Chapter: Mechanical : Dynamics of Machines : Mechanisms For Control
Important Short Questions and Answers: Mechanisms For Control
MECHANISMS
FOR CONTROL
1. What is
meant by sensitiveness of governors?
The sensitiveness is defined as the ratio of the
mean speed to the difference between the maximum and minimum speeds. A governor
is said to be sensitive, when it really to a small change of speed.
2. What is
meant by hunting?
The phenomenon of continuous fluctuations of the
engine speed above and below the mean speed is termed as hunting. This occurs
in over-sensitive governors.
3. What is
meant by isochronous condition in governors?
A governor with zero range of speed is known as an
isochronous governor. Actually the isochronism is the stake of Infinite
sensitivity.
4. What are centrifugal governor? How do they differ
from inertia governor?
·
The centrifugal governor controls the fuel supply
by means of the centrifugal forces on the governor balls.
·
Inertia governor work s based on the inertia forces
caused by an angular acceleration or retardation of the shaft.
5.
Explain
the term stability of the governor?
A governor is said to be stable if there is only
one radius of rotation for all equilibrium speeds of the balls within the
working range. If the equilibrium speed increases the radius of governor ball
must also increase.
6.Derive an expressio6. for the height in the case
of a Watt governor.
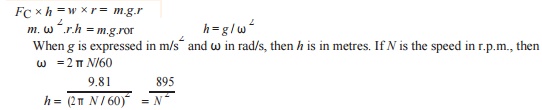
7.
Define
steering, pitching and rolling. (Or) list some of the terms related to motion
of ships using gyroscopic principle.
·
Steering is the turning of a complete ship in a
curve towards left or right, while it moves forward.
·
Pitching is the movement of a complete ship up and
down in a vertical plane about transverse axis.
·
Rolling is the movement of a ship in a linear
fashion.
8.
Write the
expression for gyroscopic couple?
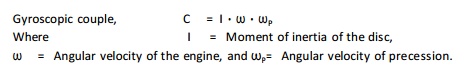
9.
What will
be the effect of gyroscopic couple on a disc fixed at a certain angle to a
rotating shaft?
The gyroscopic couple is applied through the
bearings which support the shaft. The bearings will resist equal and opposite
couple.
10. What is the effect of
gyroscopic couple on an automobile taking a turn?
While an automobile will move in a straight line,
there will not be any gyroscopic effect on it; but when it takes a turn
(towards left or right), it will be subjected to gyroscopic couple. The
tendency of this couple is to overturn the vehicle.
11. What is gyroscopic torque?
Whenever a rotating body changes its axis of rotation, a torque is
applied on the rotating body. This torque is known as gyroscopic torque.
12. Which part of the automobile
is subjected to the gyroscopic couple?
The rotating parts of automobile such as engine rotor, wheels and
bearings are subjected to the gyroscopic couple.
13. What is meant by reactive
gyroscopic couple?
When the axis of spin itself moves with angular velocity ωp,
the disc is subjected to reactive couple whose magnitude is same but opposite
in direction to that of active couple.
The reactive couple to which the disc is subjected when the axis of spin
rotates about the axis of precession is known as reactive gyroscopic couple.
14. What is meant by applied
torque and reaction torque?
The torque exerted by one body on another is called applied torque. When
one body exerts torque on another body, then the opposite torque exerted by the
second body on the first is called reaction torque.
15. What is the effect of
gyroscopic couple on rolling of ship? Why?
We know that, for the effect of gyroscopic couple to occur, the axis of
precession should always be perpendicular to the axis of spin. In case of
rolling of a ship, the axis of precession is always parallel to the axis of
spin for all positions. Hence there is no effect of the gyroscopic couple
acting on the body of the ship during rolling
Related Topics