Chapter: Embedded and Real Time Systems : Hardware Accelerates & Networks
Network-Based Design
NETWORK-BASED
DESIGN:
Designing
a distributed embedded system around a network involves some of the same design
tasks we faced in accelerated systems. We must schedule computations in time
and allocate them to PEs. Scheduling and allocation of communication are
important additional design tasks required for many distributed networks.
Many
embedded networks are designed for low cost and therefore do not provide
excessively high communication speed. If we are not careful, the network can
become the bottleneck in system design. In this section we concentrate on
design tasks unique to network-based distributed embedded systems.
We know
how to analyze the execution time of programs and systems of processes on
single CPUs, but to analyze the performance of networks we must know how to determine
the delay incurred by transmitting messages. Let us assume for the moment that
messages are sent reliably we do not have to retransmit a message.
The message
delay for a single message with no contention (as would be the case in
a point-to-point connection) can be modeled as

where tx is the transmitter-side
overhead, tn is the
network transmission time, and tr
is the receiver-side overhead. In I2C, tx and tr
are negligible relative to tn
If
messages can interfere with each other in the network, analyzing communication
delay becomes difficult. In general, because we must wait for the network to
become available and then transmit the message, we can write the message delay as

where td is the network availability delay
incurred waiting for the network to become available. The main problem,
therefore, is calculating td.
That value depends on the type of arbitration used in the network.
If the
network uses fixed-priority arbitration, the network availability delay is
unbounded for all but the highest-priority device. Since the highest-priority
device always gets the network first, unless there is an application-specific
limit on how long it will transmit before relinquishing the network, it can
keep blocking the other devices indefinitely.
If the
network uses fair arbitration, the network availability delay is bounded. In
the case of round-robin arbitration, if there are N devices, then the worst case network availability delay is N(tx+tarb),where tarb is the
delay incurred for arbitration. tarb is usually small compared to
transmission time.
Of
course,a round-robin arbitrated network puts all communications at the same
priority. This does not eliminate the priority inversion problem because
processes still have priorities. Thus far we have assumed a single-hop
network: A message is
received at its intended destination directly from the source,without going
through any other network node.
It is
possible to build multihop networks in which messages are routed through network
nodes to get to their destinations. (Using a multistage network does not
necessarily mean using a multihop network—the stages in a multistage network
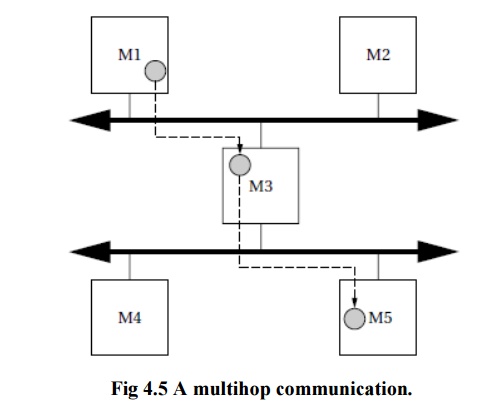
are generally much smaller than the network PEs.) Figure 4.5 shows an example
of a multihop communication.
The
hardware platform has two separate networks ( perhaps so that communications
between subsets of the PEs do not interfere),but there is no direct path from M1 to M5.The message is therefore routed through M3, which reads it from one network and sends it on to the other
one.
Analyzing
delays through multihop systems is very difficult. For example,the time that
the message is held at M3 depends on
both the computational load of M3 and
the other messages that it must handle.
If there
is more than one network,we must allocate communications to the networks. We
may establish multiple networks so that lower-priority communications can be
handled separately without interfering with high-priority communications on the
primary network.
Scheduling
and allocation of computations and communications are clearly interrelated. If
we change the allocation of computations, we change not only the scheduling of
processes on those PEs but also potentially the schedules of PEs with which they
communicate.
For
example, if we move a computation to a slower PE, its results will be available
later, which may mean rescheduling both the process that uses the value and the
communication that sends the value to its destination.
Related Topics