Chapter: Physics : Super Conducting Materials
Important Questions and Answers: Super Conducting Materials
SUPER CONDUCTING MATERIALS
1.
Define of super conductivity and super conductors.
The phenomenon of losing the resistivity
absolutely to zero, when cooled to sufficiently low temperature ie., below
critical temperature (Tc) is called superconductivity.
The materials which exhibit
superconductivity phenomena are called superconductors or superconducting
materials.
2.
What is transition temperature?
The temperature at which a normal
material changes into a superconductor is called transition temperature (or)
critical temperature (TC).
3.
Mention any four property charges that occur in super conductor (or) what are
the
properties
of a superconductor.
(i)
They have zero resistivity.
(ii)
They exhibit perfect diamagnetism.
(iii)
The super conducting property can be
destroyed due to the application of magnetic and electric fields.
(iv)
The transition temperature varies due to
the presence of isotopes.
The entropy and
specific heat decreases at transition temperature.
(vi)
The elastic properties, crystal
structure and thermal expansion remains constant.
4. What
is Meissner effect?
When a material is
cooled below its transition temperature i.e., T ≤TC, the material becomes a
perfect diamagnetic. The magnetic flux originally present in the material gets
ejected out of a superconductor. This effect is known as Meissner effect.
5. Explain the term critical magnetic
field in superconductor.
At any temperature
below the critical temperature, minimum magnetic field is required to destroy
the superconducting property. This magnetic field is known as critical magnetic
field (HC).
It
is given by the relation, Hc = Ho [1- (T / Tc)2]
HC → Critical magnetic
field at any temperature HO → Critical magnetic field at absolute zero
temperature TC →
Transitiontemperature of the material
6. What is isotope effect in
superconductivity?
In a superconducting
material, transition temperature varies with the average isotopic mass M of its
constituents.
Tc
α[1 / Mα]
Where αis called isotope effect coefficient.
7. What are high TC superconductors?
Give an example.
Any superconductor, if
transition temperature is above 10 K is called high TC superconductor.
Example.
YBa2Cu3O7
TC
= 92K La1.85Ba0.15CuO4
TC
= 36K
8. What
are the properties of High TC superconductors?
They have
high transition temperature.
They have
modified pervoskite structure.
Formation
of superconducting state in high TC superconductors is direction dependent.
They are oxides of copper in combination with other
elements.
9. What
are the applications of superconductors?
Superconductors
are used for the production of high magnetic field magnets.
By
using superconducting materials, it is possible to manufacture electrical
generators and transformers in exceptionally small sizes having effiecncy of
99.90% Superconducting materials are used in the construction of very sensitive
electrical measuring instruments such as galvanometers.
Superconducting
materials if used for power cables will enable transmission of power over very
long distances without any significant power loss or drop in voltage.
10.
What is magnetic levitation?
The magnetic levitation is based on
diamagnetic property of a superconductor which is the rejection of magnetic
flux lines. A superconductor can be suspended in air against the repulsive
force from a permanent magnet. This magnetic levitation effect can be used for
high speed transportation without frictional loss.
11.
Distinguish between type –I and II superconductors.
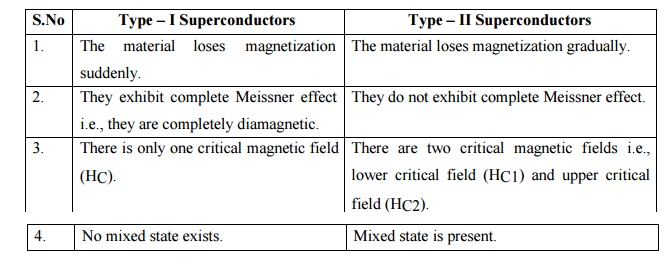
S.No Type –I Superconductors
1.
The material loses magnetization suddenly.
2.
They exhibit complete Meissner effecti.e., they are completely diamagnetic.
3.
There is only one critical magnetic field (HC).
4.
No mixed state exists.
Type –II Superconductors
The
material loses magnetization gradually.
They
do not exhibit complete Meissner effect.
There
are two critical magnetic fields i.e., lower critical field (HC1) and upper
critical field (HC2).
Mixed
state is present.
12.
What is SQUID?
SQUID is the acronym for Superconducting
Quantum Interference Device. It is a double junction quantum
interferometer. Two Josephson junctions mounted on a superconducting ring forms
this interferometer. Squids are based on the flux quantization in a
superconducting ring. The total magnetic flux passing through the ring is quantized.
It is an ultra-sensitive measuring
instrument used for detection of very weak magnetic field in the order of 10-14
tesla.
13.
What is meant by persistent current?
When a d.c current of large magnitude is
once induced in a super conducting ring, then due to the diamagnetic property
of the super conductor, the magnetic flux is trapped inside the ring and hence
the current persists in the ring for a longer time. This current is called as
persistent current.
14.
Define cooper pairs?
The
pair of electrons formed due to the electron-lattice-electron interaction, with
equal and opposite momentum and spins having the wave vector k-q and k -q are called Cooper pairs.
15.
Define coherent length.
It
is defined as the distance over which two electrons combine to form a cooper
pair.
16.
What is cryotron?
Cryotron is a type of switching element made by two
different super conductors A and B as
shown in fig(Refer cryotron fig in your book), with critical fields HcB
>HcA. Here the super conducting property vanishes for the material ‘A’due to
the magnetic field produced by material B and hence it can be used as relay
(or) switching elements.
17.Distinguish between A.C and D.C
Josephson Effect.
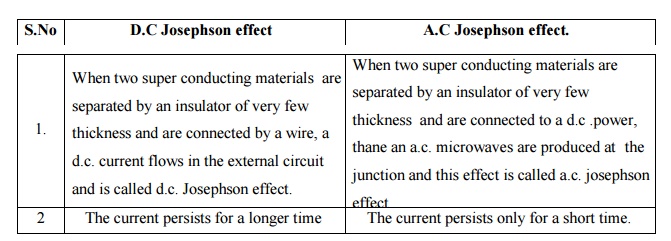
S.No D.C
Josephson effect
When two super conducting
materials are separated by an insulator of very few thickness and are connected
by a wire, a d.c. current flows in the external circuit and is called d.c.
Josephson effect.
The current persists for a
longer time
A.C Josephson effect.
When two super conducting
materials are separated by an insulator of very few thickness and are connected
to a d.c .power, thane an a.c. microwaves are produced at the junction and this
effect is called a.c. josephson effect
The current persists only
for a short time.
Related Topics