Numbers | Term 2 Chapter 1 | 6th Maths - Least Common Multiple (LCM) | 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 1 : Numbers
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 1 : Numbers
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Common
Multiples
Let us now write the multiples of 5 and 7
Multiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70,…
Multiples of 7 are 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70,…
Here, the common multiples of 5 and 7 are 35 and 70 and will
go on without ending.
As multiples of a number are infinite, we can think
of the Least Common Multiple of numbers,
shortly denoted as LCM.
1.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Think about the situation:
Situation 1: Write the multiplication table of
4 and 5 (upto 10).
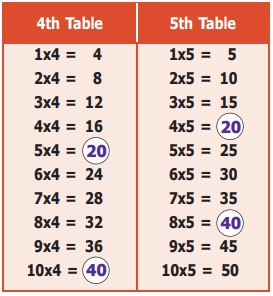
Observing the multiplication tables, can you find the multiples (product of numbers) that are the same in the 4th table and 5th table?. If yes, what are they? Yes, they are 20, 40, etc. From the multiples of 4 and 5, we can easily find that 20 is the least common multiple of 4 and 5.
Situation 2:
Anu wants to buy Ragi Laddus and Thattais
to serve at her sister’s birthday party. Ragi Laddus come in packets of 4 and Thattais
come in packets of 6. Anu has to buy these packets so that there are the same number
of Ragi Laddus and Thattais to serve at the party. How will Anu tackle this situation?

This situation can be tackled by Anu using the concept of LCM. Here, multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, ... and multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, ... We find that the common multiples are 12, 24, ... of which 12 is the least common multiple. Hence, Anu should buy a minimum of 3 packets of Ragi Laddus and 2 packets of Thattais so that there are the same number of Ragi Laddus (12) and Thattais (12) to serve at the party.
Situation 3:
Consider the red and the blue coloured floor mats
of length 4 units and 5 units as follows.

Five red coloured floor mats of 4 units each can
be arranged as follows. Its total length is 5 × 4 = 20 units.

Four blue coloured floor mats of 5 units each can
be arranged as follows. Its total length is also the same 4 × 5 = 20 units.

Note that the 5 floor mats each of length 4 units
are required to equal 4 floor mats each of length 5 units and that is, the length
20 units is the smallest common length that can be matched by both sizes. From the
above, it shows that the least common multiple of 4 and 5 is 4 × 5=20.
The Least Common
Multiple of any two non- zero whole numbers is the smallest or the lowest
common multiple of both the numbers. The Least Common Multiple of the numbers x
and y can be written as LCM (x,y).
We can find the least common multiple
of two or more numbers by the following methods.
1. Division Method
2. Prime Factorisation Method
Example 5: Find the LCM of 156 and 124.
Solution: By Division method
Step 1: Start with the smallest prime factor
and go on dividing till all the numbers are
divided as given below.
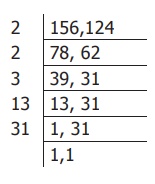
Step 2: LCM = product of all prime factors
= 2 × 2 × 3 × 13 × 31 = 4836
Thus, the LCM of 156 and 124 is 4836.
By Prime Factorisation method
Step 1: We write the prime factors of 156 and 124 as given
below (use of divisibility test rules will also help).
156 = 2 × 78 = 2 × 2 × 39 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 13
124 = 2 × 62 = 2 × 2 × 31
Step 2: The product of common factors is 2 × 2 and also
the product of the factors that are not common is 3 × 13 × 31.
Step 3: Now, LCM = product of common factors × product of
factors that are not common
= (2 × 2) × (3 × 13 × 31) = 4 × 1209 = 4836
Thus, LCM of 156 and 124 is 4836.
(or)
156 = 2 × 78 = 2 × 2 × 39 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 13;
124 = 2 × 62 = 2 × 2 × 31
The prime factor 2 appears a maximum of 2 times
in the prime factorization of 156 and 124, the prime factor 3 appears only 1 time
in the prime factorization of 156, the prime factor 13 appears only 1 time in the
prime factorization of 156 and the prime factor 31 appears only 1 time in the prime
factorization of 124.
Hence, the required LCM = (2 × 2) × 3 × 13 × 31
= 4836.
Related Topics