Chapter: Paediatrics: Child development
Paediatrics: Fine motor development
Fine motor development
Fine motor development and vision
Fine motor skills are dependent on
good vision. Therefore fine motor skills are usually assessed alongside visual
development.
Early visual alertness
·A
newborn infant will
fix and follow a near face or light moving across the field of view.
·By
6wks infant is more
alert and will turn the head through 90° to
follow an object.
·By
3–4mths a baby will spend
a lot of time watching their hands (i.e.
hand regard).
Note:
Some infants may demonstrate an
intermittent squint. Fixed squints
and all those persisting beyond the 8-week check must be referred to an
ophthalmologist.
Early fine motor skills
As the primitive grasp reflex
starts to decrease infants will start to reach for objects.
·At
6mths:
· grip is usually with the whole
palm (palmar grasp);
· holds objects with both hands and
will bang them together;
· transfers objects between hands.
·By
10mths infant is
developing a pincer grip using thumb and first finger.
·By
12mths infant will use
index finger to point to objects.
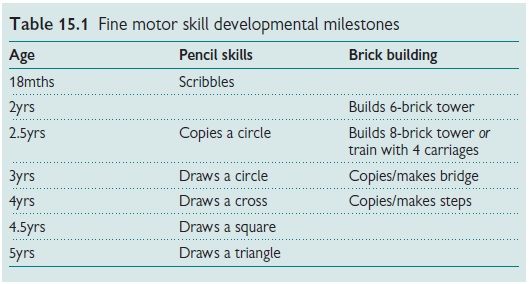
Preschool fine motor development
Fine motor skills can be assessed
with pencil control and with building bricks (Table 15.1).
Related Topics