Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Secondary metabolites fulfill specific ecological functions in plants
Plants protect themselves by tricking herbivores with false amino acids
Plants protect themselves by tricking herbivores with false amino acids
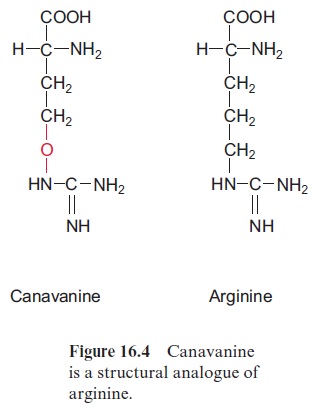
Many plants contain unusual amino acids with a structure very simi-lar to that of protein building amino acids (e.g., canavaninefrom Jackbean (Canavalia ensiformis), a structural analogue of arginine (Fig. 16.4)). Herbivores take up canavanine with their food. During protein biosynthesis, the arginine-transfer RNAs of animals cannot distinguish between arginine and canavanine and incorporate canavanine instead of arginine into proteins. This exchange can alter the three-dimensional structure of proteins, which then lose their biological function partially or even completely. Therefore canavanine is toxic for herbivores. In those plants which synthesize cana-vanine, the arginine transfer RNA does not react with canavanine, therefore it is not toxic for these plants. This same protective mechanism is used by some insects, which are specialized in eating leaves containing canavanine.
Related Topics