maximum
voltage across it. As we move towards the cross-arm, the voltage across each
disc goes on decreasing.
o
The unit nearest to the conductor is under maximum
electrical stress and is likely to be punctured. Therefore, means must be
provided to equalize the potential across each unit.
o If the
voltage impressed across the string were d.c., then voltage across each unit
would be the same. It is because insulator capacitances are ineffective for d.c.
Related Topics