Features (or) Characteristics, Advantages | Auditing - Audit of Accounts of Joint Stock Company | 11th Auditing : Chapter 2 and 3 : Classifications of Audit
Chapter: 11th Auditing : Chapter 2 and 3 : Classifications of Audit
Audit of Accounts of Joint Stock Company
Audit of Accounts of Joint
Stock Company
Companies formed and registered under the Companies
Act, 1956 have to compulsorily audit its books of accounts as the owners
(shareholders) and the management of the company is different. The company
auditor’s rights, duties, appointment, remuneration etc. are governed by the
provisions of the Companies Act. This type of audit is called as Statutory
Audit and the person who conducts the audit is called as Statutory Auditor.
The main objective of external or statutory audit
is to examine the accuracy that the financial statements reflect a true and
fair view of the state of affairs of the business. In other words, the company
auditor has to verify that the books of accounts and certify that the books of
accounts and financial statements exhibit a true and fair view of the state of
affairs of the business concern in the form of a report to the shareholders of
the company.

Characteristics (or) Feartures
1. The main objective of external or statutory
audit is to examine the accuracy that the financial statements reflect a true
and fair view of the state of affairs of
the business.
2. The scope of work is determined by the Companies
Act and the auditor possesses an independent status and the management has no
control over the auditor.
3. Auditor should be a qualified Chartered
Accountant as laid down in the provisions of the Companies Act.
4. Statutory auditor is appointed and removed by
the shareholders of the company.
5. The powers and duties of statutory audit are
determined by the Companies Act.
6. Statutory or Company auditor is liable both to
shareholders and to the third parties.
7. After audit of accounts of a company, auditor
has to submit a audit report to the shareholders at annual general meeting in
prescribed format.
8. Company or statutory auditor is responsible to
shareholders and acts as a watch-dog for the shareholders.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of auditing the
accounts of a Joint Stock Company.
1.
Verification
of Accuracy of Books of Accounts: Audit of accounts helps to verify the correctness of the
financial transaction and accuracy of books of accounts.
2.
Detection
and Prevention of Errors and Frauds: Audit helps in detecting and preventing both errors and frauds and
also exhibits a true and fair view of state of affairs of the company to the
shareholders who are the owners of the company.
3.
Moral
Check on the Management: Audit of accounts enables to have a moral check on
the management in order to protect the interest of the shareholders.
4.
Safeguards
Interest of Shareholders: When accounts are audited by an independent and a
qualified auditor, the interest of the shareholders and third parties are
protected and safeguarded against any frauds committed by the directors,
promoters or managers.
5.
Valuable
Suggestions: Besides the above
advantages, auditor who is in touch with the company operations can provide
valuable suggestions.
Preliminaries Before Conduct of Audit
A company is an artificial judicial person and has
separate legal entity. The share holders of the company are interested to know
the financial position of the company. Hence, the audit of books of accounts
for the limited company is compulsory. The auditor has to produce a report on
the books examined by him and express a true and fair view of the profit and
loss account prepared by the client. Before commencing the audit work, the
auditor has to undertake certain preliminary steps. They are:
1. Examining the validity of his appointment
2. Inspection of Documents, Contracts and Registers
3. Other Information.
1. Examining the Validity of his Appointment
The auditor has to check that his appointment has
been made as per the provisions of Companies Act. He has to ensure that his
appointment has been validly made based on the different provisions for the
appointment of auditor under Companies Act. The following are the various
circumstances of appointment of auditor:
·
Where he is appointed as first auditor, get a copy
of the resolution by the directors about his appointment;
·
Where he is appointed in the place of retiring
auditor, he should enquire from the retiring auditor in writing, whether due
notice was given to him and also the circumstances under which he retired, and
also if the retiring auditor has any objection to his accepting the
appointment. Failure on the part the auditor shall be treated as a breach of
professional ethics.
·
Where his appointment is made by the shareholders
in annual general meeting, he should procure a copy of the shareholders
resolution regarding his appointment, and inform the Registrar within 30 days
whether he is accepting the appointment.
·
Where he is appointed in a casual vacancy, by the
directors, he should obtain a copy of the director’s resolution to this effect.
2. Inspection of Documents, Contracts and Registers
He should obtain a certified list of all the books
used in the company and examine the records, documents and registers with
reference to the following:
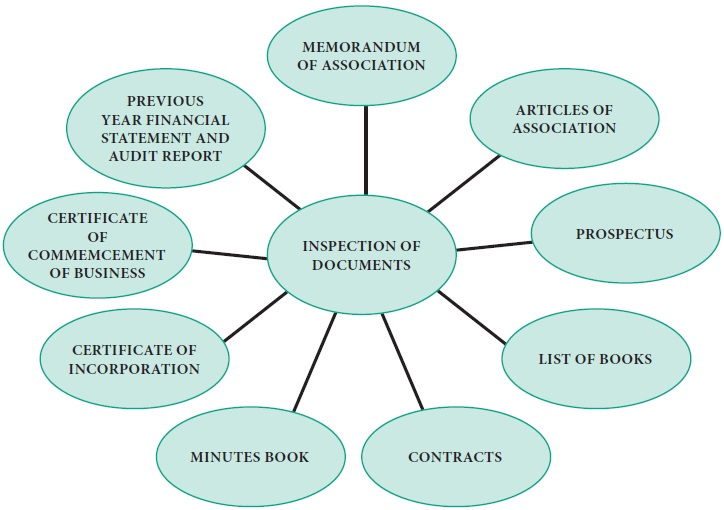
(A) Memorandum
of Association: The Memorandum
of Association is the basic document of the company.
It authorizes a company to engage in specific
activities. Therefore, it is necessary for the auditor to examine the scope and
powers of the company. The auditor should have a complete study of Memorandum
of Association in the following aspects:
·
Whether the transactions carried by the company is
subject to the clauses in the Memorandum of Association, if not the
transactions of the company become ultravires.
·
The auditor has to check the share capital issued
is within the authorized capital.
·
He should scrutinize the object clause and
borrowing powers of the company.
·
He has to check other provisions, which are likely
to affect the accounts of the company.
(b) Articles
of Association: The Articles
of Association deals with rules and regulations of the internal management
of the company. The auditor has to examine the following particulars in the
Articles of Association:
·
Issue, allotment and forfeiture of shares and
declaration of dividend.
·
Appointment and removal of directors and officers
of the company and the provisions relating thereto.
·
Provisions regarding meeting and voting rights of
share holders.
·
Borrowing powers of company.
·
Payment of interest on capital, under writing
commission and brokerage.
·
The auditor has to make thorough study of the
Articles of Association and he has to apply his skill and knowledge on various
transactions of the company.
(c) Prospectus:
A
Prospectus is an invitation to the
public to subscribe for shares and debentures of the company. It holds all the
rules and regulations for the issue of shares. Normally all the matters which
are in the articles of association are also found in the prospectus. The auditor
should make a detail study in the following matters:
·
He should verify the name, addresses, remuneration
of directors and other statutory officers whose particulars are specified in
the prospectus.
·
He should see that all the statements made in the
prospectus are true.
·
He should examine in the prospectus that the amount
payable at the time of allotment and call.
·
He has to examine that any material contract made
by the company within two years from the date of issue of prospectus.
(d) List
of Books: Auditor should ask the
company to submit a list of all the books of accounts, statistical and
statutory books maintained by the company. Important books are kept at the
Registered Office of the company.
(e) Contracts:
The
auditor has to check the date of agreement
or contracts made by the company with other parties, like, vendors,
underwriters, promoters or brokers etc. Further, the auditor should verify
whether the agreements are made by the authorized person of the company. He
should see that entries relating to contracts are recorded correctly.
(f) Minutes
Book: Every company has to maintain
a book in order to record the proceedings in the general meetings, meetings of
board of directors and committee of the board. They are in the form of a bound
note book. The auditor has to verify that the chairman has certified the
minutes book with date and signature. The audit of the Minutes Book helps the
auditor in vouching various transactions e.g., adoption of the annual accounts,
calls on shares, directors fees and expenses, appointment of first auditor and
his remuneration and authorization of capital expenditure etc.
(g) Certificate
of Incorporation: Certificate of Incorporation is an important
document which brings the company into legal existence.
The auditor has to check that all legal official
procedures have been fulfilled subject to the provisions of the Companies Act.
(h) Certificate
of Commencement of Business: A public company has to get Certificate of Commencement of
business before it commences its business. The auditor should examine the
Certificate of Commencement of business in case of a public company.
(i) Previous
Year Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Account and Audit Report: The
auditor has to verify the last year Balance Sheet and ensure that the balances
are correctly recorded in the current books. He has to check the minutes book
of the share holders about the adoption of the accounts. Moreover, he has to
get the copies of last year’s Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet which
is required for conduct of his audit work. He should ensure that the objections
or qualifications raised in the previous audit report have been duly met by the
company. He should examine the Directors report to the members containing the
recommendations of the Directors in respect of the appropriations of profits
made last year.
3. Other Information
(a) System
of Accounting: The auditor has
to study the accounting system followed in the company and has to observe the
inefficiencies.
(b) List of
Officers: The auditor has to obtain
the list of officers in the company with their specimen signature.
(c) Evaluation
of Internal Check and Control System: The auditor has to obtain detailed information about the
internal check and internal control system in the company. This will enable him
to identify the defects in the accounting system. Further, he has to verify the
recommendations, if any, made in the last year audit report.
Related Topics