Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Vitamins
Pantothenic Acid
Pantothenic Acid
Pantothenic acid is appropriately named
because the Greek wordpantothenmeans
“from many places.” It is fairly stable, but it can be damaged by acids and
alkalies.
Functions.Pantothenic acid is involved in metabolism of
carbohydrates,fats, and proteins. It is also essential for the synthesis of the
neurotransmitter acetylcholine and of steroid hormones.
Sources.Pantothenic acid is found extensively in
foods, especially animalfoods such as meats, poultry, fish, and eggs. It is
also found in whole-grain cere-als and legumes. In addition, it is thought to
be synthesized by the body.
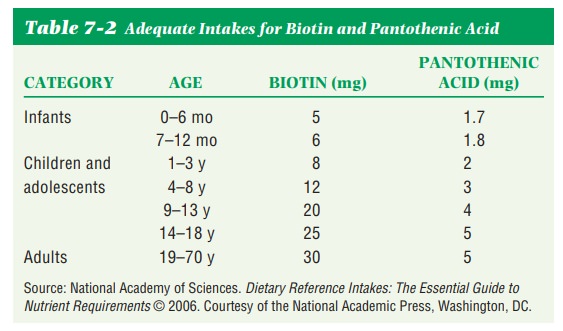
Requirements.There is no DRI for pantothenic acid, but the
Food andNutrition Board has provided an estimated intake of 4 to 7 mg a day for
normal adults (see Table 7-2).
Deficiency.Natural deficiencies are unknown. However,
deficiencies havebeen produced experimentally. Signs include weakness, fatigue,
and a burning sensation in the feet. Toxicity from excessive intake has not
been confirmed.
Related Topics