Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 6 : Lipids
Classification of Fatty acids
Fatty acids
Fatty
acids are the building blocks of hydrolysable lipids.
Classification of Fatty acids:
A simple
fatty acid consists of a long linear hydrocarbon chain that may be saturated as
in palmitic acid or it may have one or more double bonds as in linoleic acid.
Few fatty acids like Arachidonic acid and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) contain
more than three double bonds. Each fatty acid differs from the other, primarily
in chain length, number and position of their double bonds. They are often
symbolized by the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain and number
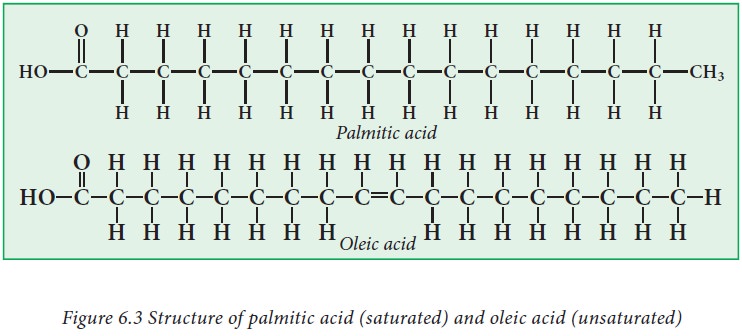
and position of the double bonds. Palmitic acid (Figure 6.3) is symbolized as
16:0 and oleic acid (Fig.6.3) as 18:1(Δ9), indicates the position of
the double bond.
There
are many kinds of fatty acids, isolated from various plant and animal lipids.
Fatty acids with odd number of carbon atoms are significantly present in many
marine organisms.
Saturated Fatty acid
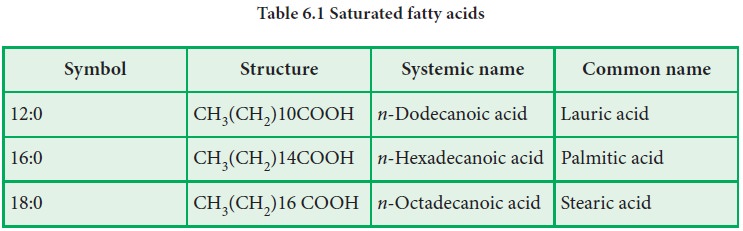
The
general formula of saturated fatty acid is CnH2n+1COOH.
If all carbon-carbon bonds in the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acid are
single covalent bonds, then the fattyacid is said to be a saturated fatty acid.
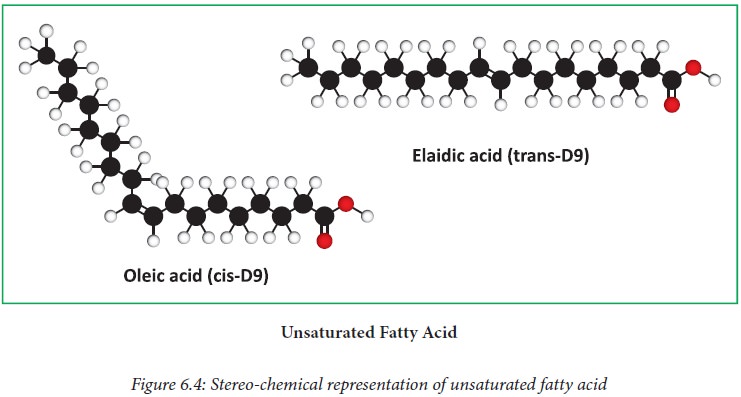
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
When one
or more carbon-carbon double bonds are present, the fatty acid is called
unsaturated. Depending on the number of double bonds present in the hydrocarbon
chain, the fatty acid can be classified as:
· Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) and
· Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid:
A
monounsaturated fatty acid contains one carbon-carbon double bond. Higher
quantity monounsaturated fatty acids are present in olive oil, canola oil
(mustard oil), peanut oil and sesame oil. The general formula is CnH2n-1COOH.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid:
Fatty
acids with more than one double bond are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Foods
with high amounts of polyunsaturated fats include: Walnuts, Sunflower seeds,
Flax seeds or flax oil, Fish (such as salmon, mackerel, herring, albacore tuna,
and trout), Corn oil and Soybean oil.
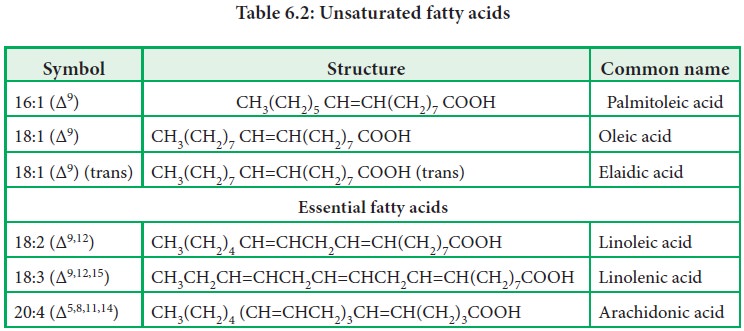
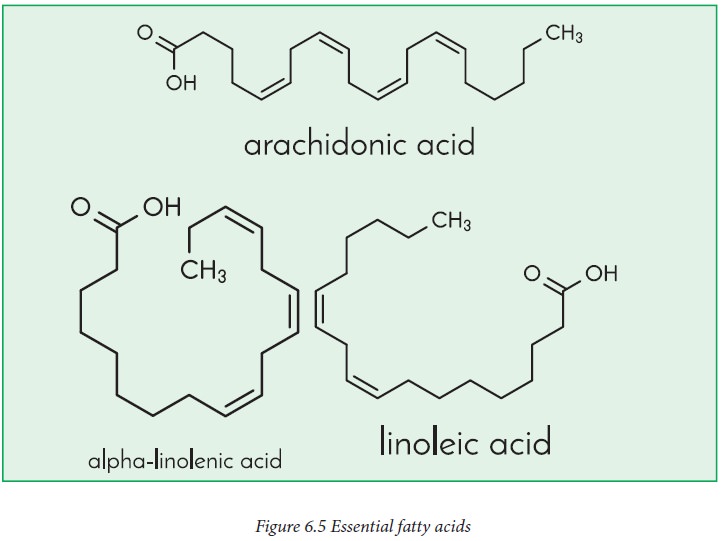
Essential fatty acid (EFA)
Fatty
acids that must be obtained from the diet as they cannot be synthesized by our
body are essential fatty acids (Figure 6.5). EFA are polyunsaturated fatty
acids. They are precursors of prostaglandins, a family of physiologically
potent lipids.
Related Topics