Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : Sustaining Employee Interest
Compensation Plan
Compensation
Plan:
1 Compensation(Meaning and Definition of Compensation)
2 Objectives
of Compensation Planning
3 Factors
Affecting Compensation Planning
4 Various
Modes of Compensation
Compensation Plan
1 Compensation is a tool
used by management for a variety of purpose to further the existence of the company. It is a remuneration
that an employee receives in return for his or her contribution in
theorganisation. So, the employee compensation programs are designed to attract
capable employees to the organisation, to motivate them towards superior
performance and to retain their services over an extended period of time.
Meaning and Definition of
Compensation
In
layman‘s language the word ‗compensation‘ means something, such as money, given
or received as payment for service. The word compensation may be defined as
money received in the performance of work, plus the many kinds of benefits and
services that organization provides their employee. It refers to wide range of
financial and non-financial rewards to employee for their service rendered to
the organization. It is paid in the form of wages, salaries , special allowance
and employee benefits such as paid vacation, insurance, maternity leaves, free
travel facility , retirement benefits etc.
According to Wendell French,‖ Compensation is a comprehensive term
which includes wages, salaries and
all other allowance and benefits.‖
Wages are
the remuneration paid for skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled operative
workforce. Salaryis the remuneration of those employees who provides mental
labour to the employer such as supervisor, office staff, executive etc wages
are paid on daily or hourly basis where as salary is paid on monthly basis.
2 Objectives of Compensation
Planning
The basic
purpose or objective of establishing sound compensation is to establish and
maintain an equitable rewards system. The other aim is the establishment and
maintenance of an equitable compensation structure i.e an optimal balancing of
conflicting personnel interest so that the satisfaction of employees
andemployers is maximised and conflicts minimized, the compensation management
is concerned with the financial aspect of employees need, motivation and
rewards.
A sound
compensation structure tries to achieve these objectives:
To
attract manpower in a competitive market.
To control wages and salaries and labour costs by
determining rate change and frequency of increment.
To
maintain satisfaction of employees by exhibiting that remuneration is fair
adequate and equitable. To induce and improved performance, money is an
effective motivator.
a)To
Employees:
i. Employees
are paid according to requirement of their jobs i.e highly skilled jobs are
paid more compensation than low skilled jobs. This eliminates inequalities.
ii. The
chances of favouritism are minimised.
iii.
Jobs sequence and lines of promotion are
established wherever they are applicable.
iv.
Employee‘s moral and motivation are increased
because of the sound compensation structure.
b)To
Employers:
i. They can
systematically plan for and control the turnover in the organization.
ii. A sound
compensation structure reduces the likelihood of friction and grievance over
remunerations.
iii.
It enhance an employee morale and motivation
because adequate and fairly administrative incentives are basis to his wants
and need.
iv.
It attracts qualified employees by ensuring and
adequate payment for all the jobs.
v. In
dealing with a trade union, they can explain the basis of their wages programme
because it is based upon a systematic analysis of jobs and wages facts.
3 Factors Affecting Compensation
Planning
Factors
determining compensation of an employee considerable amount of guess word and
negotiation are involved. But following are the certain factors which have been
extracted as having an important bearing upon the final decision:
Supply and Demand of Labour:
Whatever the organization produces as commodity they desire services and it must pay a price that of workers acting in
concert. If more the labour is required, such as at war time prosperity, there
will be tendency to increase the compensation; whereas the situation when
anything works to decrease the supply of labour, such as restriction by a
particular labour union, there will be a tendency to increase the compensation.
The reverse of each situation is likely to result in a decrease in employee
compensation, provided, labour union, ability to pay, productivity, government
do not intervene.
b)
Ability
to Pay: Labour Unions has often demanded an increase in compensation on the
basis that the firm is prosperous
and able to pay.
c)
Management’s
Philosophy: Management‘s desire to maintain or improve moral,
attract high calibre employees,
reduce turnover, and improve employees standard of living also affect wages, as
does the relative importance of a given position to a firm.
d)
Legislation:
Legislation
related to plays a vital role in determining internal organization practices. Various acts are prescribed by
government of country for wage hours laws. Wage-hour laws set limits on minimum
wages to be paid and maximum hours to be worked. In India minimum wages act
1948 reflecting the wage policy for an organization and fixation of minimum
rates of wages to workers in sweated industries. In 1976 equal remuneration act
was enacted which prohibits discrimination in matters relating to remuneration
on the basis of religion, region or gender.
4 Various Modes of Compensation
Various
modes of compensation are as follows-
a)
Wages and
Salary- Wages represent hourly rates of pay and salary refers to monthly rate of
pay irrespective of the number of hours
worked. They are subject to annual increments. They differ from employee to
employee and depend upon the nature of jobs, seniority and merit.
b)
Incentives-
These are
also known as payment by results. These are paid in addition to wages and salaries. Incentive depends upon
productivity, sales, profit or cost reduction efforts. Incentive scheme are of
two types:
Individual incentive schemes.
Group incentive schemes.
c)
Fringe
Benefits- These are given to employees in the form of benefits such as provident
fund, gratuity, medical care,
hospitalization, accident relief, health insurance, canteen, uniform etc.
d)
Non-
Monetary Benefits- They include challenging job responsibilities,
recognition of merit, growth
prospects, competent supervision, comfortable working condition, job sharing
and flexi time.
Incentives
Incentives
are monetary benefits paid to workmen in lieu of their outstanding performance.
Incentives vary from individual to individual and from period to period for the
same individual. They are universaland are paid in every sector. It works as
motivational force to work for their performance as incentive forms the part
total remuneration. Incentives when added to salary increase the earning thus
increase the standard of living. The advantage of incentive payment are reduced
supervision, better utilisation of equipment, reduced scrap, reduced lost time,
reduced absenteeism and turnover & increased output.
According to Burack & Smith, ―An incentive scheme is a plan or
programme to motivate individual or group
on performance. An incentive programme is most frequently built on monitory
rewards ( incentive pay or monetary bonus ), but may also include a variety of
non monetary rewards or prizes.‖
Kinds of Incentives
Incentives
can be classified under the following categories:
1.
Individual and Organizational Incentives
2.
Financial and Non-Financial Incentives
3.
Positive and Negative Incentives
1) Individual and Organizational
Incentives- According to L.G. Magginson, ―Individual
incentives are the extra
compensation paid to an individual for all production over a specified
magnitude which stems from his exercise of more than normal skill, effort or
concentration when accomplished in a predetermined way involving standard
tools, facilities and materials.‖ Individual performance is measured to
calculate incentive where as organizational or group incentive involve
cooperation among employees, management and union and purport to accomplish
broader objectives such as an organization-wide reduction in labour, material
and supply costs, strengthening of employee loyalty to company, harmonious
management and decreased turnover and absenteeism
I) Individual Incentive System is of two types:
a)Time
based System- It includes Halsey Plan, Rowan Plan, Emerson Plan and Bedeaux
Plan
b)Production
based System- it includes Taylor‘s Differential Piece Rate System, Gantt‘s Task
and Bonus Plan
II)Group
Incentive System is of following types
a)Scalon
Plan
b)
Priestman‘s Plan
c) Co-Partnership
Plan
d)
Profit Sharing
Some
important these plans of incentive wage payments are as follows:
Halsey Plan- Under
this plan a standard time is fixed in advance for completing a work. Bonus is rewarded to the worker who perform
his work in less than the standard time and paid wages according to the time
wage system for the saved time.
The total earnings of the worker
= wages for the actual time + bonus
Bonus =
33.5% of the time saved (standard time set on past experience)
Or
50% of
the time saved (standard are scientifically set)
Example: Time
required to complete job (S) = 20 hours
Actual
Time taken (T) = 15 hours Hourly Rate of Pay (R) = Rs 1.5
Calculate the wage of the worker.
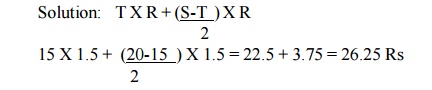
In this
equation 3.75 Rs are the incentives for saving 5 hours.
Rowan Plan – Under this method minimum wages
are guaranteed given to worker at the ordinary rate for the time taken to complete the work. Bonus is that
proportion of the wages of the time taken which the time saved bears to the
standard time allowed.
Incentive = Wages for actual time
for completing the work + Bonus where,
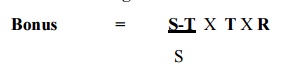
Emerson Plan – Under
this system, wages on the time basis are guaranteed even to those workers whose output is below the standard.
The workers who prove efficient are paid a bonus. For the purpose of
determining efficiency, either the standard output per unit of time is fixed,
or the standard time for a job is determined, and efficiency is determined on
the basis of a comparision of actual performance against the standard.
Bedeaux Plan – It
provide comparable standards for all workers. The value of time saved is divided both to the worker and his
supervisor in the ratio of ¾ and ¼ respectively. A supervisor also helps a
worker in saving his time so he is also given some benefit in this method. The
standard time for each job is determined in terms of minutes which are called
Bedeaux points or B‘s. each B represents one minute through time and motion
study. A worker is paid time wages upto standard B‘s or 100% performance. Bonus
is paid when actual performance exceeds standard performance in terms of B‘s.
Taylor’s Differential Piece Rate
System - F.W. Taylor, founder of the scientific management evolved this system of wage payment. Under this system, there is
no guarantee of minimum wages. Standard time and standard work is determined on
the basis of time study. The main characteristics of this system is that two
rates of wage one lower and one higher are fixed. Those who fail in attaining
the standard, are paid at a lower rate and those exceeding the standard or just
attaining the standard get higher rate. Under this system, a serve penalty is
imposed on the inefficient workers because they get the wages at lower rates.
The basic idea underlying in this scheme is to induce the worker at least to
attain the standard but at the same time if a worker is relatively less
efficient, he will lose much. For example, the standard is fixed at 40 units
per day and the piece rate are 40 P. and 50 P. per unit. If a worker produces
40 units or more in a day, he will get the wages at the rate of 50 P per unit
and if he produces 39 units will get the wages at 40 paise per unit for the
total output.
Gantt’s Task and Bonus Plan - In this,
a minimum wage is guaranteed. Minimum wage is given to anybody, who completes the job in standard time. If the
job is completed in less time, then there is a hike in wage-rate. This hike
varies between 25% to 50% of the standard rate.
Profit Sharing – It is a
method of remuneration under which an employer pay his employees a share in form of percentage from the
net profits of an enterprise, in addition to regular wages at fixed intervals
of time.
2) Financial and Non-financial Incentives- Individual
or group performance can be measured in financial
terms. It means that their performance is rewarded in money or cash as it has a
great impact on motivation as a symbol of accomplishment. These incentives form
visible and tangible rewards provided in recognition of accomplishment.
Financial incentives include salary, premium, reward, dividend, income on
investment etc. On the other hand, non-financial incentives are that social and
psychological attraction which encourages people to do the work efficiently and
effectively. Non-financial incentive can be delegation of responsibility, lack
of fear, worker‘s participation, title or promotion, constructive attitude,
security of service, good leadership etc..
Positive and Negative Incentives-
Positive
incentives are those agreeable factors related to work situation which prompt an individual to attain or excel the
standards or objectives set for him, where as negative incentives are those
disagreeable factors in a work situation which an individual wants to avoid and
strives to accomplish the standards required on his or her part. Positive
incentive may include expected promotion, worker‘s preference, competition with
fellow workers and own ‗s record etc. Negative incentives include fear of lay
off, discharge, reduction of salary, disapproval by employer etc.
Fringe Benefits
Employees
are paid several benefits in addition to wages, salary, allowances and bonus.
These benefits and services are called ‗fringe benefits‘ because these are
offered by the employer as a fringe. Employees of the organization are provided
several benefits and services by the employer to maintain and promote employee‘s
favorable attitude towards the work and work environment. It not only increases
their morale but also motivate them. These provided benefits and services forms
the part of salary and are generally refereed as fringe benefits.
According to D. Belcher, ―
Fringe benefits are any wage cost not directly connected with the employees productive effort, performance,
service or sacrifice‖. According to
Werther and Davis, ―Fringe embrace a broad range of benefits and services
that employees receive as part of their total compensation, package-pay or
direct compensation and is based on critical job factors and performance‖.
According to Cockman, ―
Employee benefits are those benefits which are supplied by an employer to
or for the benefits of an employee
and which are not in the form of wages, salaries and time rated payments‖.
These are indirect compensation as they are extended condition of employment
and are not related to performance directly.
Kinds of Fringe Benefits
The
various organizations in India offers fringe benefits that may be categorized
as follows:
1)
Old Age
and Retirement Benefits - these include provident fund schemes, pension
schemes, gratuity and medical
benefits which are provided to employee after their retirement and during old
age as a sense of security about their old age.
2)
Workman’s
Compensation - these benefits are provided to employee if they
are got ignored or die under the
working conditions and the sole responsibility is of the employer.
3)
Employee
Security- Regular wage and salary is given to employee that gives a feeling of
security. Other than this
compensation is also given if there is lay-off or retrenchment in an
organization.
4)
Payment
for Time Not Worked – Under this category of benefits, a worker is
provided payment for the work that
has been performed by him during holidays and also for the work done during odd
shifts. Compensatory holidays for the same number in the same month are given
if the worker has not availed weekly holidays.
5)
Safety
and Health – Under this benefit workers are provided conditions
and requirements regarding working
condition with a view to provide safe working environment. Safety and Health
measures are also taken care of in order to protect the employees against
unhealthy working conditions and accidents.
6)
Health
Benefits – Employees are also provided medical services like
hospital facility, clinical facility
by the organization.
Related Topics