Definition, Over View and Characteristics of Nursing Process - Definition of Nursing Process | 11th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Nursing - Health Care Delivery System in India
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 2 : Nursing - Health Care Delivery System in India
Definition of Nursing Process
Definition of Nursing Process
The nursing process is a critical
thinking process that professional nurses uses to apply the best available
evidence to care giving and promoting human functions and responses to health
and illness
-American Nurses Association, 2010
It is the fundamental blue print
for how to care for patients. The nursing process is also a standard of practice,
which when followed correctly, protects nurses against legal problems related
to nursing care.
Over View of Nursing Process
The nursing process is
goal-oriented method of caring that provides a framework to nursing care. It
involves five major steps:
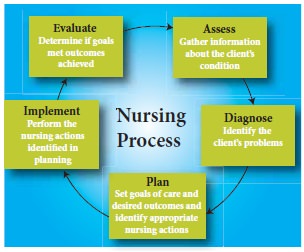
A -
Assess (what data is collected?)
D -
Diagnose (what is the problem?)
P -
Plan (how to manage the problem)
I -
Implement (putting plan into action) with
Rationale (Scientific reason of the implementations)
E -
Evaluate (did the plan work?)
According to some theorists, this
seven-steps description of the nursing process is outdated and misrepresents
nursing as linear and atomic.
Assessing phase-Nursing assessment
The nurse completes an holistic
nursing assessment of the needs of the individual/ family/community, regardless
of the reason for the encounter. The nurse collects subjective data and
objective data using a nursing framework, such as Marjory Gordon’s functional
health patterns.
Methods for data collection
Nursing assessments provide the
starting point for determining nursing diagnosis. It is vital that a recognized
nursing assessment framework is used in practice to identify the patient’s
problems, risks and outcomes for enhancing health. The use of an evidence-based
nursing framework such as Gordon’s Functional Health Pattern Assessment should
guide assessments that support nurses in determination of NANDA-I nursing
diagnosis. For accurate determination of nursing diagnosis, useful,
evidence-based assessment framework is best practice.
Methods
·
Client
Interview
·
Physical
Examination
·
Obtaining
a health history (including dietary data)
·
Family
history/report
Diagnosing phase-Nursing diagnosis
Nursing diagnosis represent the
nurse’s clinical judgment about actual or potential health problems/life
process occurring with the individual, family, group or community. The accuracy
of the nursing diagnosis is validated when a nurse is able to clearly identify
and link to the defining characteristics, related factors and/or risk factors
found within the patients assessment. Multiple nursing diagnosis may be made
for one client.
Planning phase-Nursing care plan
In agreement with the client, the
nurse addresses each of the problems identified in the diagnosing phase. When
there are multiple nursing diagnosis to be addressed, the nurse prioritizes
which diagnosis will receive the most attention first according to their
severity and potential for causing more serious harm. For each problem a
measurable goal/outcome is set. For each goal/outcome, the nurse selects
nursing interventions that will help achieve the goal/outcome. A common method
of formulating the expected outcomes is to use the evidence-based Nursing
Outcomes Classification to allow for the use of standardized language which
improves consistency of terminology, definition and outcome measures. The
interventions used in the Nursing Interventions Classification again allow for
the use of standardized language which improves consistency of terminology,
definition and ability to identify nursing activities, which can also be linked
to nursing workload and staffing indices. The result of this phase is a nursing
care plan.
Implementing Phase
The nurse implements the nursing
care plan performing the determined interventions that were selected to help
meet the goals/ outcomes that were established. Delegated tasks and the
monitoring of them is included here as well.
Activities
·
pre-assessment
of the client-done before just carrying out implementation to determine if it
is relevant
·
determine
need for assistance
·
implementation
of nursing orders
·
delegating
and supervising-determines who to carry out what action
Evaluating Phase
The nurse evaluates the progress
toward the goals/outcomes identified in the previous phases. If progress
towards the goal is slow, or if regression has occurred, the nurse must change
the plan of care accordingly. Conversely, if the goal has been achieved then
the care can cease. New problems may be identified at this stage, and thus the
process will start all over again.
Characteristics of Nursing Process
The nursing process is a cyclical
and ongoing process that can end at any stage if the problem is solved. The
nursing process exists for every problem that the individual/family/community
has. The nursing process not only focuses on ways to improve physical needs,
but also on social and emotional needs as well.
·
Cyclic
and dynamic
·
Goal
directed and client centred
·
Interpersonal
and collaborative
·
Universally
applicable
·
Systematic
The entire process is recorded or
documented in order to inform all members of the health care team.
Related Topics