Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : Sustaining Employee Interest
Motivation theories
Motivation theories
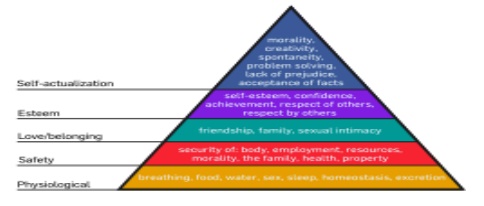
An
interpretation of Maslow's hierarchy of needs, represented as a pyramid with
the more basic needs at the bottom
Motivational
theories are split into two groups as process and content theories. Content
theories endeavor to name and analyze the factors which motivate people to
perform better and more efficiently while process theories concentrate on how
different types of personal traits interfere and impact the human
behavior.Content theories are highly related with extrinsic rewards, things
that are concrete like bonuses and will help improve employees' physiological
circumstances whereas process theories are concerned with intrinsic rewards,
such as recognition and respect, which will help boost employees confidence in
the work place and improve job satisfaction.
A famous
content theory would be Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, and a famous process
theory would be the equity theory.
Theories
of motivation provide a theoretical basis for reward management though some of
the best known ones have emerged from the psychology discipline. Perhaps the
first and best known of these comes from the work of Abraham Maslow. Maslow‘s
Hierarchy of Needs describes a pyramid comprising a series of layers from at
the base the most fundamental physiological needs such as food, water, shelter
and sex, rising to the apex where self-actualisation needs included morality
and creativity. Maslow saw these levels of needs being fulfilled one at a time
in sequence from bottom to top. Employment and the resources it brings are
classed under ‗safety needs‘ (level 2) while the workplace may also contribute
to a sense of ‗belonging‘ (level 3) and recognition at work can satisfy the
need for ‗self-esteem‘ (level 4).
Frederick
Herzberg‘s motivator-hygiene theory, first published in 1959, argues that an
employee‘s job satisfaction or dissatisfaction is influenced by two distinct
sets of factors and also that satisfaction and dissatisfaction were not at
opposite ends of the same continuum but instead needed to be measured
separately. The two sets of factors are motivator factors and hygiene factors.
According to Herzberg, real motivation comes from the work itself, from
completing tasks, while the role of reward is to prevent dissatisfaction
arising. Expectancy Theory is the theory which posits that we select our
behaviour based on the desirability of expected outcomes of the action. It was
most prominently used in a work context by Victor Vroom who sought to establish
the relationship between performance, motivation and ability and expressed it
as a multiplicative one – where performance equals motivation x ability. There
are a lot of attractions for this kind of approach, particularly for employers
who can target their motivation effort and anticipate a definable mathematical
return for them. As this is a cognitive process theory it relies on the way
employees perceive rewards These three theories plus variants of them have been
used in countless research studies and continue to inform the practice of
reward management up to the present day.
Job evaluation
Job
evaluation is closely related to reward management. It is important to
understand and identify a job's order of importance. Job evaluation is the process
which job's are systematically assessed to one another within an organization
in order to define the worth and value of the job, to ensure the principle of
equal pay for equal work. In the United Kingdom, it is now illegal to
discriminate worker's pay levels and benefits, employment terms and conditions
and promotion opportunities Job Evaluation is one method that can be adopted by
companies in order to make sure that discrimination is eliminated and that the
work performed is rewarded with fair pay scales. This system carries crucial
importance for managers to decide which rewards should be handed out by what
amount and to whom. Job evaluation provides the basis for grading, pay
structure, grading jobs in the structure and managing job and pay relativities.
It has
been said that fairness and objectivity are the core principals using an
assessment of the nature and size of the job each is employed to carry out.
There
also many different methods of job evaluation which can be used, but the three
simplest methods are ranking, classification and factor comparison. However,
there are more complex variations of methods such as the point method which
uses scales to measure job factors. This method does not not rank employees
against one another but looks at the job as a whole. A disadvantage of these
methods of job evaluation are that they are very static and it would be very
difficult to perform a job evaluation quickly if it was needed.
An
advisory company named ACAS stated that there were five main reasons why
employers look at performing a job evaluation. These include: When deciding on
a pay scale: Making sure that the current system is fair and equal for
employees, Deciding on benefits such as bonuses,Comparing pay against other
companies and reviewing all jobs after a major company pay change . Employees
need to feel that they are being paid a fair wage compared to the same job with
the competition. If this is true it may help reduce staff turnover which is very
beneficial for employers as it reduces the cost of hiring new staff.
Research
regarding job evaluation has mainly been conducted using qualitative data
collection methods such as interviews, large scale surveys and basic
experimental methods. Therefore, there is a large gap for research on job
evaluation collecting quantitative data for a more statistical analysis. A
comparison between public and private sectors and the methods of job evaluation
is another area that should be considered for further research.
Related Topics