Chapter: Electrical machines : Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic Materials
Important Short Questions and Answers : Electrical machines - Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic Materials
MAGNETIC
CIRCUITS AND MAGNETIC MATERIAL
1. Mention the types of
electrical machines.
There are
three basic rotating machines types, namely
a.
The dc machines
b.
the poly phase synchronous machine (ac), and
c.
Poly and single phase induction machine (ac)and a
stationary machine,
namely
Transformer
2. State Ohm’s law for magnetic
circuit.
It states
that the magneto motive force across the magnetic element is equal to the
product of the magnetic flux through the magnetic element and the reluctance of
the magnetic material. It is given by
MMF =
Flux X Reluctance
3. Define leakage flux
The flux
setup in the air paths around the magnetic material is known as leakage flux.
4. Define magnetic reluctance
The
opposition offered by the magnetic circuit for the magnetic flux path is known
as magnetic reluctance. It is analogous to electric resistance.
5.
Draw the
typical normal magnetization curve of ferromagnetic material.
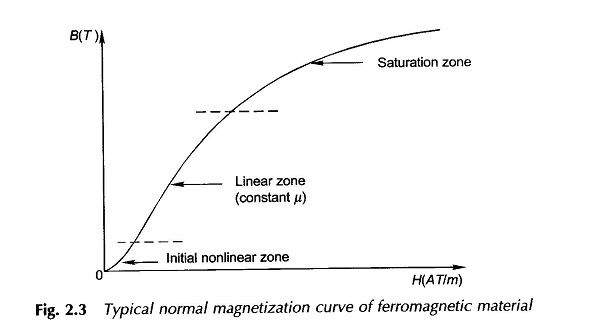
6.
What is
fringing?
In the
air gap the magnetic flux fringes out into neighboring air paths due to the
reluctance of air gap which causes a non uniform flux density in the air gap of
a machine. This effect is called fringing effect.
7. State stacking factor.
The
stacking factor is defined as the ratio of the net cross sectional area of a
magnetic core to the gross cross sectional area of the magnetic core. Due to
lamination net cross sectional are will be always less than gross cross
sectional area. Therefore the value of stacking factor is always less than
unity.
8.Mention some magnetic materials
Alnicos,
chromium steels, copper–nickel alloy, nickel, cobalt, tungsten and aluminium.
9. What is magnetostriction?
When
ferromagnetic materials are subjected to magnetizing mmf, these may undergo
small changes in dimension; this phenomenon is known as magnetostriction.
10.Define statically induced emf.
The coil
remains stationary with respect to flux, but the flux through it changes with
time. The emf induced is known as statically induced emf.
11. Define dynamically induced
emf.
Flux density
distribution remains constant and stationary but the coil move relative to
it.The emf induced is known as dynamically induced emf.
12.
State
Fleming’s right hand rule.
Extend
the thumb, fore and middle finger of the right hand so that they are mutually
perpendicular
to each other. If the thumb represents the direction of movement of conductor
and the fore finger the direction of magnetic flux, then the middle finger
represents the direction of emf
13.State Fleming’s Left hand
rule.
Extend
the thumb, fore and middle finger of the right hand so that they aremutually
perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger represents the direction of flux
and the middle finger the direction of current, then the middle finger
represents the direction of movement of conductor.
14. What are the losses called as
core loss?
Hysteresis
loss and eddy current loss.
15.Define coercivity.
It is the
measure of mmf which, when applied to the magnetic circuit would reduce its
flux density to zero, i.e., it demagnetizes the magnetic circuit.
Related Topics