Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 10 : Mental Health Nursing
Mental Disorders
Mental Disorders
Mental illness is maladjustment in living. It produces disharmony
in the person’s ability to meet the human needs. In general, the physical
health of an individual is given greater importance and mental health aspect is
often neglected.
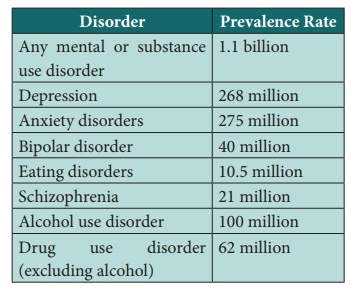
World wide Prevalence Rates of Mental Disorders are
Classification Of Mental Disorders
Classification of mental disorders is also known as psychiatric
“nosology” or “taxonomy”.
Classification of Mental Disorders Under (International Classification of Diseases) ICD-10
·
Organic including
symptomatic mental disorders
·
Mental and behaviour
disorders due to psychoactive substance use
·
Schizophrenia,
schizotypal and Delusional disorders
·
Mood (Affective)
Disorders
·
Neurotic, Stress related
and Somatoform disorders
·
Behavioural syndromes
associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors
·
Disorders of adult
personality and behaviour
·
Mental retardation
·
Disorders of
psychological development
·
Behavioural and
emotional disorders with onset occurring in childhood and adolescence
·
Unspecified mental
disorders
Indian Classification of Mental Disorders
It is a modification of ICD-8 to suit Indian conditions. It is
broadly grouped as follows
·
Psychosis
o
Functional
o
Affective
o
Organic
·
Neurosis
·
Special disorders
o
Childhood disorders
o
Conduct disorders
o
Substance abuse
o
Psycho physiological disorder
o
Mental retardation
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Illness
·
Alterations in
personality and behaviour
·
Alterations in
biological functions (sleep, appetite, sexual desire)
·
Disorders of
consciousness (conscious, unconscious, coma, drowsy, and stupor)
·
Disorders in orientation
(time, place and person)
·
Disorders of attention
and concentration
·
Disorders of thought
·
Disorders of motor
activity (increased, decreased, stereotype, violence, echolalia, echo praxia,
waxy flexibility, restlessness and excitement)
·
Disturbances in speech
(word salad, circumstantiality, mutism and neologism)
·
Disturbances in
perception (hallucination, delusion and illusion)
·
Disturbances in emotions
(elevation, panic, agitation, hostile, depressed and anxiety)
Management of mental disorders
·
Antidepressants
·
Antipsychotics
·
Mood stabilizing drugs
·
Anxiolytics, hypnotics
and sedatives
·
Anti parkinsonian drugs
·
Psychoanalytic therapy
·
Supportive psychotherapy
·
Benzodiazepines
·
Psychotherapy
·
Behaviour therapy
·
Cognitive therapy
·
Group therapy
·
Play therapy
·
Interpersonal
psychotherapy
·
Stress reducing
techniques – Music , Dance, Yoga, Medication and breathing exercises
1. Schizophrenia
Meaning
The term schizophrenia was coined in 1908 by the Swiss
psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler. The word was derived from Schizo (split) and phren
(mind).
Definition
Schizophrenia a psychotic condition characterized by a disturbance
in thinking, emotions, volitions and clear consciousness which usually leads to
social withdrawal.
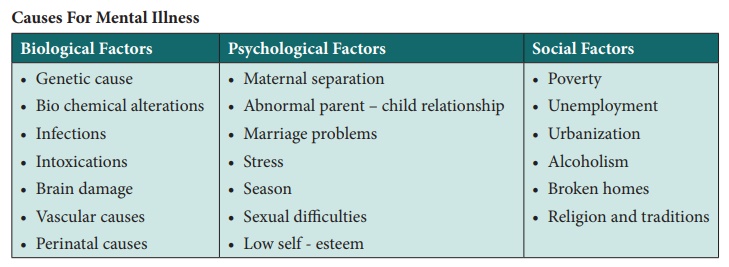
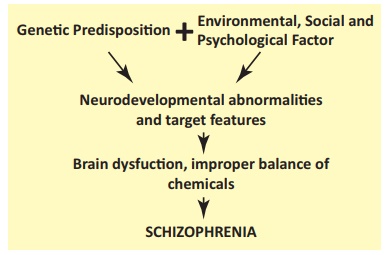
Causes: The exact cause is not known
·
Genetic causes and
hereditary
·
Bio chemical –
abnormalities in dopamine, epinephrine, serotonin.
·
Psychological factors –
impaired ego, crisis situation
·
Family factors – parent
– child relationship, family dysfunction
·
Social causes – social
crisis,
·
Endocrine and metabolic
causes.
Types of Schizophrenia
·
Paranoid Schizophrenia -
·
Hebephrenic
Schizophrenia
·
Catatonic Schizophrenia
·
Undifferentiated
Schizophrenia
·
Post schizophrenic
depression
·
Residual Schizophrenia
·
Simple Schizophrenia
·
Schizo typal disorder
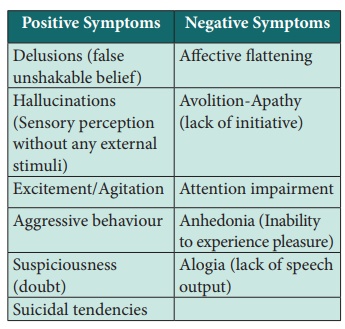
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
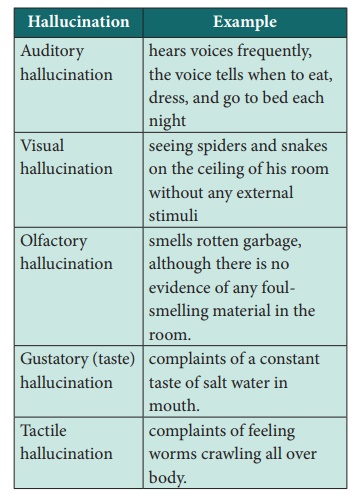
Types of Hallucinations
Diagnosis
·
History collection
·
Substance history
·
CT, MRI and brain
studies
·
Blood investigations
·
Mental status
examination
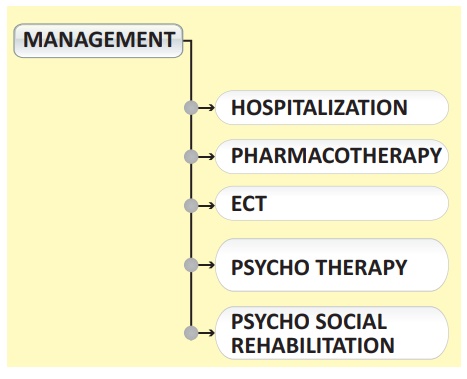
Management of Schizophrenia
Nursing Management
·
Nursing assessment
·
Health education
2. Paranoid
Definition
Paranoid is a thought process that causes an irrational suspicion
(doubtfulness) or mistrust of others.
Cause
Genetics, stress, brain chemistry and also drug abuse.
Symptoms:
·
A consistent stress or
anxiety beliefs about others
·
A mistrust of others
·
Feeling disbelieved
/misunderstood
·
Isolation
Diagnosis
History collection, physical examination and mental status
examination.
Management
·
Accept their
vulnerability
·
Develop trust in others
·
Encourage to express
emotions in positive manner.
·
Psychotherapy
3. Depression
Depression (The Common Cold of Psychiatric Disorders)
Definition
“An alteration in mood that is expressed by feelings of sadness,
despair, and pessimism. There is a loss of interest in usual activities, and
somatic symptoms may be evident. Changes in appetite and sleep pattern are
common”.
- Mary C. Townsend
Etiology
·
Due to loss of loved
object
·
Repeated losses in the
past
·
Negative expectations of
environment, Negative expectations of the self
·
Negative expectations of
the future
·
Stressful life events,
Death, Marriage, Financial loss

Symptoms of Depression
·
Sadness
·
Sleep disturbances
Insomnia -early morning or over sleeping
·
Hopelessness,
Helplessness, Worthless ness, restless, irritable.
·
Guilt,
·
Anger
·
Fatigue
·
Thoughts of death
·
Spontaneous crying
·
Avoids interactions with
family or friends.
Diagnostic Measure for Depression
·
History collection
·
Mental status
examination
·
Depression assessment
tools
Treatment for Depression
·
Medication -
antidepressants
·
Electro Convulsive
Therapy
·
Psychotherapy
4. Mania
Mania refers to a syndrome in which the central features are over
activity, mood changes which may be towards elation or irritability and
self-important ideas.
- Dr. R. Sreevani
5. Postpartum Psychosis

Postpartum psychosis (some times called puerperal psychosis) that
occurs in women who have recently delivered a baby. The syndrome is often
characterized by the mother’s depression, delusions, and thoughts of harming
either herself or her baby.
- Sadock and Sadock
6. Neurotic (Stress related) Disorders
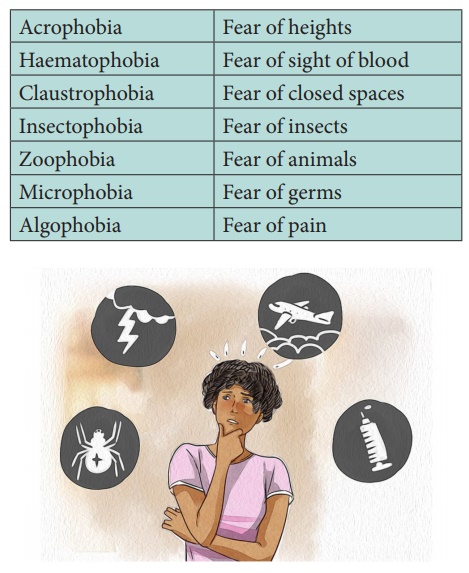
A. Phobia
Phobia is defined as unreasonable fear of a specific object,
activity or situation.
Examples
B. Panic Attack
Intense feeling of fear or terror that occurs suddenly and
intermediately without warning.
C. Anxiety
Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness or tension that a person
experience to an unknown object or situation.
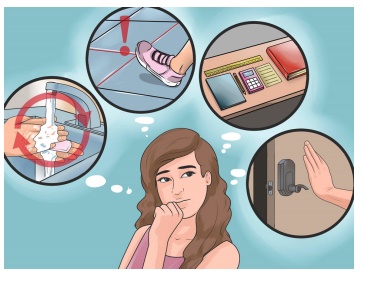
D. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder is a common chronic and long
lasting disorder in which a person has uncontrollable recurrent thoughts and
behaviour that he/she feels the urge to repeat over and over like frequent hand
washing, checking the doors.
E. Conversion Disorder
Conversion disorder formerly known as HYSTERIA, which is a loss of
or change in body function resulting from a psychological conflict, the
physical symptoms of which cannot be explained in terms of any known medical
disorder or pathophysiological mechanism.
F. Psychosomatic Disorders
The term psychosomatic disorder is mainly used to mean a physical
disease that is thought to be caused or made worse by mental factors. Eg. Chest
pain may be caused by stress and not by physical disease.
The word psychosomatic is now replaced with psychophysiologic
disorder. They are also called as stress related disorders. Most of the
symptoms are treated in general hospital rather than in mental hospital.
G. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-traumatic stress disorder is a severe anxiety disorder that
can develop after exposure to any event which results in psychological trauma.
H. Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalised anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive anxiety
and worry about every day life events with no obvious reasons for worry. It may
be about money, health, family, work or school
7. Personality Disorders
(Refer Applied psychology Chapter/Section.)
8. Eating Disorders
Definition
An eating disorder is when you have an unhealthy attitude to food,
which can take over your life and make you ill.
Types Of Eating Disorder
ANOREXIA NERVOSA: anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder in
which people have an intense fear of gaining weight and can become dangerously
ill.
BULIMIA NERVOSA: Bulimia nervosa is a psychological and
severe life threatening eating disorder characterised by ingestion of an
abnormally large amount of food in short time followed by attempt to avoid
weight gain, they induce vomiting.
Usually found in school girls and college students.
Management:
·
Medications
·
Behaviour modification
therapy
·
Psychotherapy
9. Sleep Disorders
Definition
Sleep disorders are changes in sleeping pattern or habit that can
negatively affects health.
Types Of Sleep Disorders:
·
Insomnia:
Disorder of initiation
and maintenance of sleep
·
Hypersomnia:
Excessive sleep pattern
Sleep Disorders
·
Sleep walking
(somnambulism)
·
Bruxism (Tooth grinding)
·
Sleep talking
(somniloqy)
·
Sleep enuresis (Bed
wetting)
Night terrors
Management
·
Treat the cause
·
Medications
·
Sleep hygiene
·
Relaxation techniques
10. Sexual Disorder
Definition
Any disorder that involving sexual functioning, desire or
performance
Types Of Sexual Disorders:
1. Gender Identity Disorders
TRANSSEXUALISM: Sense of discomfort about one’s own sex. They want
to change their sex permanently. (Male to female or female to male)
DUAL ROLE TRANSVESTISM: Wearing clothes of opposite sex to enjoy
temporarily, but they do not want to change their sex
·
Psychological and
behavioural problems related to sexual development and maturation
·
Homosexuality of females
(Lesbians)
·
Homosexuality of males
(Gay)
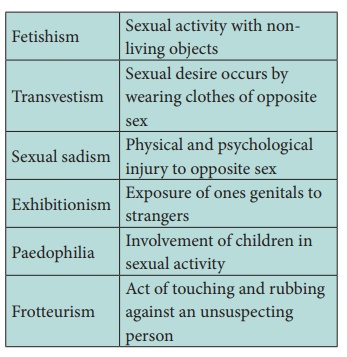
3. Paraphilias
Management:
·
Treat the underlying
physical and psychological problems
·
Medications
·
Psychotherapy
Behaviour therapy
Related Topics