Chapter: Object Oriented Programming and Data Structure : Sorting And Searching
Merge Sort
Merge Sort
We now
turn our attention to using a divide and conquer strategy as a way to improve
the performance of sorting algorithms. The first algorithm we will study is the
merge sort. Merge sort is a
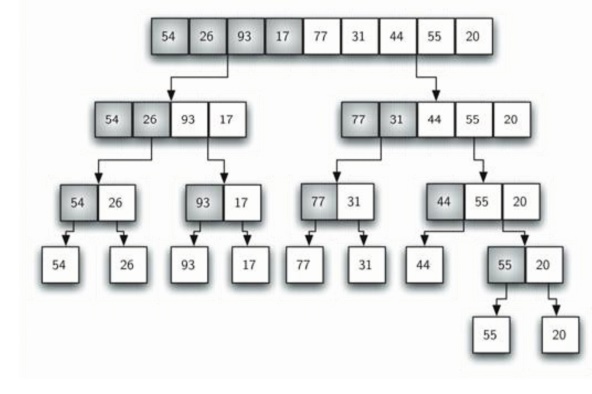
recursive algorithm that continually splits a list in half. If the list is
empty or has one item, it is sorted by definition (the base case). If the list
has more than one item, we split the list and recursively invoke a merge sort
on both halves. Once the two halves are sorted, the fundamental operation,
called a merge, is performed.
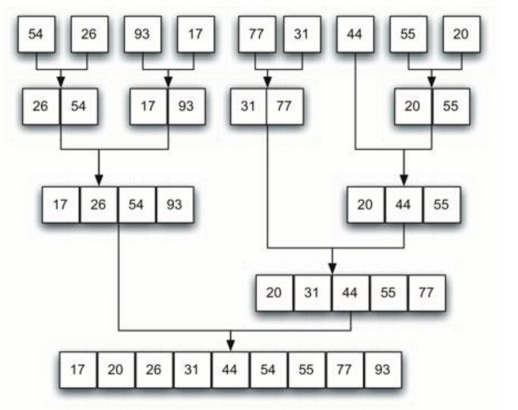
Merging is the process of taking two smaller sorted lists and combining them
together into a single, sorted, new list. Figure below shows our familiar
example list as it is being split by mergeSort. figure 4shows the simple lists,
now sorted, as they are merged back together. The mergeSort function shown in
ActiveCode 6 begins by asking the base case question. If the length of the list
is less than or equal to one, then we already have a sorted list and no more
processing is necessary. If, on the other hand, the length is greater than one,
then we use the Python slice operation to extract the left and right halves. It
is important to note that the list may not have an even number of items. That
does not matter, as the lengths will differ by at most one.
MERGE SORT for PSEUDOCODE:
def mergeSort(alist):
print("Splitting ",alist)
if len(alist)>1:
mid = len(alist)//2
lefthalf = alist[:mid]
righthalf = alist[mid:]
mergeSort(lefthalf)
mergeSort(righthalf)
i=0
j=0
k=0
while i<len(lefthalf) and j<len(righthalf):
if lefthalf[i]<righthalf[j]: alist[k]=righthalf[j]
j=j+1
k=k+1
while i<len(lefthalf): alist[k]=lefthalf[i] i=i+1
k=k+1
while j<len(righthalf): alist[k]=righthalf[j] j=j+1
k=k+1 print("Merging ",alist)
alist = [54,26,93,17,77,31,44,55,20]
mergeSort(alist)
print(alist)
Related Topics