Chapter: Signals and Systems : Classification of Signals and Systems
Important Short Questions and Answers: Classification of Signals and Systems
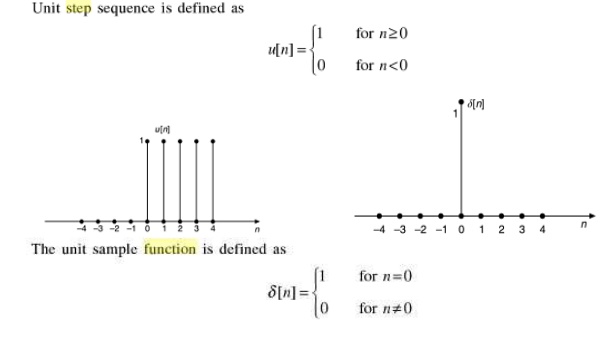
1. Define unit impulse and unit step signals.
Unit
Impulse signal:
Amplitude
of unit impulse is 1 as its width approaches zero. Then it has zero value at
all other values.
Unit Step
Signal:
The unit
step signal has amplitude of 1 for positive values of independent variable and
amplitude of 0 for negative of independent variable.
2. Give the mathematical and graphical representation of CT (continuous time) and DT (discrete time) impulse function.

3. Define step and impulse function in discrete signals.
4. State the two properties of unit impulse function.

5. Find the fundamental period of signal
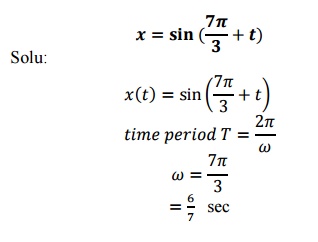
6. Check e time whether the discrete signal
sin 3n is periodic? The frequency of the discrete time signal is 3, because
it is not a multiple of .
·
Therefore the signal is aperiodic.
7. Distinguish between deterministic and random
signals. or
Define
random signal and deterministic signal.
Random
Signal:
It has some degree of uncertainty before
it actually occurs. The random signal cannot be defined by mathematical
expressions.
Deterministic
Signal:
There
is no uncertainty
occurrence. It is
completely represented by mathematical expressions.
8. Determine the period of the signal

9. When is a system said to be memory less?
Give an example.
If the
system output does not depend the previous input, it only depends the present
input. Then the system is called memory less or static system.
y(t) = 2x(t) + x(t)
y(n) = x(n) + √x(n)
10. Define energy and power signals.
Energy
Signal:
• A signal is said to be an energy signal if
its normalized energy is non zero and finite.
• For an energy signal, P = 0.
i.e., 0 < E < ∞
Power Signal:
• A signal is said to be the power signal if it satisfies 0 < P < ∞
• For a power signal, E = ∞
11. What is the classification of system?
The
classification of systems is,
(i).
Linear and Non-Linear systems
(ii).
Time invariant and Time varying systems.
(iii).
Causal and Non causal systems.
(iv).
Stable and unstable systems.
(v).
Static and dynamic systems.
(vi).
Invertible and non invertible systems.
12. Verify whether the system described by the
equation :
·
The system is linear since output is direct
function of input.
·
The system is time variant since time parameter is
squared in the given equation.
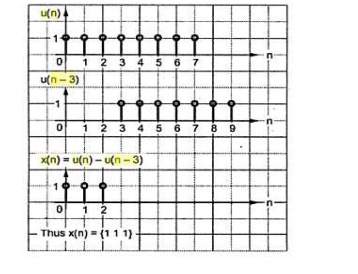
13. Draw the signal x(n) = u(n) – u(n-3)
14.
Check
whether the following system is static/dynamic and casual/non casual y(n) =
x(2n).
·
If n=1, y(1) = x(2). This means system requires
memory. Hence it is dynamic system.
·
Since y(1) = x(2), the present output depends upon
future input. Hence the system is non casual.
15.
Distinguish
between static and dynamic system.
Static system:
• Does
not require memory
• Impulse
response is of the form h(t)=cω(t)
Dynamic system:
•
Requires memory
• Impulse
response can be any form except h(t)=cω(t)
Related Topics