Chapter: Mechanical : Fluid Mechanics And Machinery : Pumps
Lobe pumps
Lobe pumps
In principle the lobe pump is similar to the external gear pump; liquid flows into the region created as the counter-rotating lobes unmesh. Displacement volumes are formed between the surfaces of each lobe and the casing, and the liquid is displaced by meshing of the lobes. Relatively large displacement volumes enable large solids (nonabrasive) to be handled. They also tend to keep liquid velocities and shear low, making the pump type suitable for high viscosity, shear-sensitive liquids.
Two lobe pump Three lobe pump
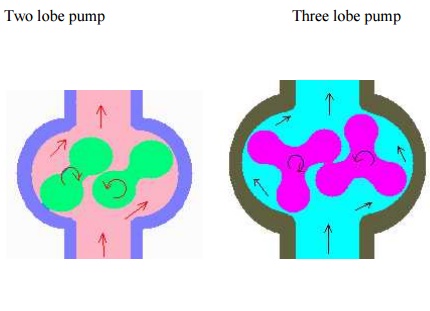
The choice of two or three lobe rotors depends upon solids size, liquid viscosity, and tolerance of flow pulsation. Two lobe handles larger solids and high viscosity but pulsates more. Larger lobe pumps cost 4-5 times a centrifugal pump of equal flow and head.
Internal-gear Pump
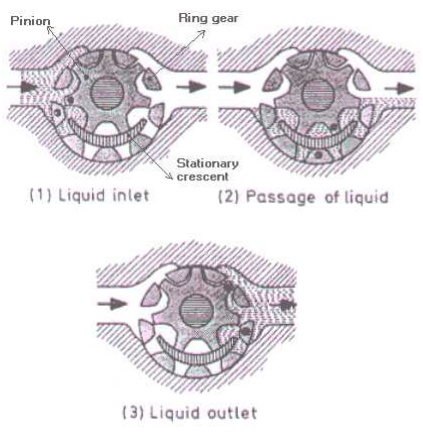
The above figure shows the operation of a internal gear pump. In the internal-gear pump a spur gear, or pinion, meshes with a ring gear with internal teeth. Both gears are inside the casing. The ring gear is coaxial with the inside of the casing, but the pinion, which is externally driven, is mounted eccentrically with respect to the center of the casing. A stationary metal crescent fills the space between the two gears. Liquid is carried from inlet to discharge by both gears, in the spaces between the gear teeth and the crescent.
Related Topics