Classification/Types, Functions | Animal Tissue - Muscular Tissue | 9th Science : Organization of Tissues
Chapter: 9th Science : Organization of Tissues
Muscular Tissue
Muscular Tissue
Muscular tissues are
made of muscle cells and form the major part of contractile tissue. The muscle
cells are elongated, large sized and are composed of numerous myofibrils.
Each muscle is made up of many long cylindrical fibres arranged parallel to one
another. The movement of the body and limbs are brought about by the
contraction and relaxation of contractile proteins present in muscle
cells. According to their structure, location and functions, there are three
main types of muscles
a. Skeletal muscle (or)
striated muscle
b. Smooth muscle (or) non-striated muscle
c. Cardiac muscle
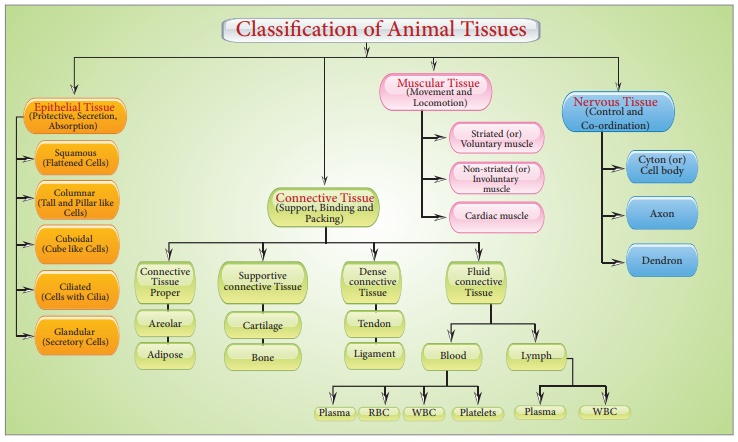
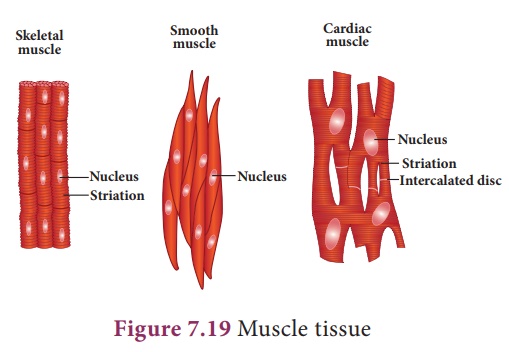
a. Skeletal muscle:
These muscles are attached
to the bones and are responsible for the body movements and are called skeletal
muscles. They work under our control and are also known as voluntary muscles.
The muscle fibres are elongated, non-tapering, cylindrical, unbranched
and showing alternating dark and light bands, giving them the striped or
striated appearance. These cells possess many nuclei (multinucleate).
They occur in the muscles of limbs (biceps and triceps of arms).They undergo
rapid contraction.
b. Smooth muscle:
These muscles are
spindle shaped with broad middle part and tapering ends. There is a
single centrally located nucleus (uninucleate). These fibrils do not
bear any stripes or striations and hence are called non-striated. They
are not under the control of our will and so are called involuntary muscles.
The walls of the internal organs such as the blood vessels, gastric
glands, intestinal villi and urinary bladder contain this type of smooth
muscle. Movement of food in the alimentary canal or the contraction and
relaxation of blood vessels are involuntary movements.
c. Cardiac muscle:
It is a contractile
tissue present in the heart. The muscle fibres are cylindrical,
branched and uninucleate. The branches join to form a network
called as intercalated disc which are unique distinguishing features of
the cardiac muscles. The intercellular spaces of the cardiac muscle are filled
with loose connective tissue supplied with blood capillaries. The contraction
of cardiac muscle is involuntary and rhythmic.
Related Topics