Chapter: Anatomy of Flowering Plants: An Introduction to Structure and Development : Organs, Cells and Tissues
Plant Meristems: Apical and Lateral Meristems
Meristems
Meristematic tissue consists of thin-walled, tightly packed living cells which undergo frequent divisions. Meristematic cells undergo cell division and wall formation followed by differential cell expansion. After nuclear division there is progressive deposi-tion of membranes in the cytoplasm into a cell plate that is located in the equatorial zone between the two daughter nuclei. The cell plate extends to join the cell walls, thus depositing a new wall. Most of the plant body is differentiated at the meristems in well-defined zones, though cells in other regions may also occasionally divide. There are some remarkable examples of fully-differentiated cells giving rise to entire plantlets, notably on leaves of Crassulaceae, such as Kalanchoe.
Apical Meristems
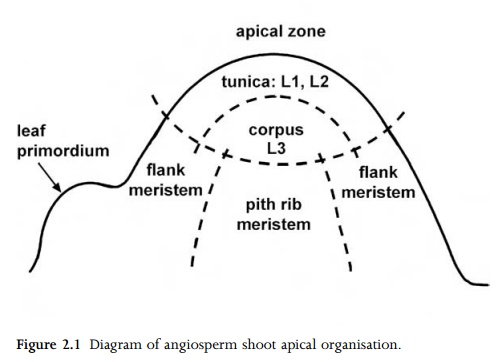
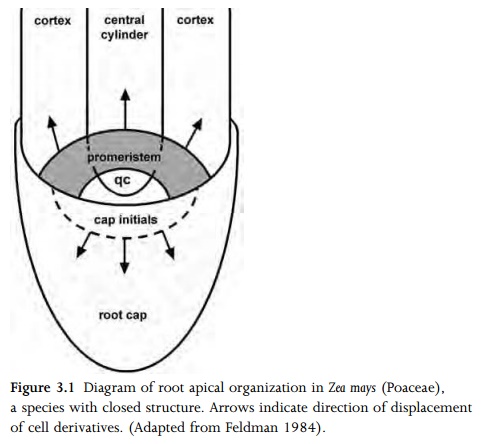
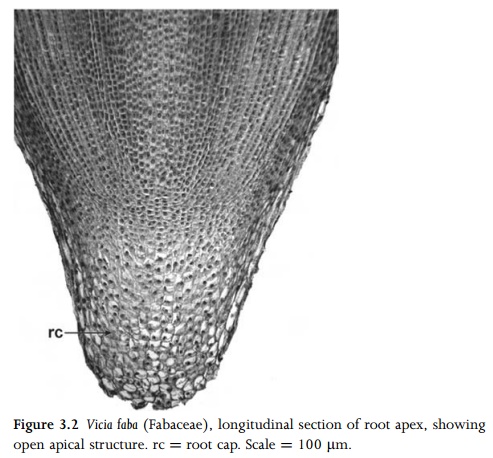
Apical meristems are located at the shoot apex (Fig. 2.1), where primary stem, leaves and flowers differentiate, and at the root apex (Figs 3.1, 3.2), where primary root tissue is produced. Subsequent elongation of the shoot axis may occur by random cell divisions and growth throughout the youngest internodes. This region of diffuse cell division is termed an uninterrupted meristem, and is continuous with the apical meristem. However, in some plant stems, particularly in grasses, most cell divisions contributing to stem elongation occur in a limited region, usually at the base of the internode, which is then termed an intercalary meristem. Both intercalary and uninterrupted meristems represent growth in regions of already differentiated tissues.
Lateral Meristems
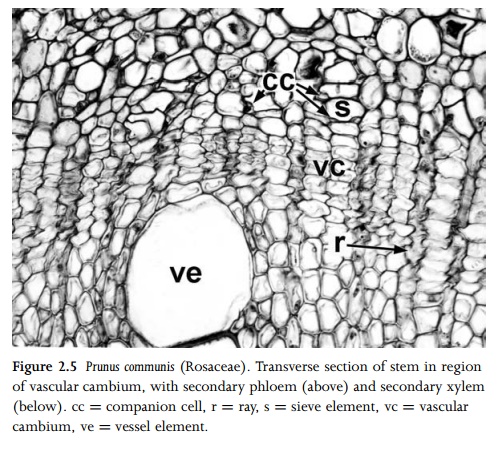
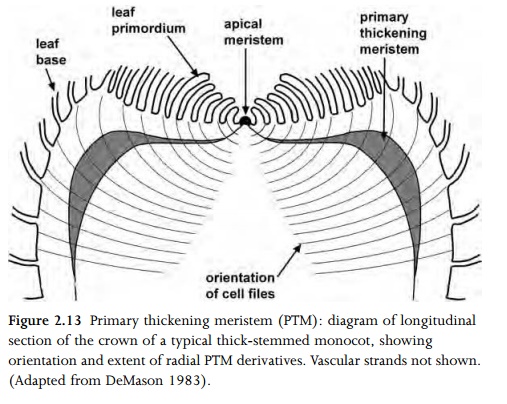
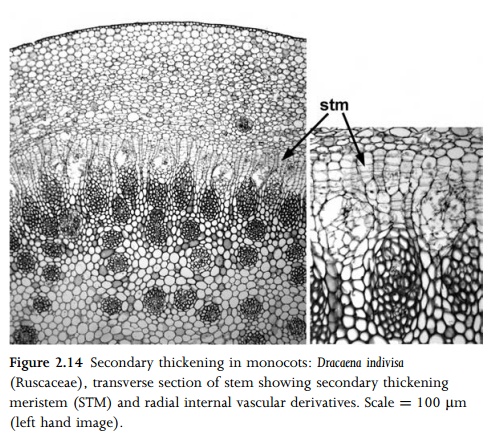
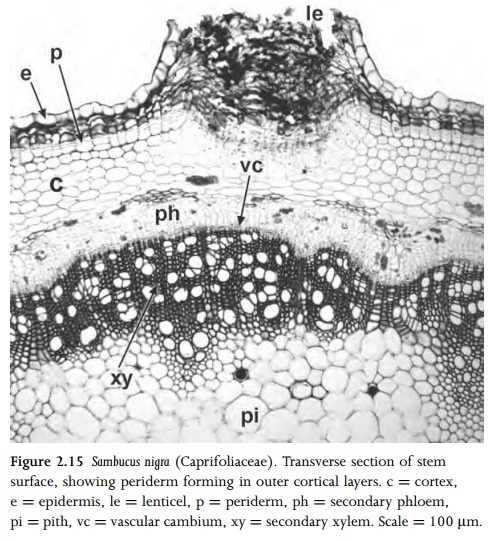
Lateral meristems are located parallel to the long axis of a shoot or root, most commonly in the pericyclic region, at the junction between vascular tissue and cortex. Examples of lateral meristems include primary and secondary thickening meristems (PTM and STM) and vascular cambium. Primary and secondary thicken-ing meristems produce both ground tissue and vascular bundles (Figs 2.13, 2.14). Vascular cambium produces secondary xylem and phloem (; Fig. 2.5). Adventitious roots are typically formed in the root pericycle; in these cases the pericycle could be termed a lateral meristem. The phellogen (cork cambium) is a lateral meristem that occurs in the stem or root cortex, where it forms a protective corky layer (Fig. 2.15). A phellogen may also develop in the region of a wound, or at the point of leaf abscission.
Meristemoids and Asymmetric Cell Division
Meristemoids are individual cells that are responsible for the differentiation of distinct structures. In many cases meristemoids represent the smaller, densely cytoplasmic, daughter cell that results from an unequal (asymmetric) cell division; the larger daughter cell is less active. Asymmetric divisions are caused by cell polarization resulting from organized arrays of actin filaments in the dense cytoplasm during determination of cell plate alignment42. Examples of unequal cell divisions include cleavage of the microspore into a larger vegetative cell and smaller generative cell, formation of a root hair initial (trichoblast), a protophloem division to form a larger sieve tube element and smaller companion cell, and division of an epidermal cell into two cells of unequal sizes, the smaller of which is the meristemoid that will divide to form the guard cells of a stoma.
Related Topics