Structure, Classification | Lipids - Phospholipids | 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 6 : Lipids
Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 6 : Lipids
Phospholipids
Phospholipids
Phospholipids
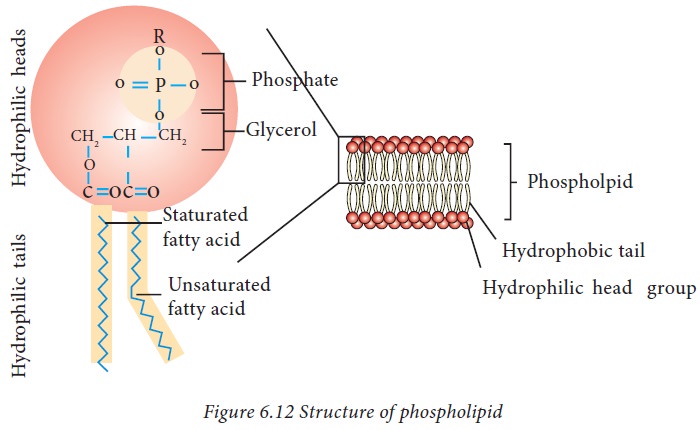
are compound lipids. They are amphipathic molecules, meaning they have a
hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head group. Phospholipids are major
components of the plasma membrane, which serves as a barrier between the cell
and its surroundings. In a membrane, phospholipids are arranged in a structure
called a lipid bilayer, with their phosphate heads facing the water and their
tails pointing towards the interior of the membrane.
Classification:
Phospholipids
are typically composed of fatty acid chains attached to a backbone of glycerol.
Instead of having three fatty acid tails, phospholipids generally have two, and
the hydroxyl group attached to the third carbon of the glycerol backbone is
esterified by a modified phosphate group.
According
to their alcohol content phospholipids are classified into two major types:
·
Glycerophospholipids
·
Sphingophospholipids
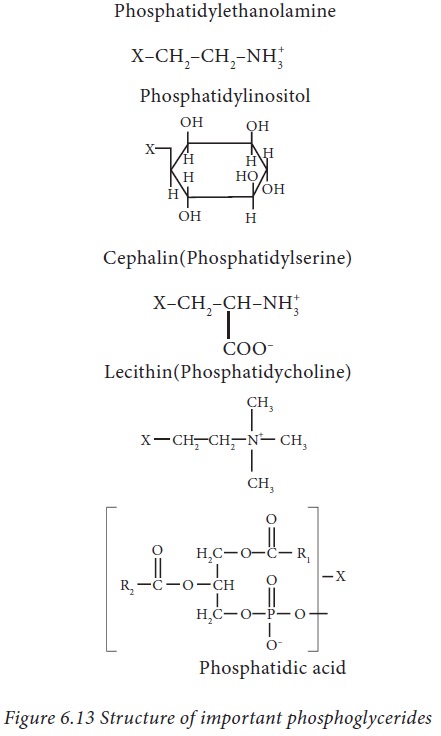
i. Glycero phospholipids
Glycerophospholipids
are abundantly present in heart, brain, kidney, egg yolk and soyabean.
In
glycerophospholipids the alcohol is glycerol, to which two fatty acids, one
phosphate group and an alcohol (inositol), alcohol amine (ethanol amine,
serine) or a nitrogenous base (choline) are attached. It is also known as
phosphoglyceride.
There
are different types of phosphoglycerides based on the attachment to the
phosphate group, that confers different properties and role of the different
glycerophospholipids.
The important phosphoglycerides are:
· Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin): Choline as nitrogenous base.
· Phosphatidylserine (cephalin): Serine as alcohol amine
· Phosphatidylethanolamine: Ethanol amine an alcohol amine.
· Phosphatidylinositol: Inositol a hexahydric alcohol.
ii Sphingophospholipids
They contain a sphingosine back bone,
fatty acid, phosphate and base. They are abundantly present in brain and nerve
tissues. These compounds play important role in signal transmission and cell
recognition.
Sphingosine + Fatty acid = Ceramide Ceramide+base=sphingophospholidpid
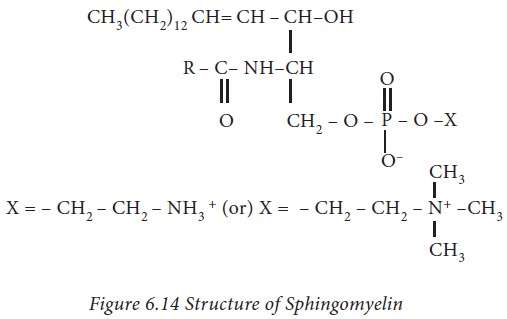
Sphingomyelins have a phosphocholine
or phosphoethanolamine molecule with an ester linkage to the 1-hydroxy group of
a ceramide.
Related Topics