Chapter: Pathology: Female Genital Pathology
Placenta - Pathology
PLACENTA
Hydatidiform mole (molar pregnancy) is a tumor of placental trophoblastic tissue.
Incidence in the United States is 1 per 1,000 pregnancies, with an even higher
inci-dence in Asia. Women ages <15 and >40 are at increased risk.
Complete mole results from
fertilization of an ovum that lost all of its chro-mosomal material, so that
all chromosomal material is derived from sperm.
•
90% of the time, the molar karyotype is 46,XX
•
10% of the time, the molar karyotype includes a Y chromosome
•
The embryo does not develop
Partial mole results from
fertilization of an ovum (that has not lost its chro-mosomal material) by 2
sperms, one 23,X and one 23,Y.
•
Results in a triploid cell 69, XXY (23,X [maternal] + 23,X [one sperm] +
23,Y [the other sperm])
•
The embryo may develop for a few weeks
Patients with hydatidiform mole
typically present with the following:
•
Excessive uterine enlargement (“size greater than dates”)
•
Vaginal bleeding
•
Passage of edematous, grape-like soft tissue
•
Elevated beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG)
Microscopically, molar tissue
will show edematous chorionic villi, trophoblast pro-liferation, and fetal
tissue (only in partial mole). Diagnosis is by U/S. Treatment is endometrial
curettage and following of β-hCG levels.
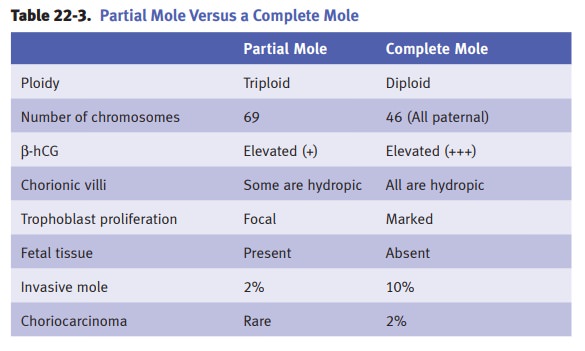
Invasive mole is a mole that invades the myometrium of the uterine wall.
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant germ cell tumor derived from the trophoblast that forms
a necrotic and hemorrhagic mass. Almost 50% arise from complete moles. The most
common presentation is a rising or plateaued titer of hCG after a molar
pregnancy, abortion, or ectopic pregnancy.
Microscopically, choriocarcinoma
shows proliferation of cytotrophoblasts, interme-diate trophoblasts, and
syncytiotrophoblasts. Hematogenous spread can occur, with seeding of tumor to
lungs, brain, liver, etc. Treatment is chemotherapy.
Placental site trophoblastic tumor is a tumor of intermediate trophoblast which
usually presents <2 years after pregnancy with bleeding and an enlarged
uterus. Treatment is surgical; it does not respond well to chemotherapy.
In ectopic pregnancy, the fetus implants outside the normal location,
most often in the fallopian tube, and less often in the ovaries or abdominal
cavity. The fetus almost never survives. The mother is at risk for potentially
fatal intra-abdominal hemorrhage. Risk factors include scarring of fallopian
tubes from PID, endometrio-sis, and decreased tubal motility.
Enlarged placenta is common with maternal diabetes mellitus, Rh hemolytic dis-ease, and
congenital syphilis.
Succenturiate lobes are accessory lobes of the placenta which may cause hemorrhage if torn
away from the main part of the placenta during delivery.
Placental abruption is partial premature separation of the placenta away from the
endometrium, with resulting hemorrhage and clot formation. Risk factors include
hypertension, cigarette use, cocaine, and older maternal age.
Placenta previa describes when the placenta overlies the cervical os. Vaginal delivery
can cause the placenta to tear, with potentially fatal maternal or fetal
hemorrhage.
In placenta accreta, the placenta implants directly in the myometrium
rather than in endometrium. Hysterectomy is required after delivery to remove
the rest of the placenta.
Twin placentation
•
Fraternal twins always have 2 amnions and 2
chorions; placental discs are usually separate, but can grow together to appear
to be a single placental disc.
•
Identical twins have a variable pattern in the
number of membranes and discs due to variations in the specific point in
embryonic development at which the twins separated. Twin-twin transfusion
syndrome can occur if (a) there is only one placental disc and (b) one twin’s
placental vessels connect to the other twin’s placental vessels.
•
Conjoined twins are always identical twins with
one amnion, one chorion, and one disc, though there are rare reports of
diamniotic placentation.
Preeclampsia is a condition of new onset hypertension and either proteinuria or
end-organ dysfunction after 20 weeks gestation in a previously normotensive
woman. It is linked to abnormal uteroplacental blood flow.
•
The term eclampsia is used when the patient has seizures not
attributable to other causes.
•
HELLP syndrome is a rare complication of preeclampsia characterized by
hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets.
Related Topics