Chapter: Aquaculture Engineering : Buildings and Superstructures
Load carrying systems - Buildings and Superstructures in Aquaculture Engineering
Load-carrying systems
A load-carrying
system keeps the walls upright and the roof in position; it also takes the
weight of the roof which, in colder regions also includes the load from snow.
The cost of the load-carrying system is an important part of the total cost of
the building.
Various
constructions are used as load-carrying systems; these are based, among other
things, on the material used (Fig. 20.2). Either separate constructions can be
used for the wall and the roof, or combined systems can be employed, where the
walls and roof are integral parts of the load-carrying system. In the first
case the wall system carries the roof; different types are explained later.

When designing the load-carrying system, the necessary free span, i.e. the available floor area with no pillars, is
of great interest. The size of the free span determines the size of the
construction; a larger free span results in a larger construction. To reduce
the size of the free span, pillars or internal walls are used to carry the
weight of the roof at several points. The use of pillars will reduce the cost
of the load-carrying system, but inhibit the use of the building, constraining
internal handling and space utilization.
Roof
constructions that cover a large free span (above 10–15 m) are expensive. Long
distances between the outside walls, without pillars or inter-nal walls, will
increase the building costs because the size of the roof construction is
increased.
The timber
lattice roof (W) truss is quite a commonly used roof load-carrying system. It
may be built on site, but is normally prefabricated. A free span distance of up
to 12–13 m width is easily covered with such a construction. If the building is
wider, it is recommended that pillars be used to take the weight of the roof,
if the aim is to keep the cost of construction low; a load carrying internal
wall will have the same effect. This is a cheap and simple building
construction.
Steel, concrete
or wood beams or trussed beams are also much used. They can be used on large
free spans in excess of 20 m, and even up to 100 m if the beams are bowed, as
in a velodrome. Trussed beams are favoured for large constructions. However,
for this type of construction also, the costs increase exponentially with the
free span. Longitudinal beams of wood or steel in the building give quite a
simple construction, especially when used in free spans below 20–25 m; however,
pillars are recommended if the span is longer.
In combined
systems, the load-carrying system for the roof and walls is integrated. A
much-used construction here consists of large frames, either in steel or wood
and often of a bowed shape, that are set into the foundations. The distance
between the frames varies, but is normally in the range 3–5 m, or equal to a
section of the building. The rest of the wall and roof structure is also built
of steel or wood and connected directly to the frames. A great advantage of
this construction is that it is quite fast to erect, and can be used on large
buildings with a large free span. The method is fairly expensive and will
normally require cranes to put up the building.
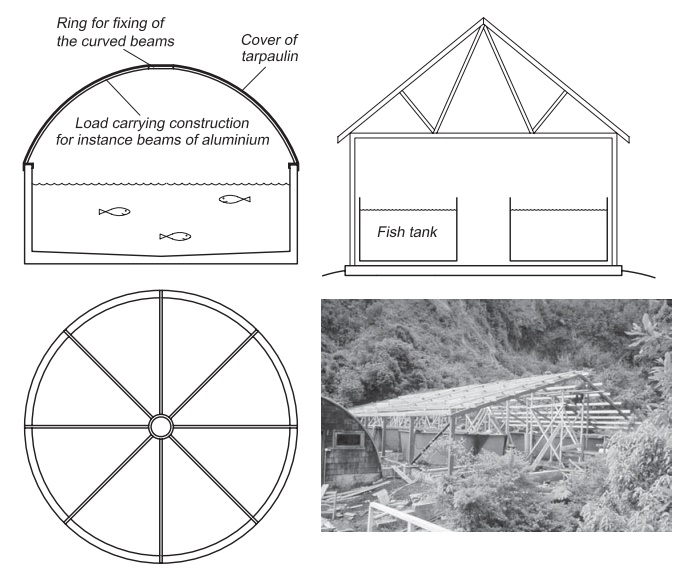
If the tanks
are large, individual superstructures for separate tanks can be used. A cheap
construction uses a hemisphere created with a frame of steel pipes and a cover
of tarpaulin.
Related Topics