Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Sulfate assimilation enables the synthesis of sulfur containing compounds
Methionine is synthesized from cysteine
Methionine is synthesized from cysteine
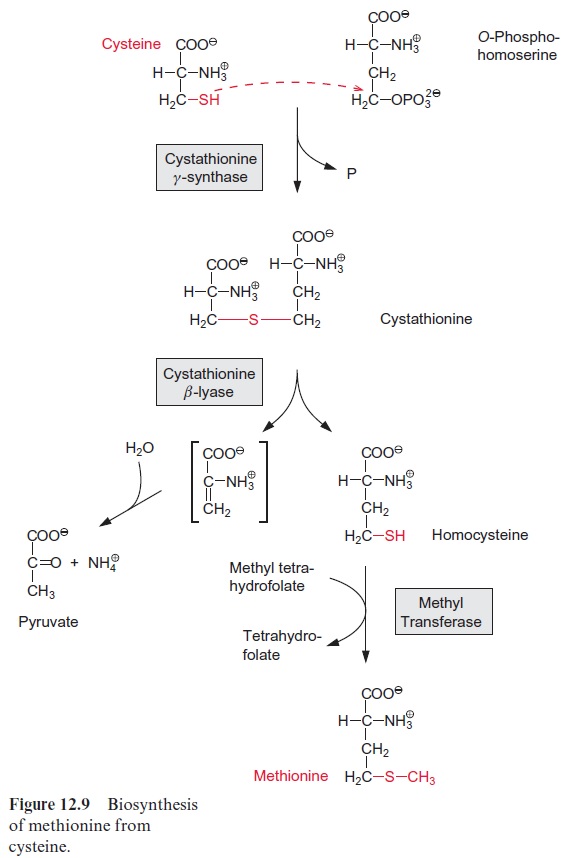
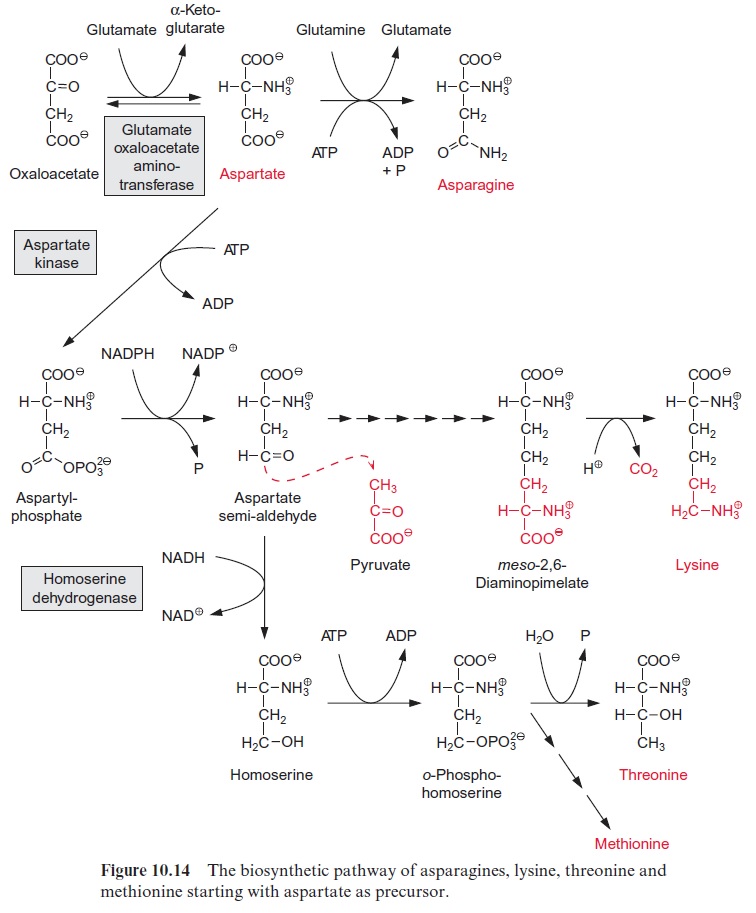
Cysteine is a precursor for methionine, which is another sulfur-containing amino acid. O-Phosphohomoserine, which has already been mentioned as an intermediate of threonine synthesis (Fig. 10.14), reacts with cysteine, while a phosphate group is liberated to form cystathionine (Fig. 12.9). The thioether is cleaved by cystathionine-β-lyase to release homocysteine and an unstable enamine, which spontaneously degrades into pyruvate and NH4+ . The sulfhydryl group of homocysteine is methylated by methyl tetrahydro-folate (methyl-THF) (see Fig. 7.6), and thus the end product methionine is synthesized.
S-Adenosylmethionine is a universal methylation reagent
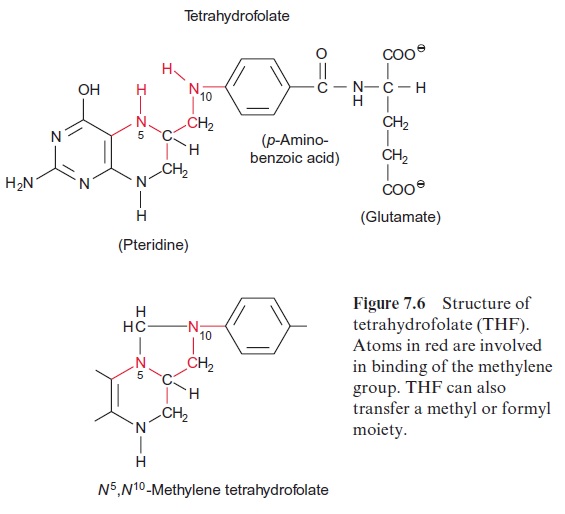
The methyl group delivered as methyl-THF derives from a formiate molecule, which has been bound upon the consumption of ATP to THF and subse-quently reduced by two molecules of NADPH to methyl-THF. Methyl-THF has only a relatively low methyl transfer potential. S-Adenosylmethionine, however, has a more general role as a methyl donor. It is involved in the methylation of nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, membrane lipids, and many other compounds such as chlorophyll, plastoquinone, biotin and polyamines and can therefore be regarded as a universal methylating agent of the cell.
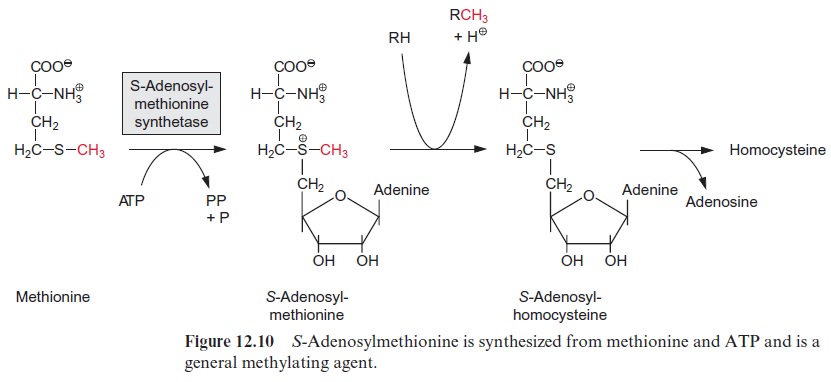
S-Adenosylmethionine is formed by the transfer of an adenosyl residue from ATP to the sulfur atom of methionine, with the release of phosphate and pyrophosphate (Fig. 12.10). The methyl group to which the positively charged S atom is linked is activated and can thus be transferred by corre-sponding methyl transferases to other acceptors. The remaining S-adenosyl homocysteine is hydrolyzed to adenosine and homocysteine and from the latter methionine is recovered by reduction with methyl tetrahydrofolate (Fig. 12.9).
Related Topics