Features (or) Characteristics, Advantages, Disadvantages | Auditing - Periodical (or) Final (or) Complete Audit | 11th Auditing : Chapter 2 and 3 : Classifications of Audit
Chapter: 11th Auditing : Chapter 2 and 3 : Classifications of Audit
Periodical (or) Final (or) Complete Audit
Periodical (or) Final (or) Complete Audit
Annual or Periodical audit is conducted after
closing the books of accounts and preparing the financial statements. In such a
case, the auditor visits the clients only once in a year and checks the
accounts in one visit. The auditor makes a detailed or random check of the
transaction which has taken place in the books of accounts and examines the
correctness and fairness of the financial statements. This type of audit is
free from the defects of continuous audit and carries other advantages with it,
but detailed checking is not possible. Hence, errors and frauds cannot be
detected easily and quickly.
Features (or) Characteristics
1. Periodical
audit work is done and completed in a continuous session.
2. The
auditor visits the clients only once in a year and checks the accounts in one
visit.
3. Auditor
makes a detailed or random check of the transactions and examines the
correctness and fairness of the financial statements.
4. Detailed
checking is not possible and hence errors and frauds cannot be detected easily
and quickly.
5.
Periodical audit is suitable in case of small
business concerns where there are only limited transactions.

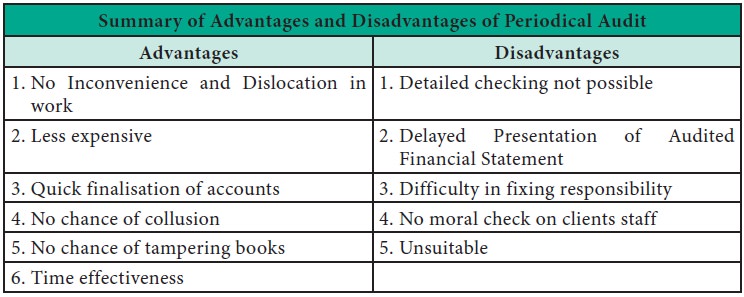
Advantages
1.
No
Inconvenience and Dislocation in Work: The work of audit does not present any inconvenience and
dislocation in the work of the concern as the auditor comes only once in a
year.
2.
Less
Expensive: Periodical audit is less expensive and more useful for small business concern than
continuous audit.
3.
Quick Finalisation of Accounts: In periodical
audit, the work of the auditor can be finished quickly and within a reasonable
time. The auditor ensures quick completion of work in one session due to
continuity.
4.
No Chance
of Collusion: In periodical
audit there is no undue collusion between the auditor and the clerk as in
the case of continuous audit.
5.
No Chance
of Tampering Books: The possibility
of tampering with the books of accounts during the audit is reduced as the
audit work starts only after the books are closed.
6. Time Effectiveness: The auditor uses statistical sampling methods and techniques which lead to time effectiveness.
Disadvantages
1. Detailed Checking not Possible: In periodical audit, detailed checking of
accounts is not possible and hence there are chances of errors and frauds which
remain undetected.
2. Delayed Presentation of Audited Financial
Statements: The work of an
auditor starts only after the close of the financial period, therefore
there is undue delay in finalising the financial statements and in preparing
the audit report.
3. Difficulty in Fixing Responsibility: Another
major drawback is that all the errors and frauds are found at the end of the
accounting year, which makes it very difficult to fix responsibility for
defalcations.
4. No Moral Check on Clients Staff: There is
no sense of moral check on the employees in clients organisation as the auditor
visits the company only after the end of the financial period.
5.
Unsuitable:
For big
concerns, periodical audit is rarely
practicable and it is not much popular for them.

Related Topics