Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: The Relationship of Nutrition and Health
Nutrients and Their Functions
NUTRIENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
To maintain health and
function properly, the body must be provided with nutrients.
Nutrients are chemical substances that are necessary for
life.They are divided into six classes:
· Carbohydrates (CHO)
· Fats (lipids)
· Proteins
· Vitamins
· Minerals
· Water
The body can make
small amounts of some nutrients, but most must be obtained from food in order
to meet the body’s needs. Those available only in food are called essential nutrients. There are about 40 of
them, and they are found in all six nutrient classes.
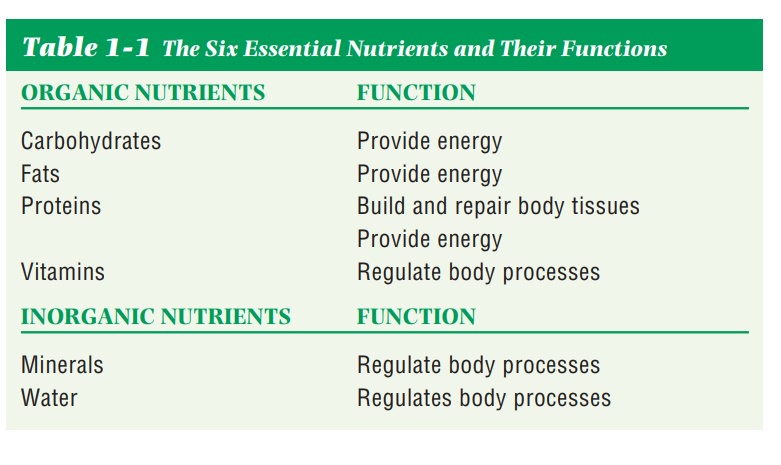
The six nutrient
classes are chemically divided into two categories: or-ganic and inorganic
(Table 1-1). Organic nutrients contain hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. (Carbon is
an element found in all living things.) Before the body can use organic
nutrients, it must break them down into their smallest compo-nents. Inorganic
nutrients are already in their simplest forms when the body ingests them,
except for water.
Each nutrient
participates in at least one of the following functions:
• Providing the body with energy
• Building and repairing body tissue
• Regulating body processes
Carbohydrates (CHO), proteins, and fats (lipids) furnish
energy.Proteins are also used to build and repair body tissues with the help of
vitamins and minerals. Vitamins, minerals, and water help regulate the
various body processes such as circulation,
respiration, digestion, and elimination.
Each nutrient is
important, but none works alone. For example, carbohy-drates, proteins, and
fats are necessary for energy, but to provide it, they need the help of
vitamins, minerals, and water. Proteins are essential for building and
repairing body tissue, but without vitamins, minerals, and water, they are
ineffective. Foods that contain substantial amounts of nutrients are described
as nutritious or nourishing.
Related Topics