Health Care Delivery System in India - Nature of Disease | 11th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Nursing - Health Care Delivery System in India
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Nursing - Health Care Delivery System in India
Nature of Disease
Nature of Disease
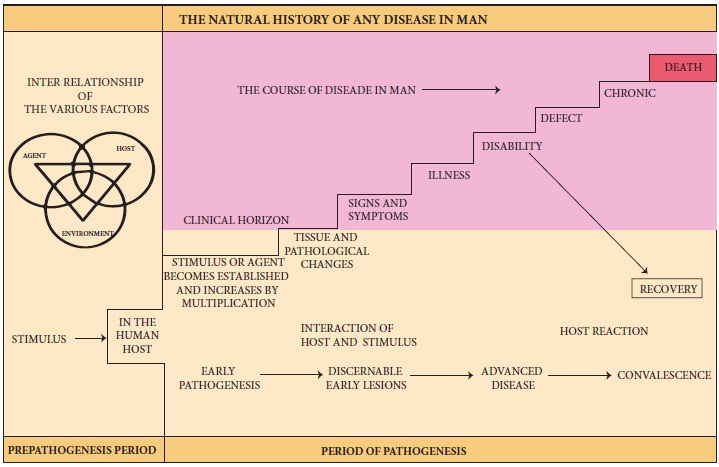
Natural history of disease refers to
the progress of a disease process in an individual over time in the absence
of intervention. The process begins with exposure to or accumulation of factors
capable of causing disease. Without medical intervention, the process ends with
recovery, disability, or death.

Knowledge of the natural history
of disease ranks along side causal understanding in importance for disease
prevention and control.
The Natural History of Disease in a Patient
·
A – Biologic onset of
disease
·
P – Pathologic evidence of disease if Sought
·
S – Signs and symptoms of disease
·
M – Medical care sought
·
D – Diagnosis and
·
T – Treatment
Levels of Disease Prevention
A. Primary Prevention
·
Measures of prevention undertaken before an individual
experiences health problem.
·
Health education programme immunization, physical and
nutritional fitness activities.
B. Secondary Prevention
Measures of prevention
focuses on individual experiencing health problem without symptoms and who are
at risk for developing complications.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES: Early diagnosis and
treatment. Eg. Medical examination of school children.
C. Tertiary Prevention
Measures undertaken when the
disease has become advanced in order to prevent disabilities and to help
individual to achieve has high level of functioning. Eg. Application of plaster
for fracture to prevent further complication.
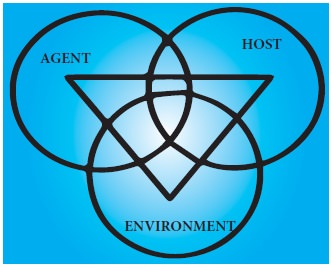
Disease Occurrence
Disease is not simply cost by a
single factor but it results from interaction of three factors. The host, The
Agent and the environment.
The interaction of three factors
the Host, Agent, and the environment. The interaction of these three factors
are called the epidemiological triad of
disease.
Presence of only one of this
factors is not enough to cause the disease. These factors must interact in a
particular way to lead to the disease.
An Agent: Is an environment factors are stressor that must be present
or absent for an illness to occur. Eg. Bacteria, Virus, Dust, Toxins,
Insecticides. Heat, Cold, Sound excess or deficient of Vitamins and Minerals.
A Host:
Is a living organism capable of being infected or affected by
an agent. Eg. Age, Sex, Health habits.
Environment: Is the conditions that. Facilitate the contact
between the host and the agent. Eg. Temperature, air, Viruses, Insects,
Animals, Plants, Cultural values habits, life styles
Eg. Burns
Host: Susceptible
person
Agent: Physical/Chemical agent
Environment: Conditions for Exposure/ Injury
Kerosene are present in all houses
and the children are at risk, but all children will not get burned. This
depends are interaction between the home environment and the children.
Related Topics