Economics - Long Run Cost Curve | 11th Economics : Chapter 4 : Cost and Revenue Analysis
Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 4 : Cost and Revenue Analysis
Long Run Cost Curve
Long
Run Cost Curve:
In the
long run all factors of production become variable. The existing size of the
firm can be increased in the case of long run. There are neither fixed inputs
nor fixed costs in the long run.
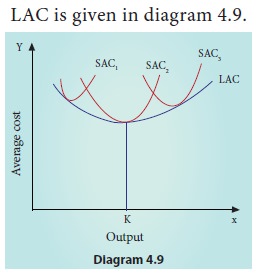
LAC is
given in diagram 4.9.
Long run
average cost (LAC) is equal to long run total costs divided by the level of
output.
LAC =
LTC/Q
where,
LAC denotes Long-Run Average Cost,
LTC
denotes Long-run Total Cost and
Q denotes
the quantity of output.
The LAC
curve is derived from short-run average cost curves. It is the locus of points
denoting the least cost curve of producing the corresponding output. The LAC
curve is called as ‘Plant Curve’ or ‘Boat shape Curve’ or ‘Planning Curve’ or
‘Envelop Curve’.
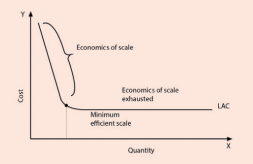
A significant recent development in cost theory is that the
long-run average cost curve is L- shaped rather than U-shaped. The L-shape of
the long-run average cost curve implies that in the beginning when output is
expanded through increase in plant size and associated variable factors, cost
per unit falls rapidly due to economies of scale.
Related Topics