Chapter: Physics : Conducting Materials
Important Short Questions and Answers: Conducting Materials
SHORT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
1.What is meant by a free electron?
The
electron moves freely in all directions in the absence of electric field is
called free electron (or) valance electron. These electrons collide with each
other, the collisions are perfectly elastic collisions hence there is no loss
of energy. Since the free electron is in random motion.
2.
Define Drift velocity of electrons.
Drift velocity (Vd) is the average velocity acquired by
an electron in a particular direction due to applied electric field.

3.
Define mobility of electrons.
The mobility is defined as the drift velocity (Vd)
acquired by the free electron per unit electric field (E)
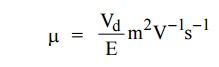
4.
Define mean free path.
5. Define relaxation time.
Relaxation time is the time taken by the
electron to reach equilibrium position from its disturbed position in the
presence of electric field.
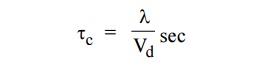
![]() 6. Define electrical conductivity.
6. Define electrical conductivity.
The
electrical conductivity is defined as the quantity of electricity flowing per
unit area per unit time at a constant potential gradient.
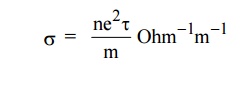
7,Define Thermal Conductivity.
Thermal
conductivity of material is defined as the amount of heat flowing through an
unit area per unit time of temperature gradient.
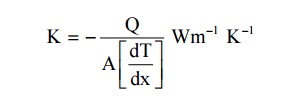
8. State Widemann-Franz law.
The
ratio between the thermal conductivity (K) and electrical conductivity ( ) of a
metal is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the metal.
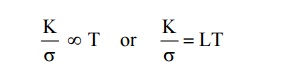
9.List out the three main theories developed to
describe the structure of materials. (or) List the types of electron theory of
metals.
Classical
free electron theory
Quantum
free electron theory
Zone
(or) Band theory
10. What are the Sources of resistance in
metals?
The resistance in metals is due to
Presence
of impurities in the metals.
Temperature
of the metal.
Number o
free electrons.
11. What
is the effect of temperature on metals
When
temperature of the metal increases, the mobility of the electron decreases and
hence the electrical conductivity decreases. The addition of impurities in the
metal decreases the electrical conductivity.
12. What are the uses (or) success of classical
free electron theory?
It is
used to verify the Ohm’s law.
It is
used to explain electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of metals.
It is
used to derive Widemann-Franz law.
3. It is used to explain the optical properties
of metal.
13.What are the drawbacks of classical free
electron theory? (or) State any four demerits of Classical free electron
theory?
It is a macroscopic theory.
According
to classical free electron theory, all the free electrons will absorb energy,
but the quantum free electron theory states that only few electrons will absorb
energy.
This
theory cannot explain the Compton effect, Photo-electric effect, para-magnetism
and ferromagnetism, etc.,
This
theory cannot explain the electron conductivity of semiconductors and
insulators.
Dual
nature of light radiation cannot be explained.
The
theoretical and experimental values of specific heat and electronic specific
heat are not matched.

The
Lorentz number obtained by classical theory does not have good agreement with
experimental value and it is rectified by quantum theory.
14. What is Lorentz Number?
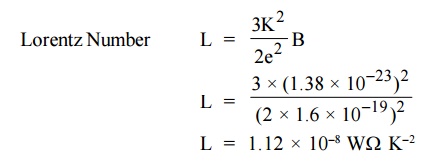
It is found that the classical value of Lorentz
number is only one half of the experimental value (2.44 × 10–8 W K–2).
The discrepancy of L value is the failure of the classical theory. This can be
rectified by quantum theory.
15.What is the basic assumption of Zone theory
or Band theory of solids?
According to quantum free electron theory, the
electrons in a metal were assumed to be moving in a region of constant
potential but it fails to explain, why some solids behave as conductors, some
as insulators and some as semiconductors.
Therefore instead of considering an electron to
move in a constant potential, the Zone theory of solids tells that the
electrons are assumed to move in a field of periodic potential.
16.Distinguish between Electrical conductivity
and Thermal conductivity.
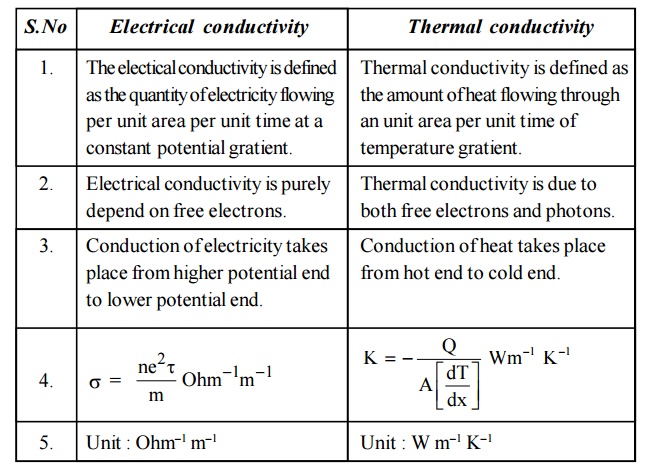
Electrical conductivity
The electical conductivity is defined as the quantity of
electricity flowing per unit area per unit time at a constant potential
gratient.
Electrical conductivity is purely depend on free electrons.
Conduction of electricity takes place from higher potential end to
lower potential end.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity is defined as the amount of heat flowing
through an unit area per unit time of temperature gratient.
Thermal conductivity is due to both free electrons and photons.
Conduction of heat takes place from hot end to cold end.
17.What are the similarities between electrical
and thermal conductivity of metals?
The
electrical and thermal conductivities decrease with the increase in temperature
and impurities.
The
electrical and thermal conductivity is very high at low temperatures.
For
non-metals the electrical and thermal conductivity is very less.
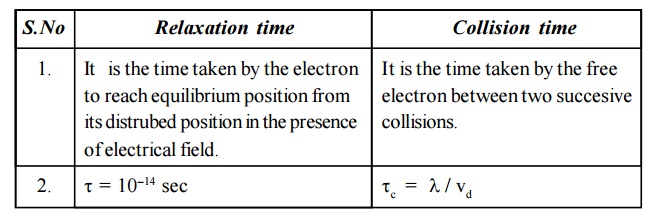
18. Distinguish between relaxation time and
collision time.
19. Write microscopic form of Ohm’s law and
state whether it is true for all temperature.
Microscopically
we can write V = IR as J = E
Since
the resistivity varies with respect to the temperature, the microscopic form of
ohm’s law is not true for all the temperature.
What are the factors that affect the electrical
resistivity of materials?
1. Temperature
2. Impurities
3. Inperfections
4. Magnetic field
5. Pressure and strain.
21. Define Fermi level, Fermi energy and this
importance.
Fermi level : The Fermi level is the highest
reference energy level of a particle at absolute zero.
Importance : It is the reference energy level which
separates the filled energy level and vacant energy levels.
Fermi energy: It is the
maximum energy of the quantum state corresponding to Fermi energy level at
absolute zero.
Importance : Fermi energy determines the energy of
the particle at any temperature.
22. Define Fermi Distribution function.
It is an expression for the distribution of electrons among the
energy levels as a function of temperature and it is the probability of finding
an electron in particular energy state of energy E is given by,
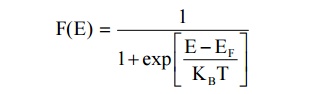
23.Define density of states and its importance.
Density of states is defined the as the number
of energy states per unit volume in an energy interval of a metal. It is use to
calculate the number of charge carriers per unit volume of any solid.1exp
E E
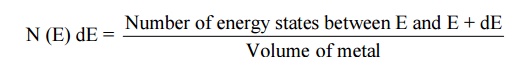
Importance : It is used for the Fermi energy calculation at
any temperature.
24.Define work function
It is define as the minimum energy required to remove an electron
from the metal surface at 0K. in order to make it escape, an additional amount
of energy equal to is required. i.e., .This difference in energy is called Work
function.
25.What do you mean by carrier concentration in
metal?
In metal carrier concentration is number of
free electrons per unit volume in between the energy interval 0 to it is given
by
Carrier concentration N D (E) F(E) dE
26. How classical free electron theory failed
to account for specific heat of solid?
According to classical free electron theory,
the experimental and theoretical value of specific heat of solid are not
matched. Hence classical free electron theory is failed.
Related Topics