Chapter: Paediatrics: Special senses
Paediatrics: Childhood deafness
Childhood deafness
Hearing loss or deafness may be
congenital or acquired and can be divid-ed into sensorineural (SN) or
conductive loss. Hearing loss of up to 20dB tends not to affect development,
but a loss of over 40dB will affect speech and language development.
Sensorineural
Inherited/genetic
•
Non
syndromic.
•
Syndromic:
•
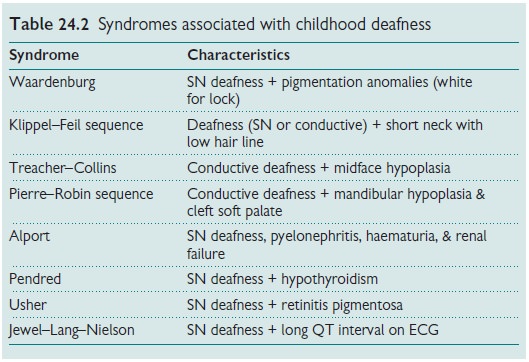
Ushers
syndrome (see Table 24.2);
•
Waardenburg
syndrome (see Table 24.2).
Acquired
•
Perinatal:
•
birth
asphyxia;
•
hyperbilirubinemia;
•
congenital
infection, e.g. rubella, CMV, syphilis.
•
Postnatal:
•
drugs,
e.g. aminoglycosides;
•
meningitis;
•
head
injury;
•
labyrinthitis;
•
acoustic
neuroma.
Conductive
External ear abnormalities
Ear canal atresia/stenosis.
Middle ear abnormalities
•
Acute
otitis media.
•
Chronic
otitis media (tympanic perforation, cholesteatoma).
Secretory otitis media.
Related Topics