Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Applied Psychology
MaslowŌĆÖs theory of Motivation
MaslowŌĆÖs theory of Motivation
MaslowŌĆÖs hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology proposed by
Abraham Maslow in 1943. This theory is often portrayed in the shape of a
pyramid with the largest, most fundamental needs at the bottom and the need for
self actualization at the top. From the bottom, the first four levels of the
pyramid contains ŌĆ£deficiency needsŌĆØ such as physiological, safety,
love/belonging and esteem needs. The basic needs must be met before the
individual will strongly desire for the next level needs. For example, an individual
will not expect safety needs until unless his physiological needs are met. He
will not desire for love and belonging before the safety needs are met. Maslow
also coined the term ŌĆśmeta motivationŌĆÖ to describe the motivation of people who
go beyond the scope of the basic needs and strive for constant betterment. If
these ŌĆ£deficiency needsŌĆØ are not met, the individual will feel anxious and
tense.
MaslowŌĆÖs Hierarchy of Needs
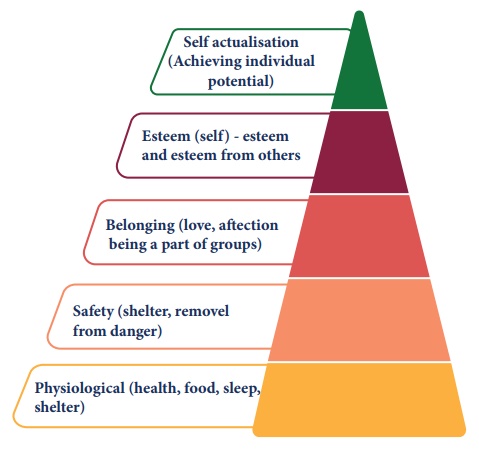
Physiological needs
Physiological needs are the physical requirements for human
survival. If these requirements are not met, the human body cannot function
properly and will ultimately fail. Physiological needs are the first and basic
need in the hierarchy. Without them, the other needs cannot follow up. Physiological
needs include breathing, water, food, sleep, clothing, shelter and sex.
Safety needs
Once a personŌĆÖs physiological needs are relatively satisfied,
their safety needs take precedence and dominate behavior. For example in the
absence of physical safety ŌĆō due to war, natural disaster etc. ŌĆō people may
experience stress and tension. Safety and Security needs include personal
security, emotional security, financial security, health and well being and
safety needs against accidents/illness and their adverse impacts.
Love/Belonging
The third level of human needs is interpersonal and involves
feelings of belongingness. Social Belonging needs include friendships, family
and intimacy. Human beings need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance
among social groups, regardless whether these groups are large or small. The
example for large social groups may include clubs, religious groups, sports
teams, gangs, etc and some small social connections include family members,
intimate partners, mentors, colleagues, etc. Human beings need to love and be
loved ŌĆō both sexually and non-sexually ŌĆō by others.
Self esteem
Self Esteem is a belief about oneŌĆÖs own worth based on an overall
self evaluation. Esteem needs are ego needs or status needs which are related
to getting recognition, status, importance, and respect from others in the
society. All humans have a need to feel respected; this includes the need to
have self esteem and self-respect. These activities give the person a sense of
contribution or value. Deficiency in this level leads to low self esteem.
Self-actualization
Self actualization refers to an individualŌĆÖs need to develop his
or her potentialities: in other words, to do what he or she is capable of
doing. It means a personŌĆÖs motivation to reach his or her full potential.
Related Topics