Chapter: Pathology: Genetic Disorders
Mendelian Disorders
MENDELIAN DISORDERS
Mendelian
disorders are characterized by single gene mutations. Common types
ofmutations include point mutations and frameshift mutations.
·
Point
mutations occur with a single nucleotide base substitution, which
mayproduce a variety of effects. The form of point mutation called synonymous
mutation (silent mutation) occurs when a base substitution results in a codon
that codes for the same amino acid. The form of point mutation called mis-sense
mutation occurs when a base substitution results in a new codon and a change in
amino acids. The form of point mutation called a nonsense mutation occurs when
a base substitution produces a stop codon and therefore produces a truncated
protein.
·
Frameshift
mutations occur when insertion or deletion of bases leads to ashift in
the reading frame of the gene.
The
location of a mutation will alter its potential effects. Mutations involving
coding regions of DNA may result in abnormal amino acid sequences; decreased
production of the protein; truncated or abnormally folded protein; or altered
or lost function of the protein. Mutations of promoter or enhancer regions may
interfere with tran-scription factors, resulting in decreased transcription of
the gene.
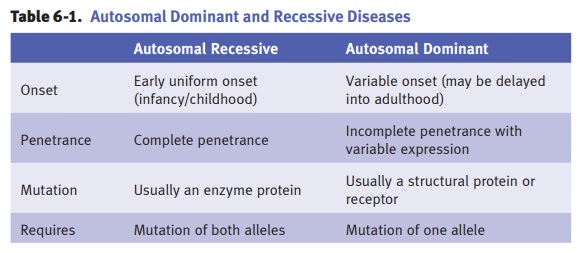
Patterns
of inheritance for genetic diseases show wide variation, and the genetic
pattern of a disease may be classified as autosomal dominant; autosomal
recessive; X-linked recessive; X-linked dominant; triplet repeat mutations;
genomic imprint-ing; mitochondrial; or multifactorial.
Related Topics