Chapter: 9th Science : Chemical bonding
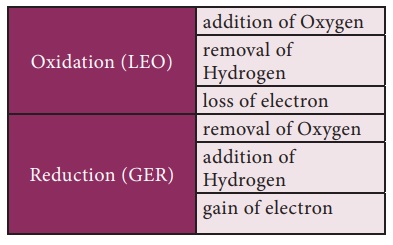
Oxidation, Reduction and Redox reactions
Oxidation, Reduction and Redox reactions
Look at the following
pictures. When an apple is cut and left for sometimes, its surface turns brown.
Similarly, iron bolts and nuts in metallic structures get rusted. Do you know
why are these happening? It is because of a reaction called oxidation.

Oxidation: A chemical reaction
which involves addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen or loss of
electrons is called oxidation.
2 Mg + O2 → 2
MgO (addition of oxygen)
CaH2 → Ca + H2
(removal of hydrogen)
Fe2+ →Fe3+
+ e− (loss of electron)
Reduction: A chemical reaction
which involves addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen or gain of
electrons is called reduction.
2 Na + H2 → 2
NaH (addition of hydrogen)
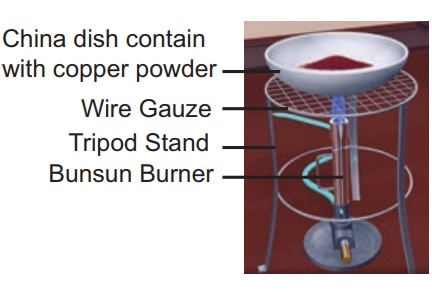
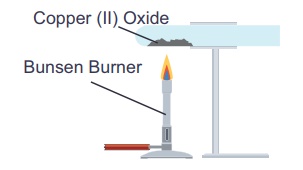
CuO + H2 → Cu
+ H2O (removal of oxygen)
Fe3+ + e−
→ Fe2+ (gain of electron)
Redox reactions: Generally, the oxidation
and reduction occurs in the same reaction (simultaneously). If one reactant
gets oxidised, the other gets reduced. Such reactions are called
oxidation-reduction reactions or Redox reactions.
Ex. 1 : 2 PbO + C → 2 Pb
+ CO2
Ex. 2 : Zn + CuSO4
→ Cu + ZnSO4
Oxidising agents and Reducing agents
Substances which have
the ability to oxidise other substances are called Oxidising agents. ese are
also called as electron acceptors because they remove electrons from other
substances.
Example: H2O2,
MnO4-, CrO3, Cr2O72-
Substances which have
the ability to reduce other substances are called Reducing agents. ese are also
called as electron donors because they donate electrons to other substances.
Example: NaBH4,
LiAlH4 and metals like Palladium, Platinum.
Oxidation reactions in daily life:
In nature the oxygen
present in atmospheric air oxidises many things, starting from metals to living
tissues.
·
The shining surface of metals tarnishes due to the formation of
respective metal oxides on their surfaces. This is called corrosion.
·
The freshly cut surfaces of vegetables and fruits turns brown a er
some time because of the oxidation of organic compounds present in them.
·
The oxidation reaction in food materials that were le open for a
long period is responsible for spoiling of food. is is called Rancidity.
Oxidation number
Oxidation number of an
element is de ned as the formal charge which an atom of that element appears to
have when electrons are counted.
Oxidation number also
called Oxidation state, the total number of electrons that an atom either gains
or losses in order to form a chemical bond with another atom.The sum of
oxidation numbers of all the atoms in the formula for a neutral compound is
ZERO. The sum of oxidation numbers of an ion is the same as the charge on that
ion. Negative oxidation number in compounds of two unlike atoms is assigned to
the more electronegative atom.
For example,
·
Oxidation number of K and Br in KBr molecule is +1 and -1 respectively.
·
Oxidation number of N in NH3 molecule is -3
·
Oxidation number of H is +1 (except hydrides)
·
Oxidation number of oxygen in most cases is -2
(Oxidation Number = ON)
Problems on determination of Oxidation Number
ON of neutral molecule
is always zero
Illustration 1 – Oxidation Number of H and O in H2O
Let us take ON of H = +1
and ON of O = -2
2 X (+1) + 1 X (-2) = 0
(+2) + (-2) = 0 thus, ON
of H is +1 and ON of O is -2
Illustration 2 – Oxidation Number of Na and Cl in NaCl
ON of Na = +1 and ON of
Cl = -1
(+1) + (-1) = 0 thus, ON
of Na is +1 and ON of Cl is -1
Illustration 3 – Oxidation Number of S in H2SO4
Let ON of S be (x) and
we know ON of H = +1 and O = -2
2 X (+1) + (x) + 4 X
(-2) = 0
(+2) + (x) + (-8) = 0
(x) = +6 therefore, ON
of S is +6
Illustration 4 – Oxidation Number of Cr in K2Cr2O7
Let ON of Cr be x and we
know ON of K = +1 and O = -2
2 X (+1) + 2 X (x) + 7 X
(-2) = 0
(+2) + (2x) + (-14) = 0
2x = +12
x = +6 therefore, ON of
Cr in K2Cr2O7 is +6
Illustration 5 – Oxidation Number of Fe in FeSO4
Let ON of Fe be x and we
know ON of S = +6 and O = -2
42. + 1 X (+6) + 4 X (-2) =
0
43. + (+6) + (-8) = 0
x = +2 therefore, ON of
Fe in FeSO4 is +2
Problems:
1. Find the oxidation number of Mn in KMnO4
2. Find the oxidation number of Cr in Na2Cr2O7
3. Find the oxidation number of Cu in CuSO4
4. Find the oxidation
number of Fe in FeO
Related Topics