Chapter: Physics : Magnetic Materials
Important Questions and Answers: Magnetic Materials
MAGNETIC MATERIALS
1. On the basic of spin how the
materials are classified as para, ferro, antiferro and ferrimagnetic.
(i) Paramagnetic
materials have few unpaired electron spins of equal magnitudes.
(ii) Ferro
magnetic materials have many unpaired electron spins with equal magnitudes.
(iii) Anti
ferro magnetic materials have equal magnitude of spins but in antiparallel
manner.
(iv)Ferrimagnetic
materials have spins in antiparallel manner but with unequal magnitudes.
2. What is Bohr magneton?
The orbital magnetic
moment and the spin magnetic moment of an electron in an atom can be expressed
in terms of atomic unit of magnetic moment called Bohr magneton.
3 What is ferromagnetism?
Certain materials like
iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni) and certain alloys exhibit Spontaneous
magnetization ie., they have a small amount of magnetization (atomic
moments are aligned) even in the absence of an external magnetic field.This
phenomenon is known as ferromagnetism.
4. What are ferromagnetic materials?
The
materials which exhibit ferromagnetism are called as ferromagnetic materials.
5. What
are the properties of ferromagnetic materials?
(i)
All the dipoles are aligned parallel to
each other due to the magnetic interaction between any two dipoles.
(ii) They
have permanent dipole moment. They attract the magnetic field strongly.
(iii)
They exhibit magnetisation even in the
absence of magnetic field. This property of ferromagnetic materials is called
as spontaneous magnetization.
6. What
is domain theory of ferromagnetism?
According to domain
theory, a virgin specimen of ferromagnetic materials consists of a number of
regions or domains which are spontaneously magnetized due to parallel alignment
of all magnetic dipoles. The direction of spontaneous magnetisation varies from
domain to domain.
7. Mention
the energies involved in origin of domains in ferromagnetic material.
(i) Magnetostatic
energy
(ii) Crystalline
energy
(iii) Domain
wall energy
(iv)Magnetostriction
energy
8. What
is antiferromagnetism?
In anti-ferromagnetism,
electron spin of neighbouring atoms are aligned antiparallel.
Anti-ferromagnetic susceptibility is small and positive and it depends greatly
on temperature.
9. What are ferrites and mention its
types.
Ferrites are modified
structure of iron with no carbon and in which the adjacent magnetic moments are
of unequal magnitudes aligned in antiparallel direction. Its general formula is
given by X2+ Fe23+ O42-.
Types: normally there are two types of
structure. 1. Regular spinel 2. Inverse spinel.
10.
State the applications of ferrites.
(i) They
are used in transformer cores for high frequencies upto microwaves.
(ii) They
are used in ratio receivers to increase the sensitivity and selectivity of the
receiver.
(iii) Ferrites
are used in digital computers and data processing circuits as magnetic storage
elements.
(iv) They
are used as an isolator, gyrator and circulator which are used in microwave
devices.
11.
What is hysteresis in magnetic
materials?
The
lagging of magnetic induction (B) behind the applied field strength (H) is
called hysteresis.
12. What is meant by hysteresis loss?
When the specimen is taken through a cycle of
magnetization, there is a loss of energy in the form of heat. This is known as
hysteresis loss 13. What are soft-magnetic materials?
Materials which are
easy to magnetize and demagnetize are called soft magnetic materials.
14.
State the properties of soft
magnetic materials.
(i) They
have high permeability
(ii) They
have low coercive force.
(iii) They
have low hysteresis loss.
15.
Mention few soft magnetic materials
and their applications. Soft magnetic materials:
(i) Pure
or ingot iron
(ii) Cast
iron (carbon above 2.5%)
(iii) Carbon
steel
Applications:
(i) Cast
iron used in the structure of electrical machinery and frame work of
d.c.machine
(ii) Carbon
steel has high mechanical strength used in making motor of turbo alternators.
16. What ate hard magnetic materials?
Materials which retain
their magnetism and are difficult to demagnetize are called hard magnetic
materials.
17. State the
properties of hard magnetic materials.
They possess high value of B-H product
They have high retentivity
They have high coercivity
They have low permeability.
18. What are ferromagnetic materials?
Materials
which exhibit ferrimagnetism are called ferromagnetic materials. They are also
known as ferrites.
19.
Mention the properties of
ferromagnetic materials.
(i) These
are the ferromagnetic materials in which equal number of opposite spins with
different magnitudes such
that the orientation of neighbouring spins is in anti parallel manner.
(ii) Susceptibility is
positive and very large for these materials.
20. Differentiate soft
and hard magnetic materials.
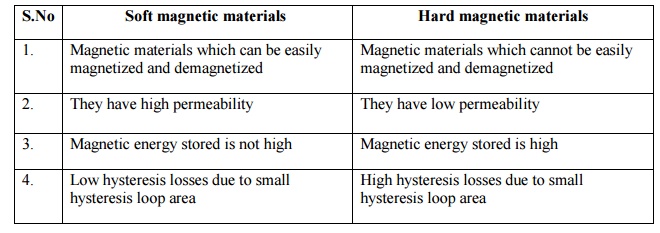
S.No Soft magnetic
materials
1. Magnetic materials which can be easily magnetized and demagnetized
2. They have high permeability
3. Magnetic energy stored is not high
4. Low hysteresis losses due to small hysteresis loop area
Hard magnetic materials
Magnetic materials which cannot be easily magnetized and demagnetized
They have low permeability
Magnetic energy stored is high
High hysteresis losses due to small hysteresis loop area
21.
Why ferrites are advantageous for use as transformer cores?
Ferrites are used as transformer cores
for frequencies up to microwaves. This is because the eddy current problem
which prevents the penetration of magnetic flux into the materials is much less
severe in ferrites than in iron.
22.
What is the origin of magnetic moment in magnetic materials?
The magnetic moment originates from the
orbital motion and spinning motion of electrons.
23.
What is diamagnetism?
When a material is placed in a magnetic
field, the material becomes magnetized. The direction of the induced dipole
moment is opposite to the externally applied magnetic field.
Due to this effect, the material gets
very weakly repelled in the magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as
diamagnetism.
24.
What are diamagnetic materials?
The
materials which exhibit diamagnetism are called diamagnetic material.
25.
What are the properties of
diamagnetic materials?
(i) Diamagnetic
materials repel the magnetic lines of force.
(ii) There
is no permanent dipole moment. Therefore, the magnetic effects are very
small.
The magnetic
susceptibility is negative and is independent of temperature and applied
magnetic field strength.
26. What is paramagnetism?
In certain materials,
net magnetic moment is zero though each atom or molecule possesses a permanent
magnetic moment in the absence of an external magnetic field.
But when an external
magnetic field is applied the magnetic dipoles tend to align themselves in the
direction of the magnetic field and the material becomes magnetized. This
effect is known as paramagnetism.
27. What are paramagnetic materials?
The
magnetic materials which exhibit paramagnetism are called paramagnetic
material.
28.
What are properties of paramagnetic
materials?
(i) Paramagnetic
materials attract the magnetic lines of force.
(ii) They
possess permanent dipole moment.
(iii) The
susceptibility is positive
Related Topics